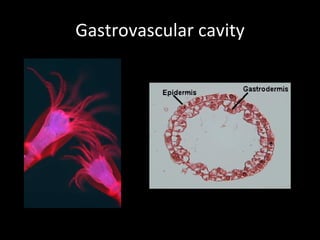
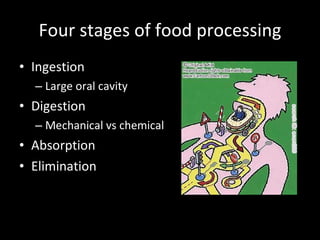
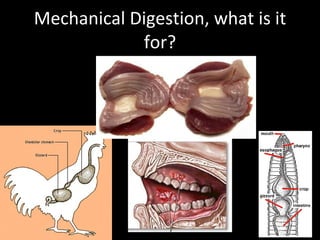
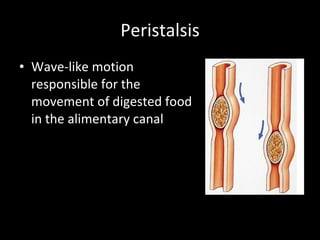
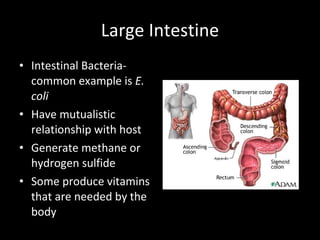
The document discusses the process of digestion in animals. It begins by explaining that digestion breaks down important substances like proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and nucleic acids that the body needs. It then covers the differences between plant and animal nutrition, and discusses how digestion provides evidence of evolution. Various aspects of digestion systems are explained, including intracellular and extracellular digestion. The stages of digestion - ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination - are outlined. Key organs involved in digestion like the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine are described along with their functions. Hormones that regulate digestion are also mentioned.