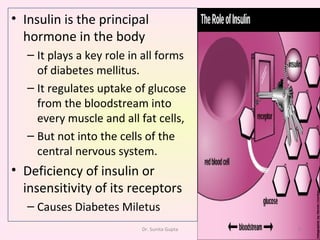
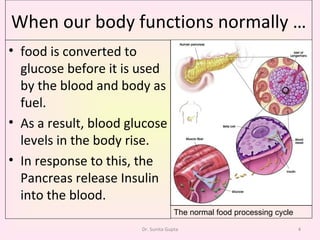
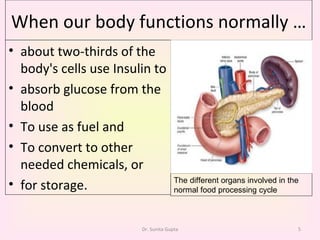
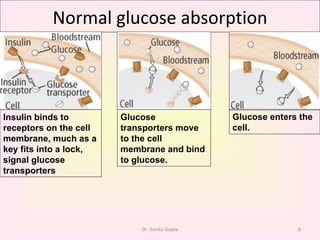
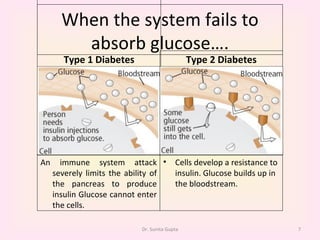
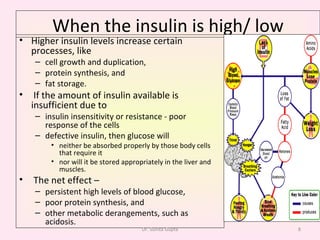
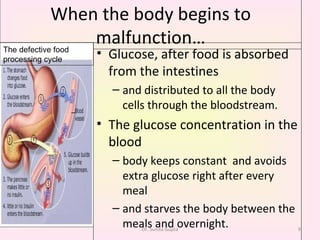
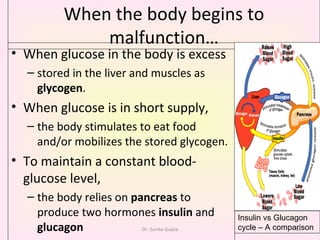
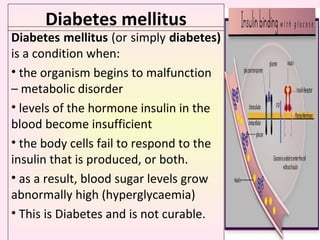
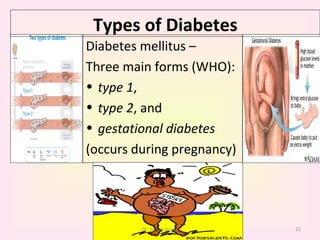
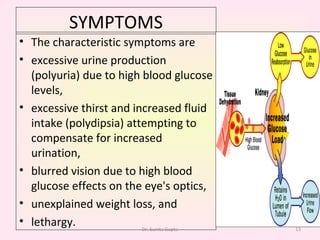
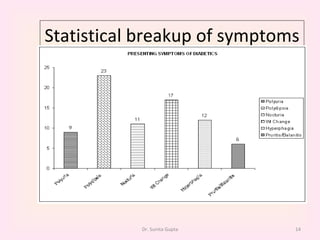
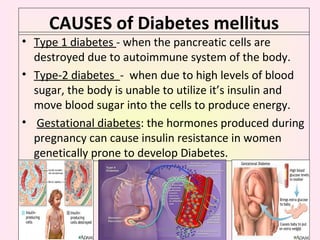
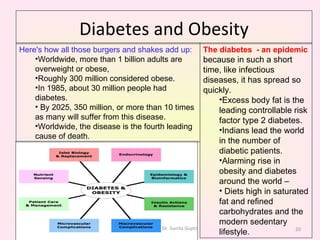
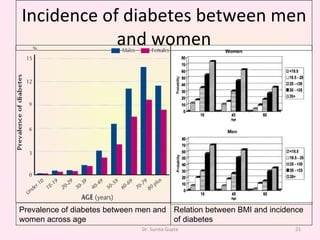
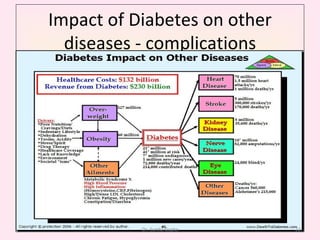
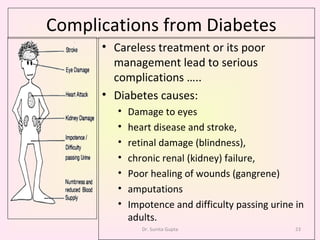
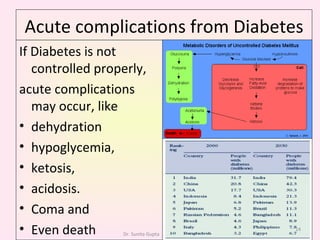
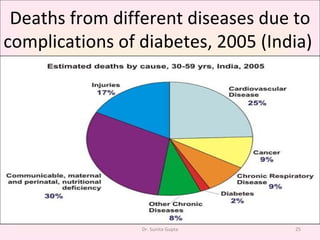
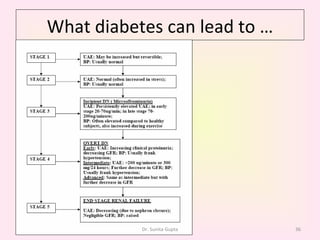
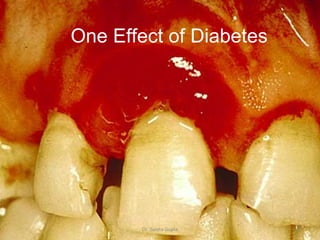
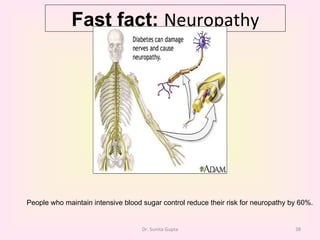
This presentation covers the main types of diabetes, how the body processes sugar normally and abnormally, diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle management of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks the pancreas, limiting insulin production. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance or insensitivity, preventing cells from absorbing glucose. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. The presentation emphasizes lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, weight control and medication adherence to manage diabetes and reduce complications.