This document provides a lesson on motion, including the following key points:
1. It describes goals to define motion, reference points, distance vs displacement, and perform speed calculations.
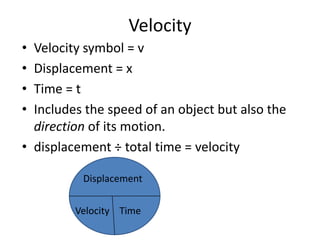
2. Key terms are introduced like speed, distance, displacement, and equations for calculating speed using distance and time.
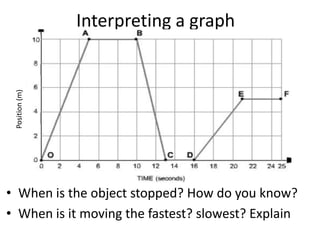
3. Graphing motion is discussed where time is plotted on the x-axis and distance on the y-axis, and slope represents speed.