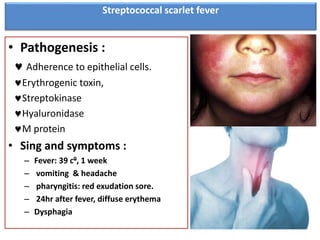
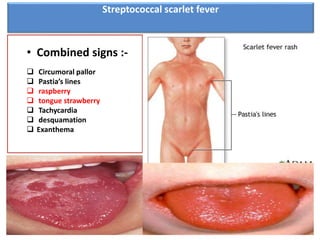
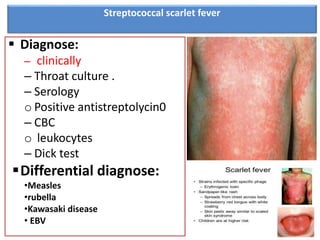
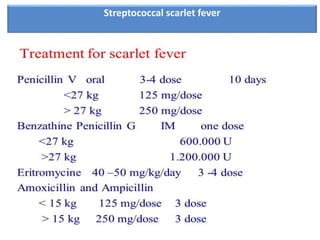
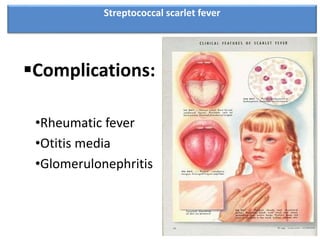
Streptococcal scarlet fever is an upper respiratory infection caused by group A streptococcal bacteria, commonly affecting children ages 4-8. It has an incubation period of 3-6 days and is highly contagious, spreading through airborne droplets or contact. Symptoms include fever, vomiting, sore throat, and a diffuse rash that appears 24 hours after fever. Diagnosis is usually clinical but can be confirmed with throat culture, serology tests, or Dick testing. Complications can include rheumatic fever, ear infections, and kidney problems.