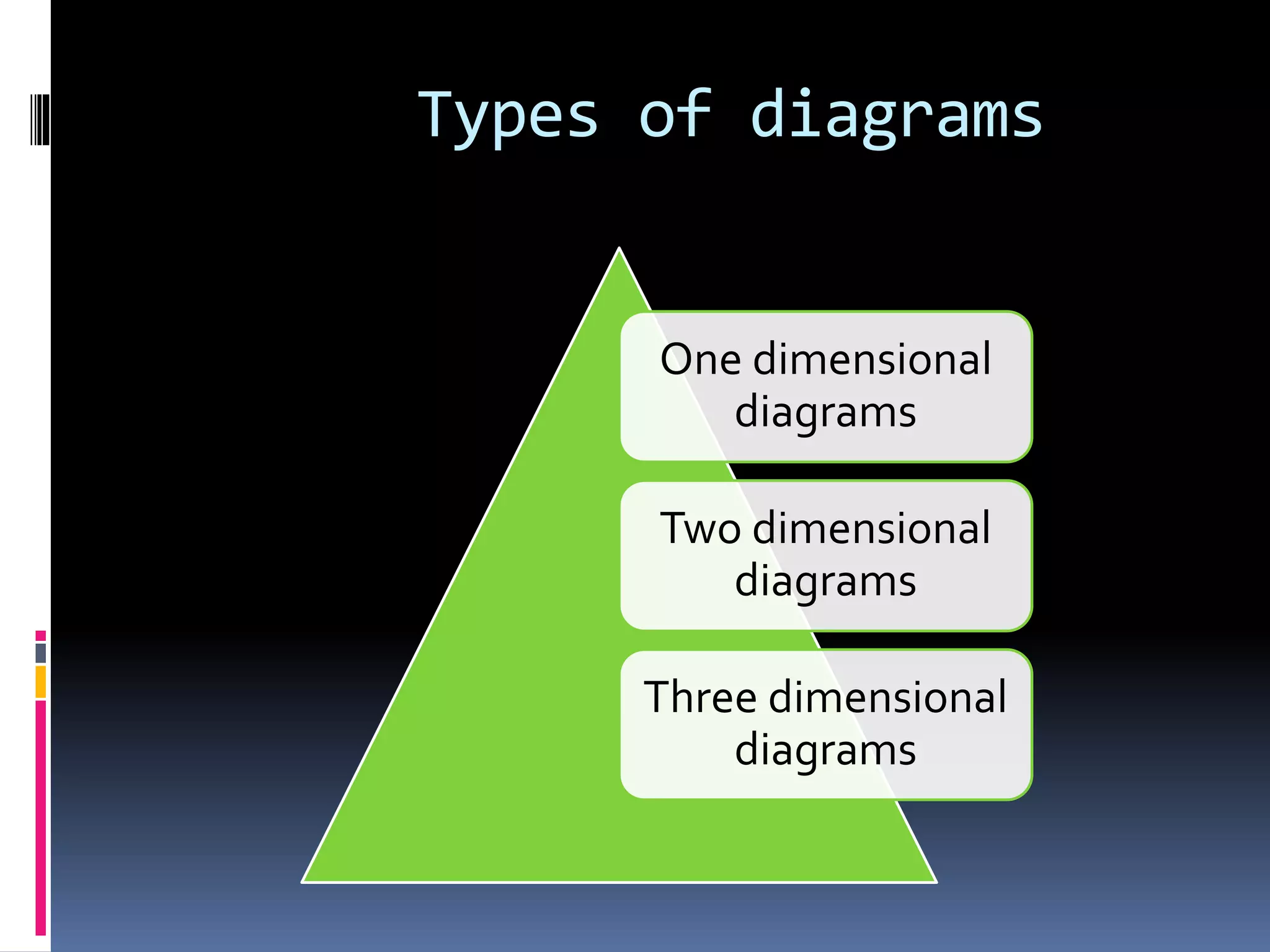
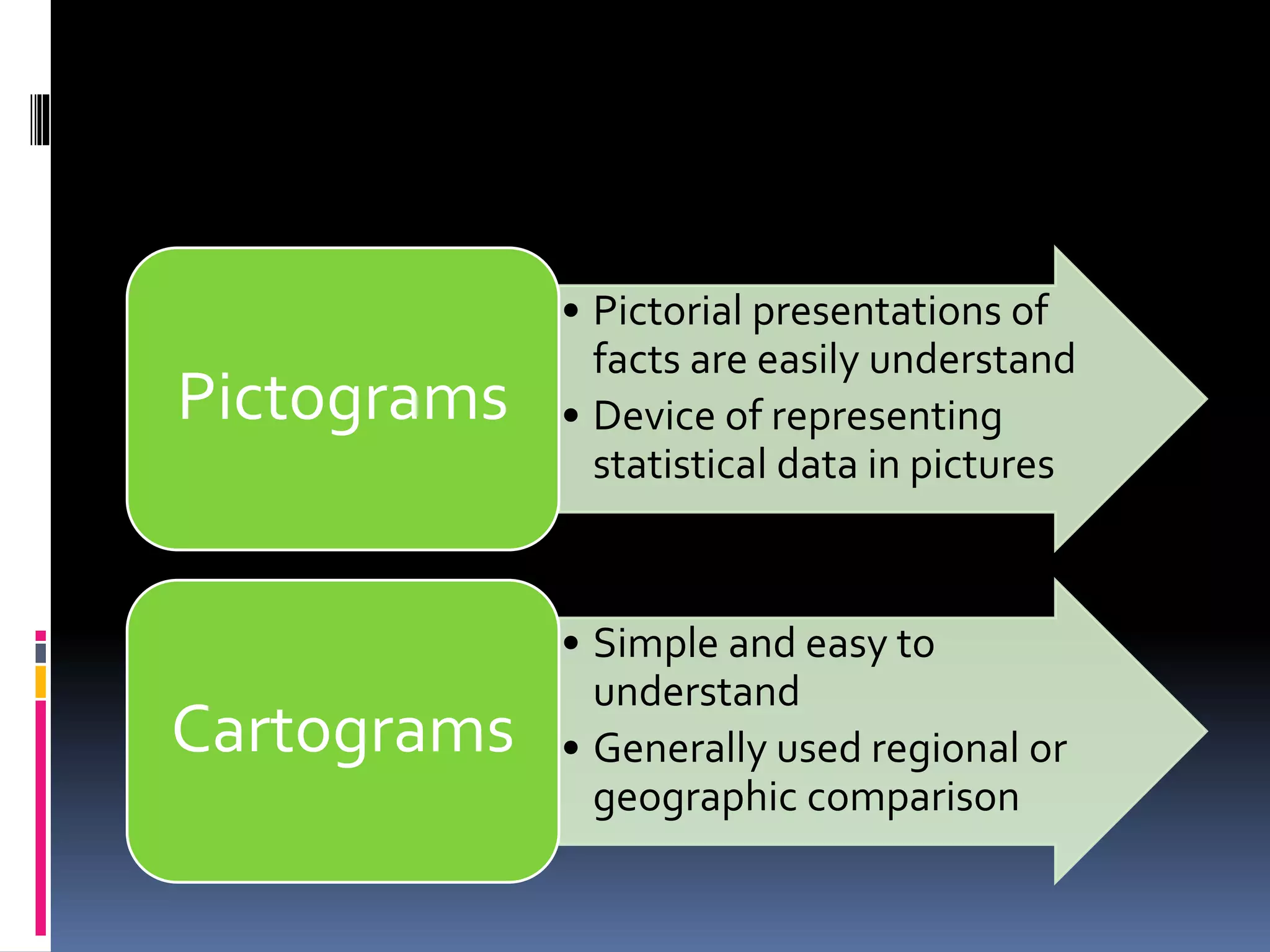
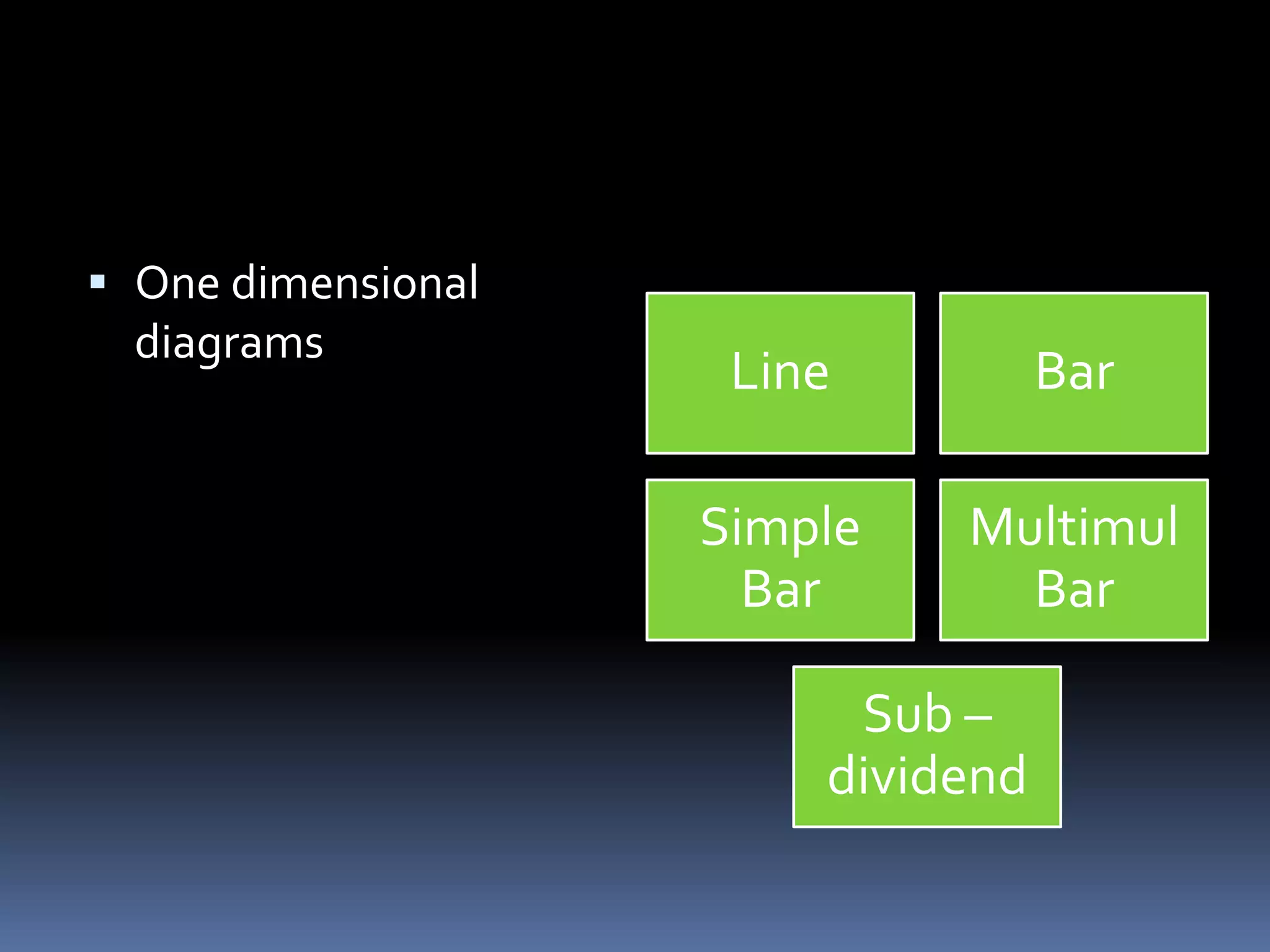
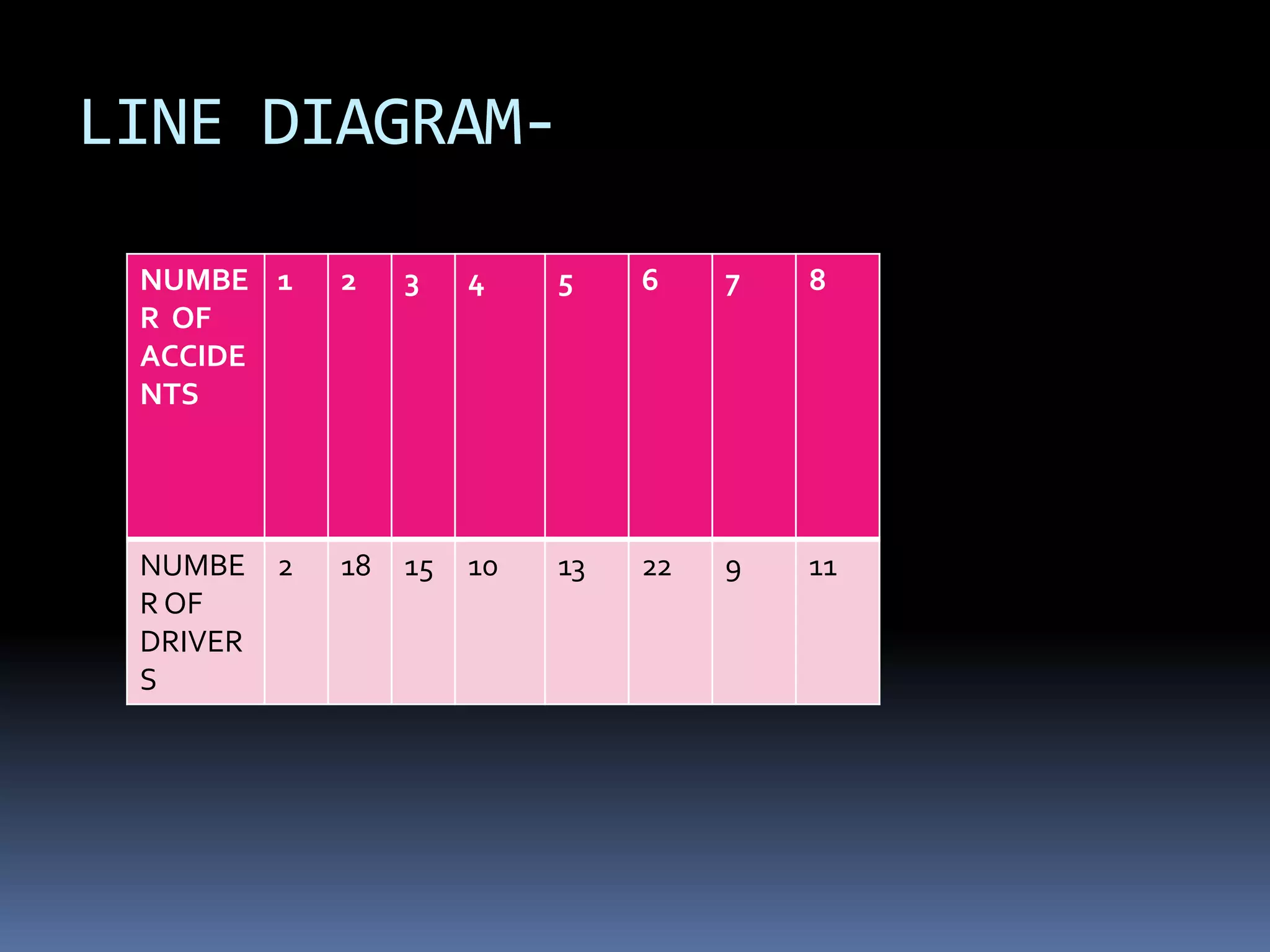
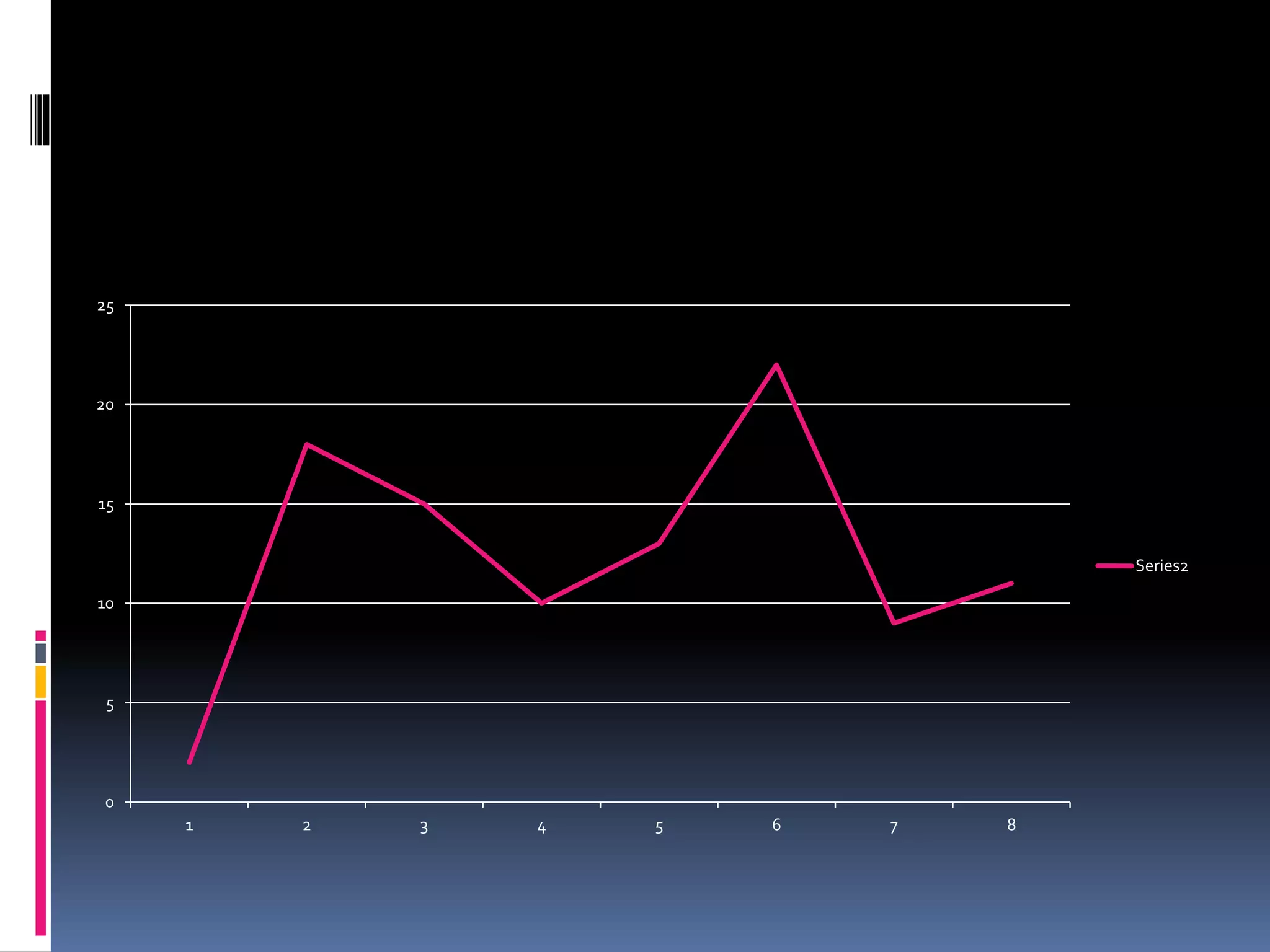
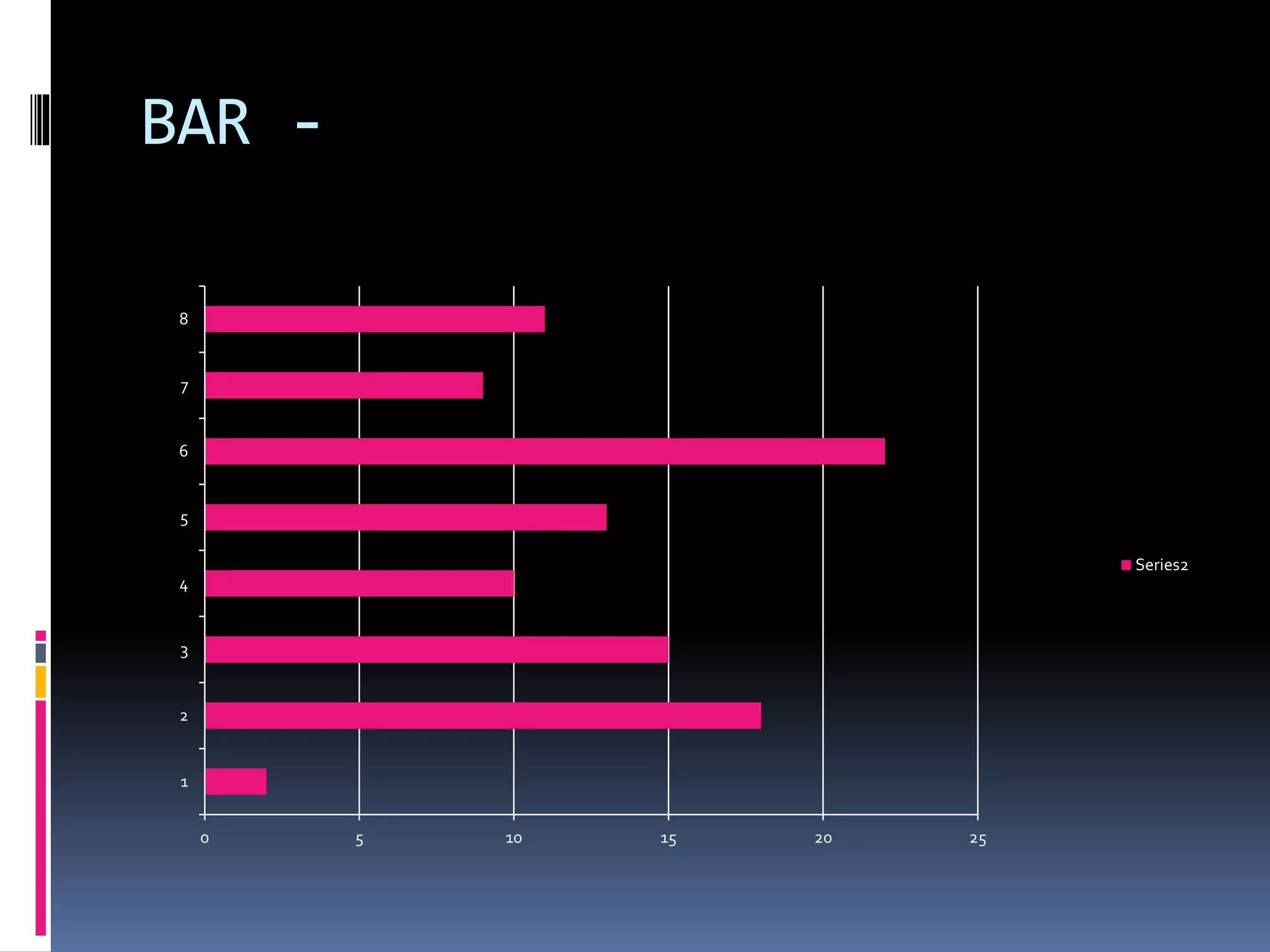
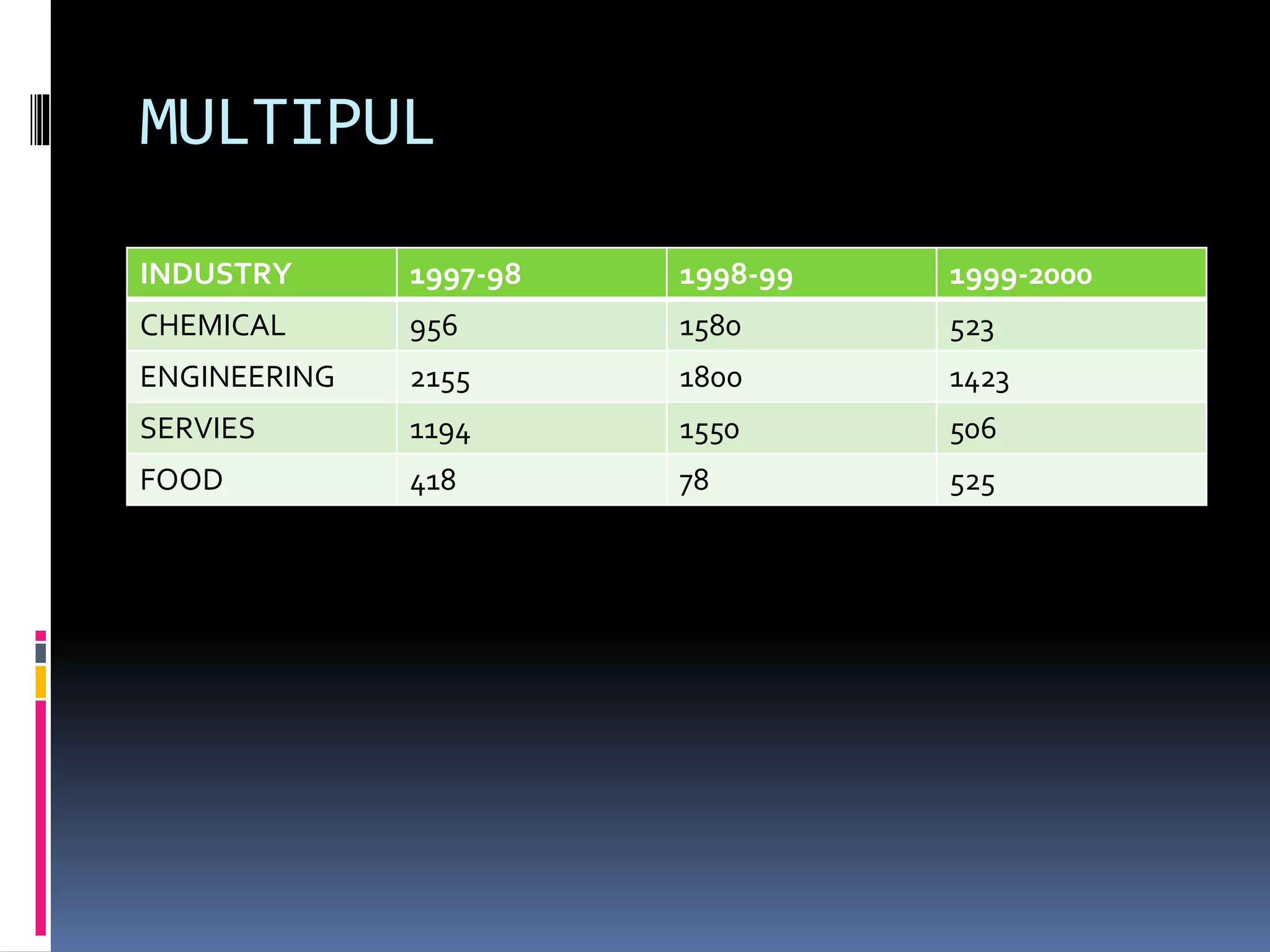
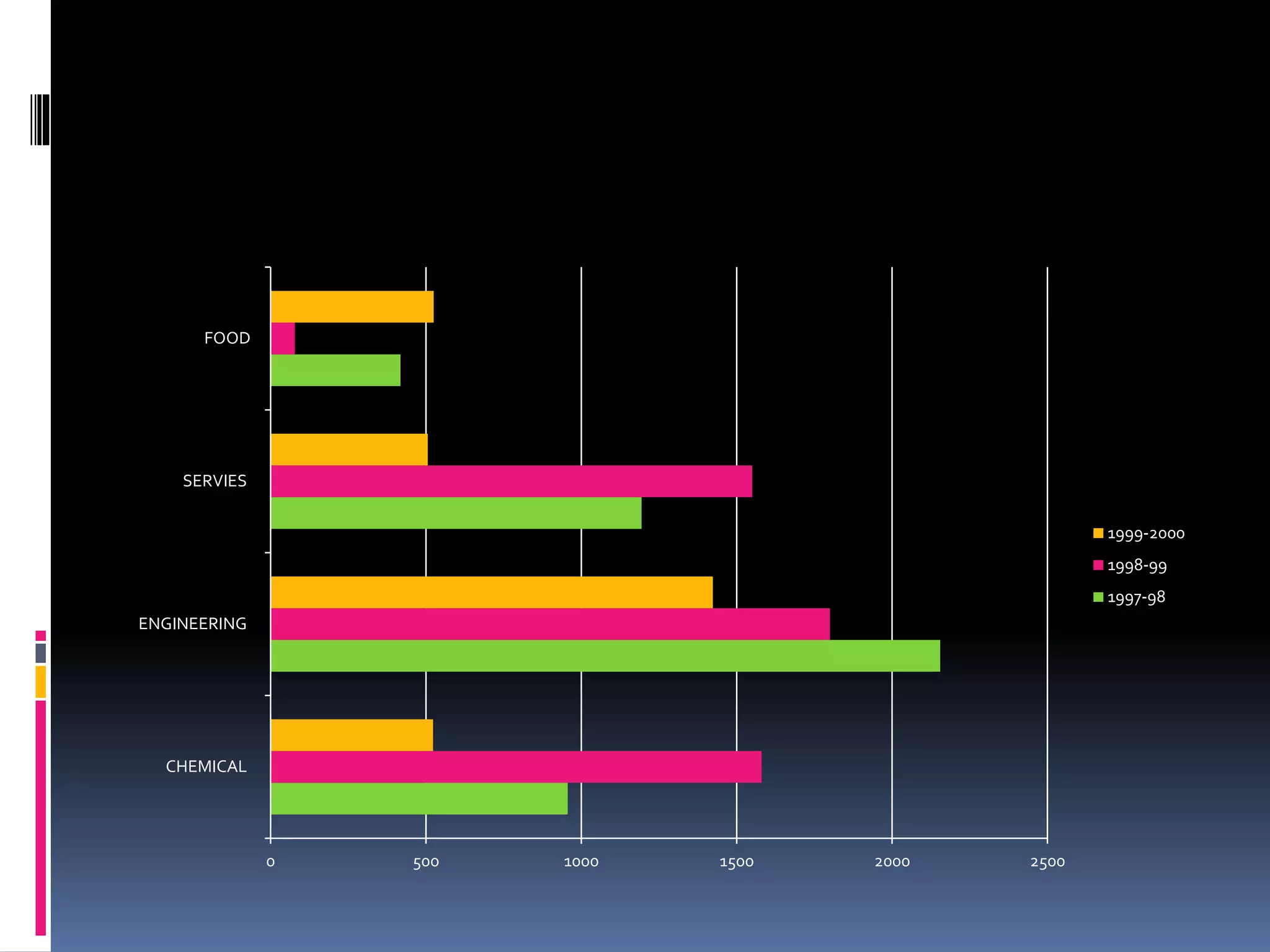
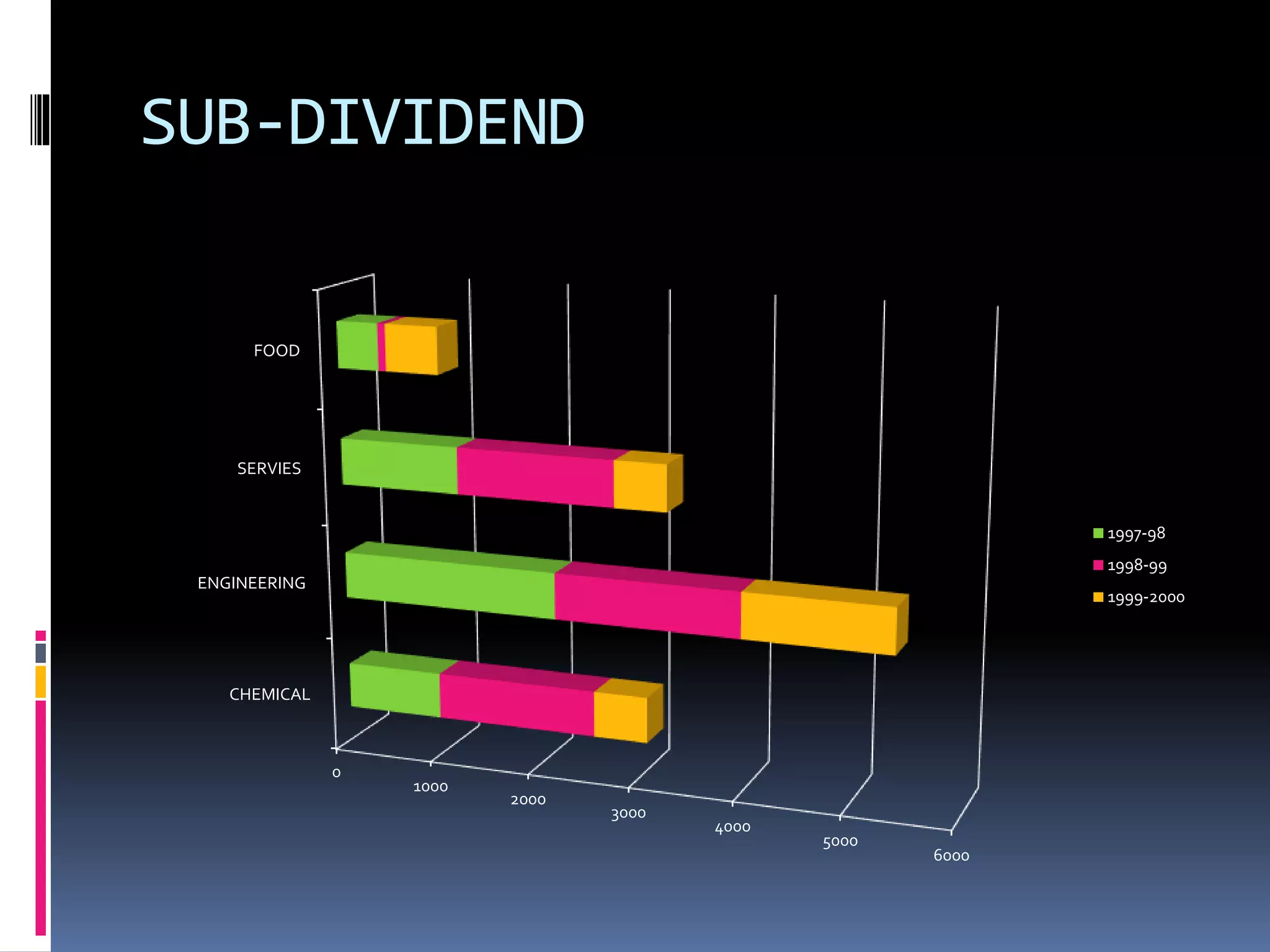
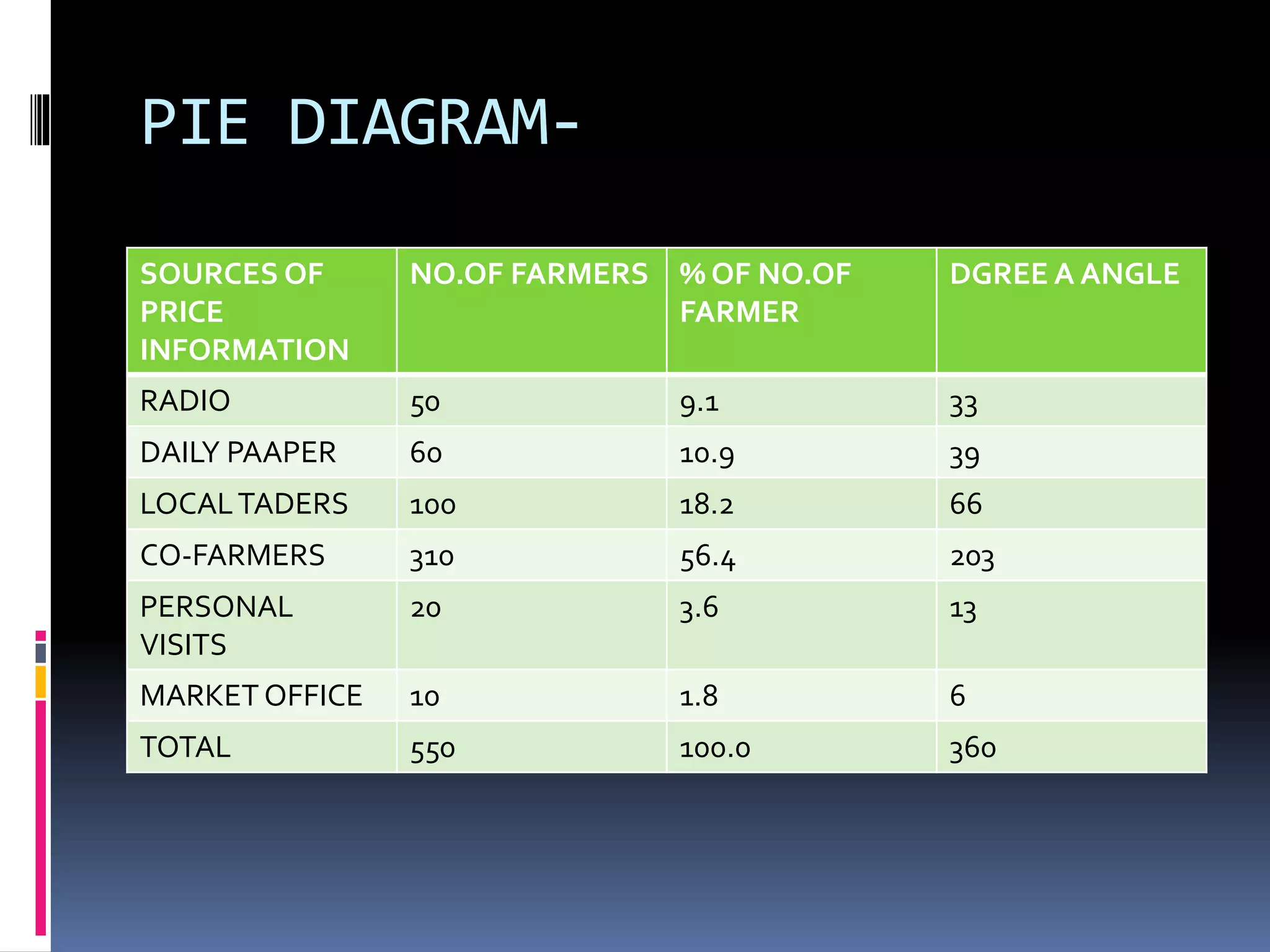
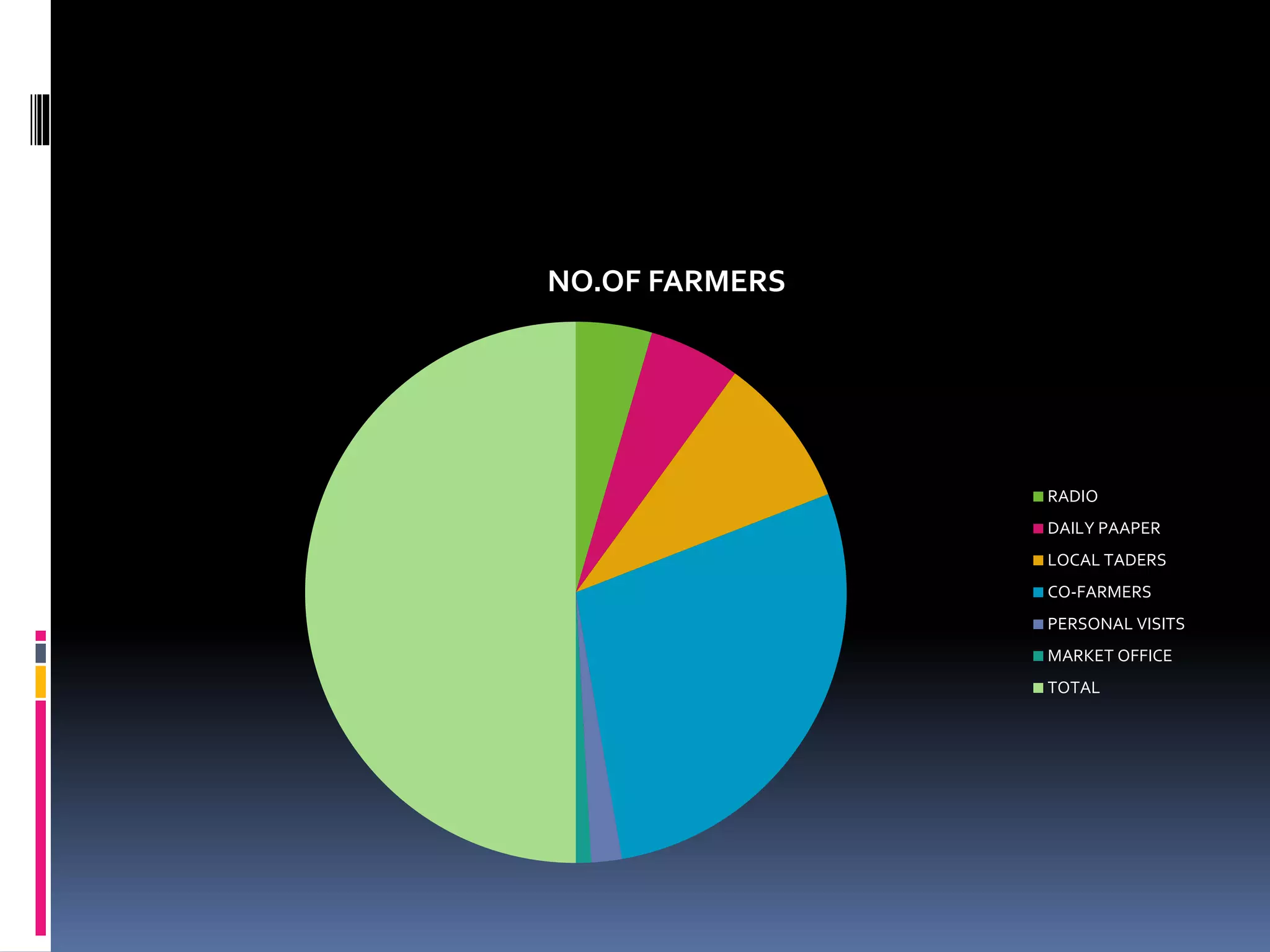
This document discusses diagrammatic presentations of data, which use geometric techniques like bar diagrams, pie charts, and cartograms to visually present numerical information. The main advantages of these diagrams are that they are attractive, easy to remember and understand, simplify complex data, and help make comparisons. There are one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional diagrams. Examples provided include line graphs, bar graphs, sub-divided bar graphs, rectangular diagrams, and pie charts. Pie charts in particular can be used to show percentages and proportional relationships between parts of a whole.