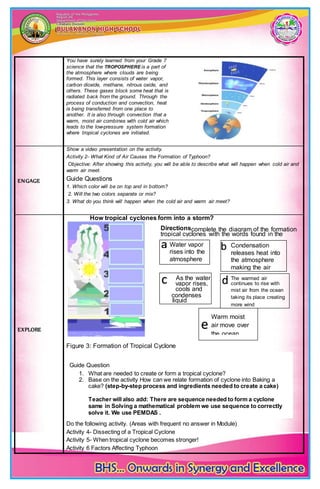
This lesson plan covers the formation and development of typhoons. It includes objectives, content understanding, learning resources, activities to engage students, and an assessment. Students will learn that typhoons form from warm, moist air rising over the ocean and condensing into clouds and rainfall. As more warm air rises to replace the air that formed the clouds, winds begin to circulate, potentially strengthening into a typhoon. The lesson uses videos, diagrams, and questions to help students understand the factors and step-by-step process of how typhoons form and develop.