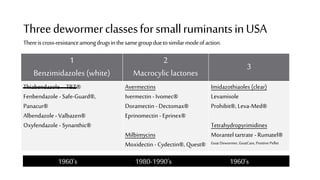
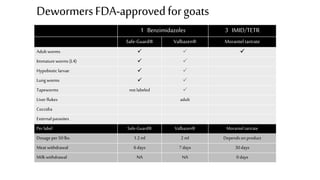
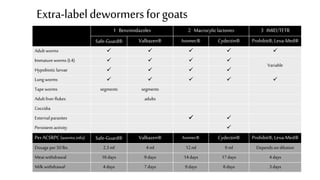
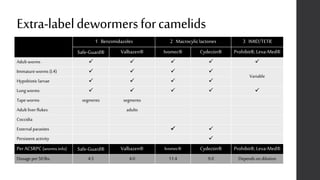
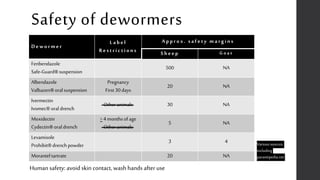
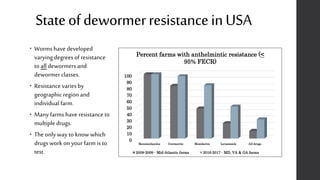
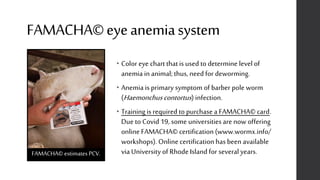
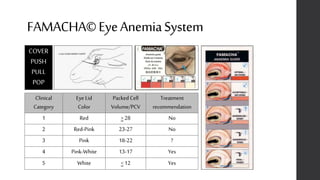
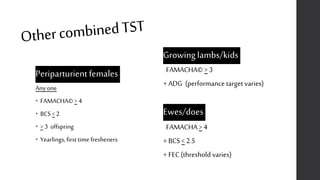
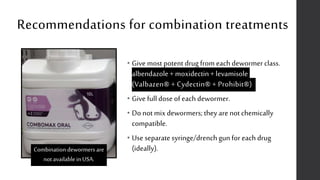
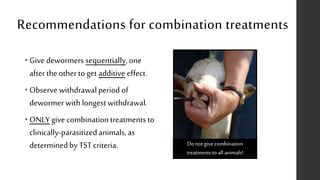
This document provides information on proper deworming practices for small ruminants. It discusses the classes of dewormers approved for use in sheep and goats, as well as extra-label dewormers. The goals of deworming and environmental considerations are covered. Targeted selective treatment is recommended over whole flock treatments to reduce dewormer resistance. Combination dewormer treatments and non-drug options like copper oxide wire particles are also discussed.