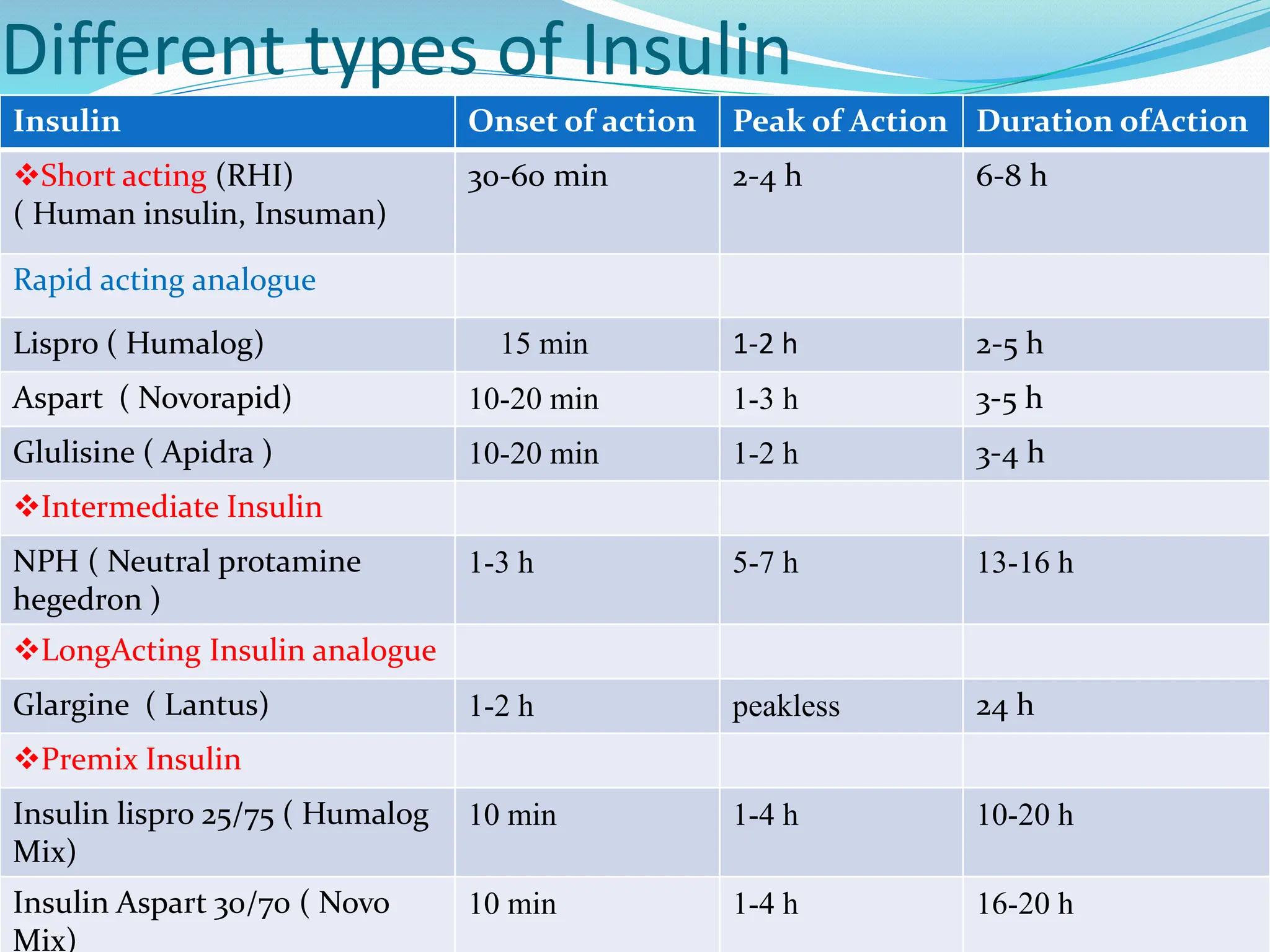
By the end of the presentation, nurses will understand diabetes and insulin therapy. They will know the criteria for diagnosing diabetes, the different types of insulin and regimens, proper administration and storage techniques, and how to use insulin devices. The document discusses myths about insulin, outlines the types and classification of diabetes, and covers topics like symptoms, goals of treatment, insulin types and regimens, administration techniques, storage, and more. Nurses will gain knowledge on properly managing diabetes with insulin.
















![Insulin
Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone secreted by
the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the
pancreas in response to increased blood glucose
levels.1
Insulin regulates the blood glucose level and stores
excessive glucose for energy.2
1. Ehrlich RA. Patient care in radiography: With an introduction to medical imaging, 8th ed. Missouri:Elsevier Mosby; 2013. P. 470.
2. Mayo Clinic. Diabetes treatment: Using insulin to manage blood sugar [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Oct 9]. Available from: www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-
depth/diabetes-treatment/art-20044084
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(Suppl 1):s15–s35.
4. Kimball DM. Perceived knowledge of the registered nurse in managing hyperglycemia according to evidence-based practice in the acute care settings. Boca Raton: Florida](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingeducationprogram-231225133443-e2ab040e/75/nursing-education-program-about-insulin-use-17-2048.jpg)
![Pharmacologic treatment of type 2 diabetes [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Oct 9]. Available from: www.columbia.edu/itc/hs/medical/clerkships/primcare/case/diabetes/diabetes01_07.html
Normal Insulin Secretion
The pancreas is constantly secreting basal insulin, which provides 50% of the body’s
requirement.
After a meal, the pancreatic beta-cells secrete bolus insulin in response to meals,
which supplies the body’s other 50% requirement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingeducationprogram-231225133443-e2ab040e/75/nursing-education-program-about-insulin-use-18-2048.jpg)
![Precautions for Storing Insulin Pens
1. GOSH NHS UK. Insulin: safe administration of [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Sept 28]. Available from: http://www.gosh.nhs.uk/health-professionals/clinical-guidelines/insulin-safe-
administration.
2. Kalra S, et al. Forum for injection techniques, India: The first Indian recommendations for best practice in insulin injection technique. Indian J Endocr Metab 2012;16:876–85.
Should be refrigerated initially (2-8°C).1
Once the pen is in use there is no requirement for
refrigeration, but do not store above 30°C.1
Pens should never be stored with needles attached.2
If using mixed insulin, i.e., cloudy insulin, before using
the pen for the first time, the pen should be rolled
between the palms about 10 times.1
Thereafter, only turn the pen up and down prior to use
and do not shake.1
Analogues such as insulin Glulisine and insulin Glargine
do not need to be rolled.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingeducationprogram-231225133443-e2ab040e/75/nursing-education-program-about-insulin-use-19-2048.jpg)


![Once-daily Dosing Regimen
1. Diapedia. Insulin regimens [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Oct 13 ]. Available from: http://www.diapedia.org/management/insulin-regimens
2. Levich BR. Diabetes management: optimizing roles for nurses in insulin initiation. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2011;4:15–24.
A single dose of insulin given each day.1,2
Long-acting insulin is given, mostly in the evening (for 24-hour
coverage). However, it can be given in the morning as well.1,2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingeducationprogram-231225133443-e2ab040e/75/nursing-education-program-about-insulin-use-23-2048.jpg)
![Taken twice daily before breakfast and dinner to provide 24-hour
coverage
Also called biphasic because a fixed mixture of a short-acting insulin
and a long-acting insulin taken at each injection.
Twice-daily (Mixed-Insulin) Dosing Regimen
Diapedia. Insulin regimens [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Oct 13]. Available from: http://www.diapedia.org/management/insulin-regimens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingeducationprogram-231225133443-e2ab040e/75/nursing-education-program-about-insulin-use-24-2048.jpg)
![Basal–Bolus Dosing Regimen
1. NHS Lanarkshire. Basal bolus regimen insulin adjustment (multiple daily injection) [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2015 Oct 12]. Available from:
www.nhslanarkshire.org.uk/Services/Diabetes/Documents/Diabetes%20-%20Basal%20Bolus%20Regimen%20Insulin%20Adjustment.pdf
2. Dunning T. Care of people with diabetes: A manual of nursing practice, 4th ed. Sussex: John Wiley & Sons; 2013.
Basal insulin helps in maintaining the basic amount of insulin needed by the body at all
times by controlling the amount of glucose released. Basal insulin is long-acting insulin or
intermediate insulin as it needs to act over a relatively long period of time.1
Bolus Insulin helps in keeping blood glucose levels under control post-meal (mimics
pancreas role). Bolus insulin is either short-acting insulin or rapid-acting insulin as it
needs to act quickly.1
Basal-bolus regimen involves taking a long-acting insulin at bedtime to supply the basal
insulin requirements through periods of fasting and separate bolus injections of rapid- or
short-acting insulin are given before each meal to prevent blood glucose levels from
rising post-meals.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingeducationprogram-231225133443-e2ab040e/75/nursing-education-program-about-insulin-use-25-2048.jpg)




![Injection sites include the subcutaneous tissue of:1
the upper arm and the anterior and lateral portion
of the thigh
buttocks (slowest absorbing)
abdomen (fastest absorption) (except a 2-inch
radius around the navel).
Avoid the lateral portion of arm in small children with
little subcutaneous fat.2
Rotation of the injection site (recommended within
one area but at least 1 cm apart) is important to
prevent lipohypertrophy or lipoatrophy.1,2
Intramuscular injection is not recommended for
routine injections.1,2
1. American Diabetes Association. Insulin Administration. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26(Suppl 1):s121–4.
2. GOSH NHS UK. Insulin: safe administration of [Internet] . 2015 [cited 2015 Sept 28]. Available at: http://www.gosh.nhs.uk/health-
professionals/clinical-guidelines/insulin-safe-administration
Abdomen Upper arm
Anterior
thighs
Posterior
thighs Buttocks
Where to Inject the Insulin?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursingeducationprogram-231225133443-e2ab040e/75/nursing-education-program-about-insulin-use-30-2048.jpg)






