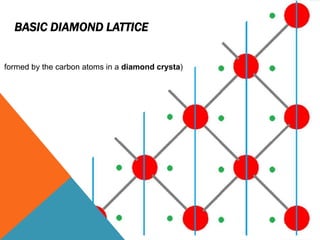
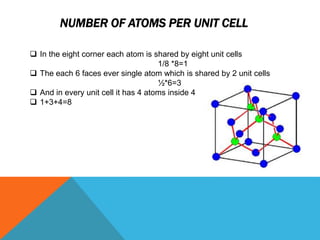
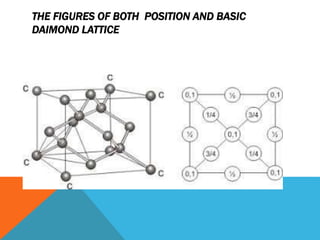
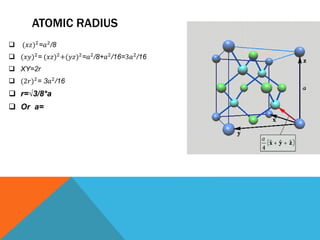
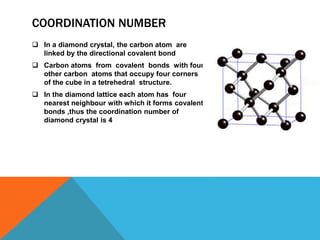
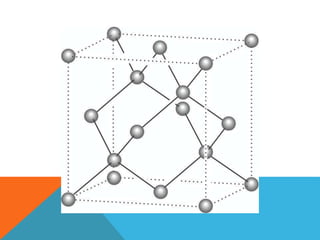
The document summarizes key aspects of the diamond lattice structure formed by carbon atoms in a diamond crystal. It describes the diamond lattice as being formed by two interpenetrating face-centered cubic (fcc) sublattices offset by 1/4 cube edge. Each carbon atom has four nearest neighbors in a tetrahedral structure, giving the diamond lattice a coordination number of 4. The packing factor of the diamond lattice is 0.34, indicating it is a loosely packed structure.