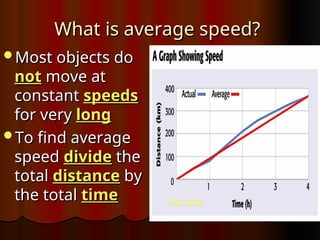
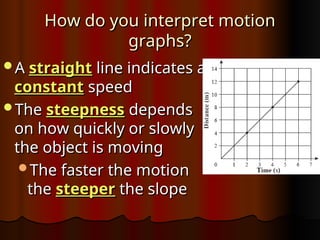
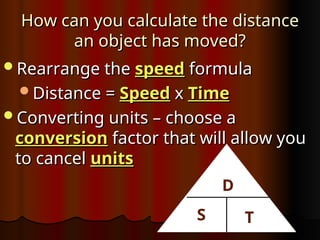
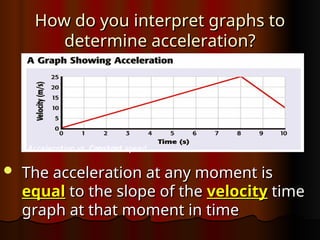
Chapter 1 covers the basics of motion, defining it as a change in position relative to a reference point. It explains concepts like speed, velocity, and acceleration, along with methods for measuring these properties, such as using meters and kilometers. The section also discusses how to interpret motion graphs and describes various examples of constant and changing speeds.