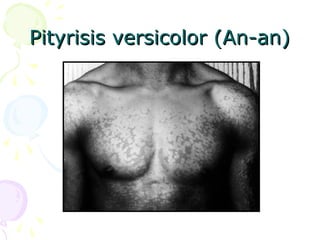
1. Superficial mycoses are limited to the outermost layer of the skin and include pityriasis versicolor, tinea nigra, black piedra, and white piedra.
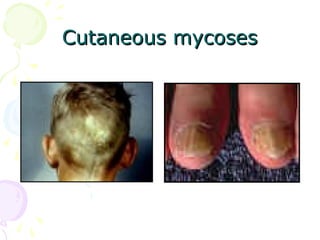
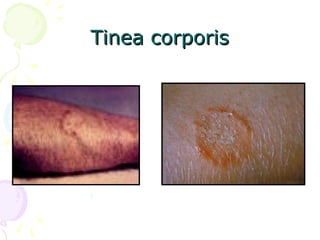
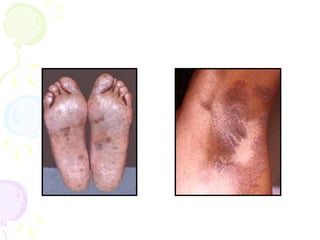
2. Cutaneous mycoses involve the skin, hair, and nails, evoke an immune response, and include dermatophyte infections known as ringworm.
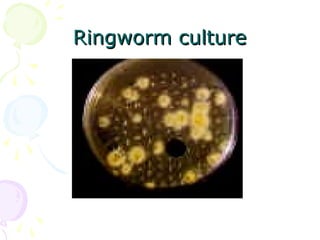
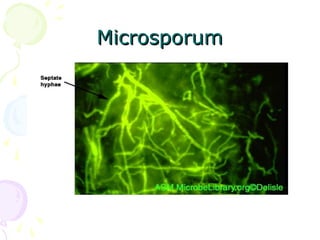
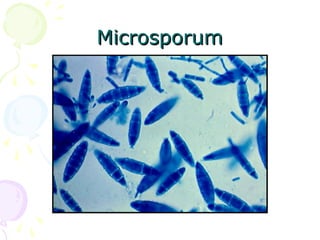
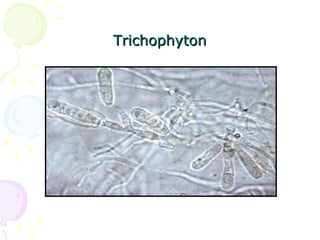
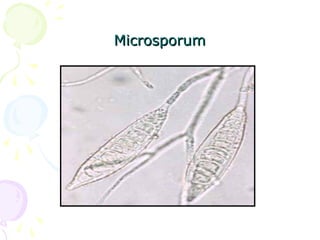
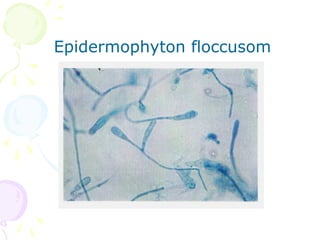
3. Common dermatophytes that cause cutaneous mycoses are Microsporum, Trichophyton, and Epidermophyton. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of skin scrapings and cultures on selective media.