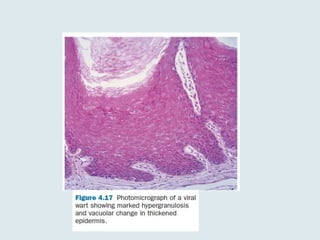
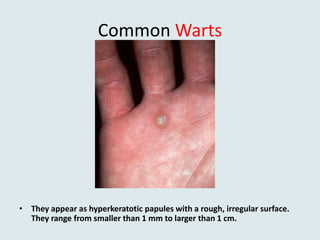
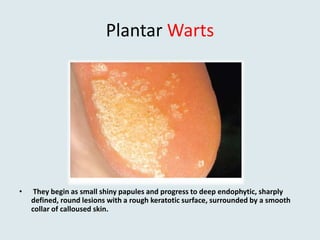
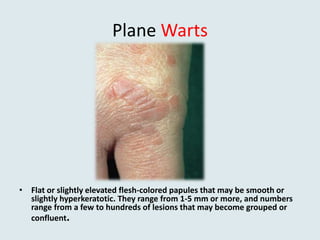
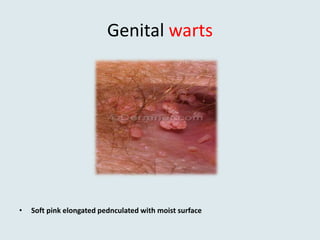
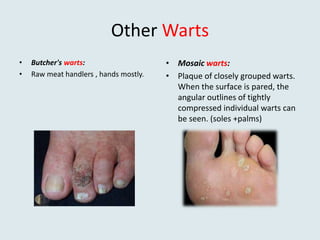
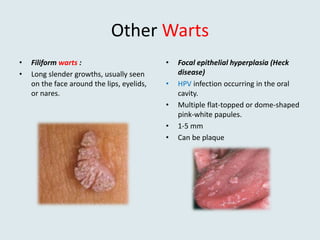
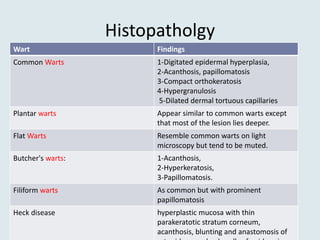
Viral warts are benign skin growths caused by various strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). There are several different clinical types of warts including common, plantar, flat, and genital warts. Warts appear as small rough bumps or flat lesions on the skin and are usually diagnosed based on their appearance. They can occur in many areas of the body depending on the type. While most warts are not harmful and may resolve on their own, some types like genital warts require treatment to remove them.