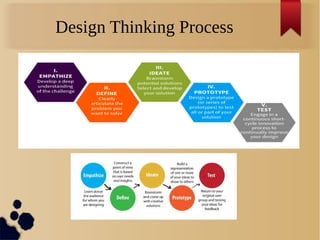
The document discusses design thinking as a process for solving problems and discovering opportunities. It defines design thinking as a human-centered, collaborative, optimistic, and experimental mindset for transforming challenges into design opportunities. The core steps of the design thinking process are described as empathizing to understand user experiences, defining insights and opportunities, ideating potential solutions, prototyping ideas rapidly, and testing prototypes with users. Each step focuses on needs, understanding, creating, thinking, and implementing solutions through an iterative process of divergent and convergent thinking.