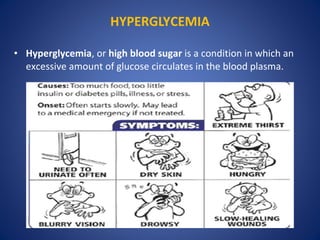
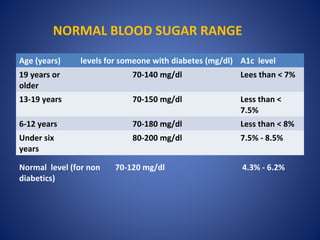
This document provides an overview of diabetes, including its causes, types, symptoms, testing, treatment, and effects on the body. It notes that diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or the cells ignore the insulin, resulting in high blood sugar. The main types of diabetes are type 1, type 2, gestational, and pre-diabetes. Symptoms include frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision. While there is currently no cure for diabetes, it can be controlled through lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and medication to prevent or reduce complications that can affect organs like the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.