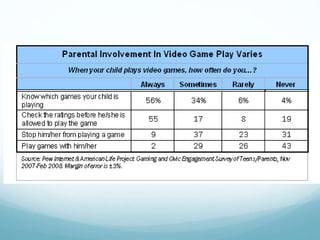
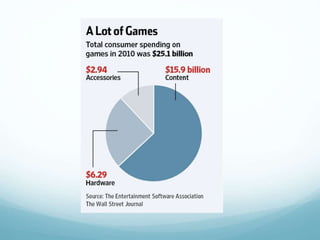
This document discusses the educational benefits of digital games. It notes that research has shown positive benefits of digital games and many students require interactive instruction. Games can engage students in new activities and sports strategies at home which builds confidence. Parents and teachers should provide guidance by setting controls and restrictions. Well-designed educational games can promote skills like problem-solving, collaboration, and perseverance. If games are selected appropriately, they can supplement learning.