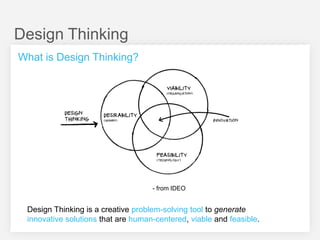
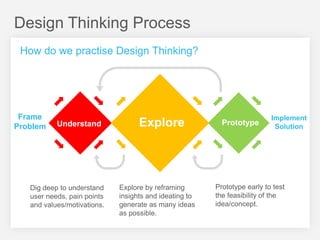
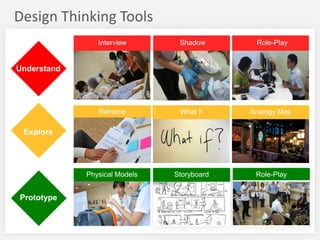
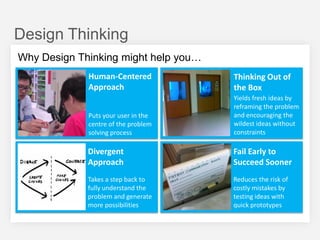
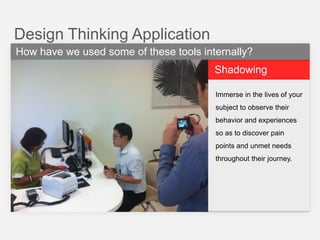
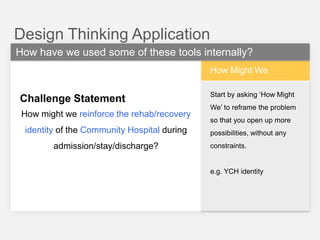
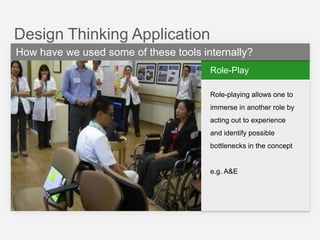
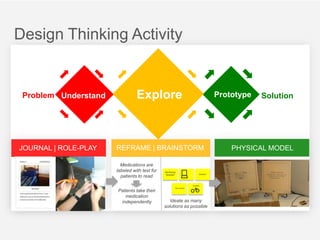
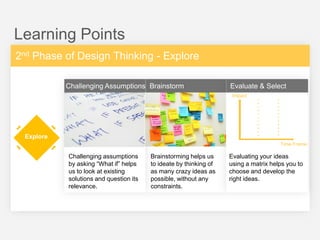
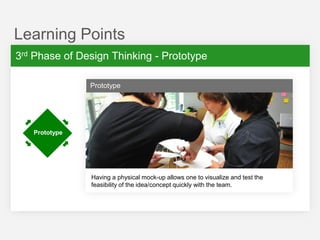
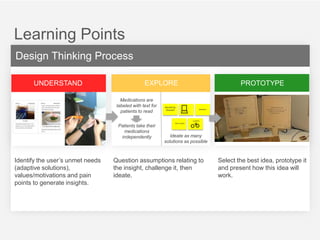
This document summarizes a design thinking workshop for AIP partners. It discusses the design thinking process which involves framing the problem, understanding user needs through tools like interviews and shadowing, exploring solutions through brainstorming and reframing, and prototyping ideas. Specific tools mentioned include role playing, analogy mapping, and physical models. The benefits of design thinking are highlighted such as taking a human-centered approach and thinking outside the box. Examples are provided of how tools like shadowing, how might we questions, and role playing have been used internally. Learning points emphasize understanding user needs, challenging assumptions during exploration, and prototyping ideas to test feasibility.