Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX















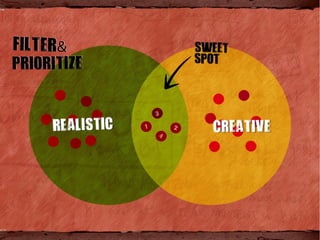




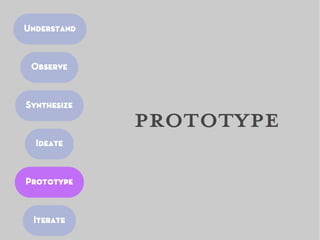




This document provides an overview of the design thinking process, which involves understanding users' needs through research, developing insights, ideating solutions, prototyping ideas, and iterating based on feedback. The key steps discussed are understanding users through methods like interviews and observation; synthesizing insights to inform a point of view statement; generating many ideas through techniques like brainstorming; prototyping ideas to make them tangible; and iterating the solutions based on learnings from user reactions to prototypes. The overall goal is to solve design problems by gaining a deep empathy for users and tightly focusing solutions on their specific needs and insights.






























