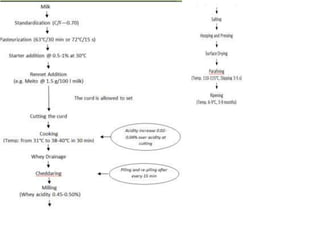
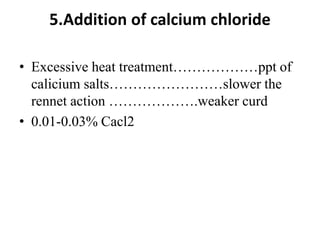
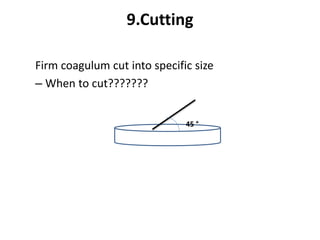
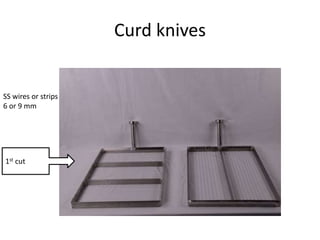
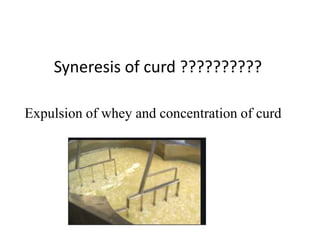
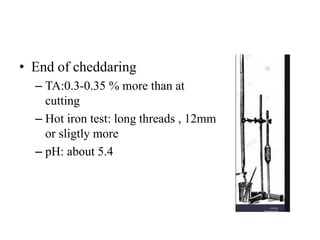
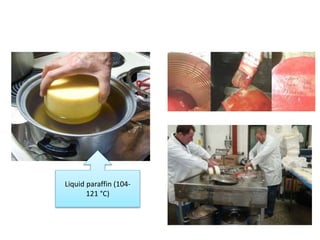
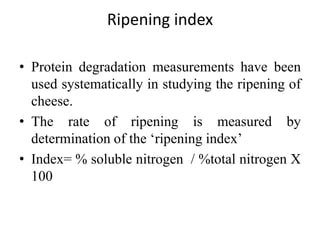
Cheddar cheese is a hard pressed cheese made by coagulating heated or pasteurized milk with cultures of lactic acid bacteria or coagulating enzymes. It is formed into a hard pressed block that may be coated in wax or wrapped in cloth or polyfilm. Fully ripened cheddar cheese has a firm, smooth and waxy texture ranging from pale straw to orange color without gas holes. The cheese making process involves steps like standardization, pasteurization, addition of starter culture, renneting, cutting, cooking, draining, cheddaring, milling, salting, hooping, pressing, paraffining, and curing. During curing, the cheese develops its characteristic flavor, body and