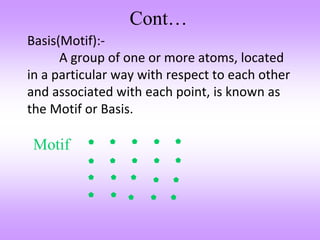
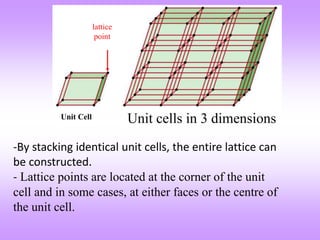
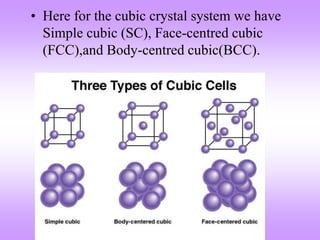
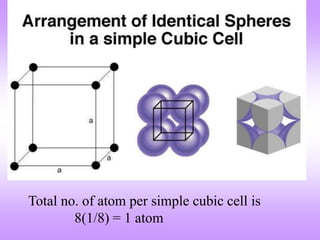
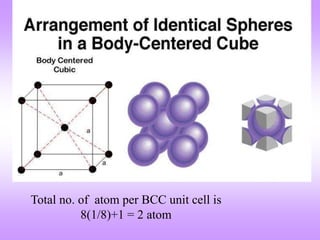
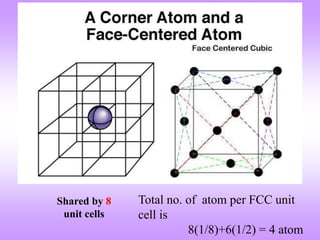
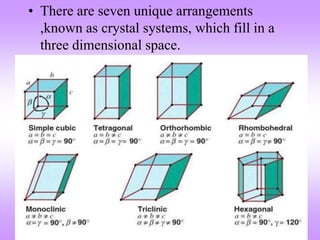
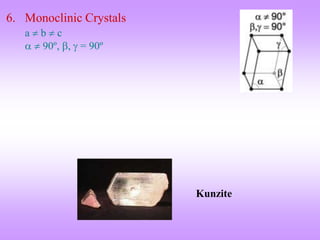
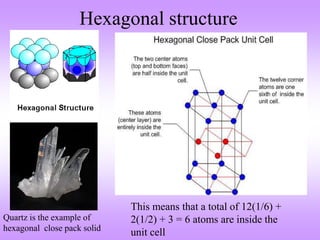
This document discusses crystal structures, including the definition of a crystal structure as a lattice plus a basis. It describes different types of crystal structures such as polycrystalline and single crystalline structures. Common unit cell structures are described like simple cubic, body-centered cubic, and face-centered cubic unit cells. The seven crystal systems are listed. Examples of unit cells and structures for different materials are provided, including the hexagonal close-packed structure.