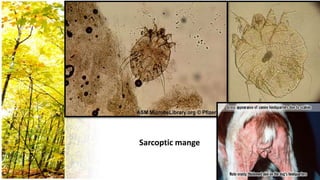
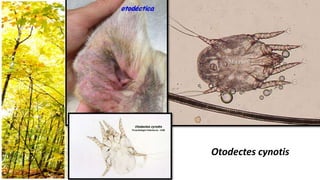
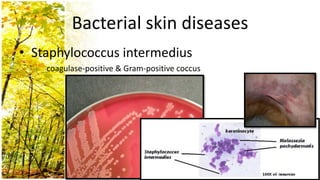
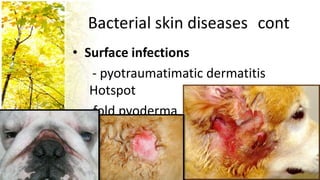
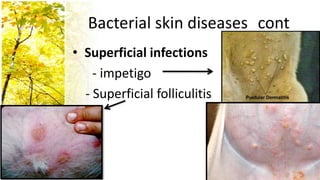
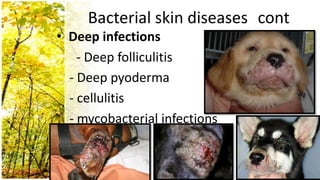
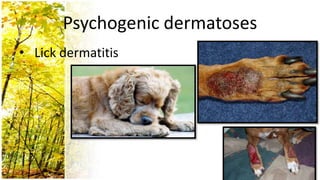
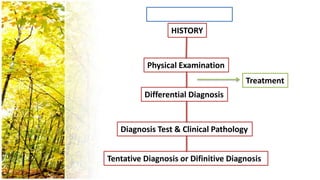
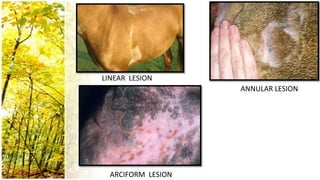
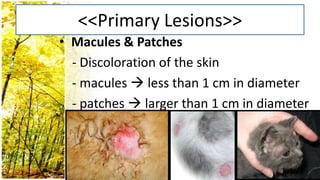
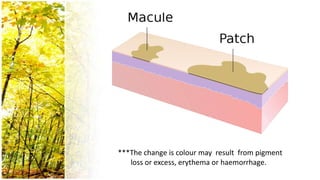
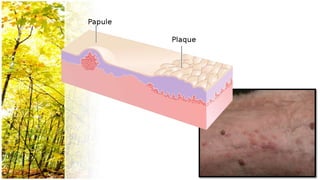
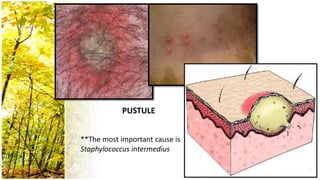
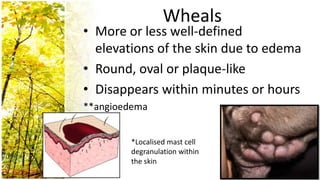
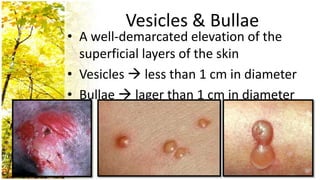
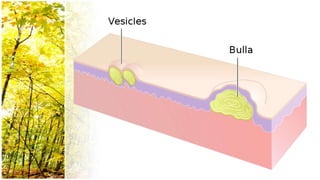
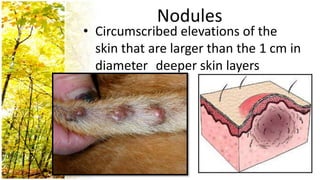
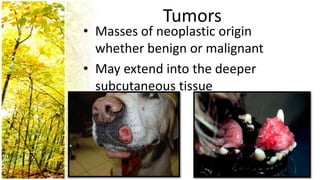
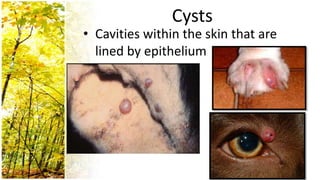
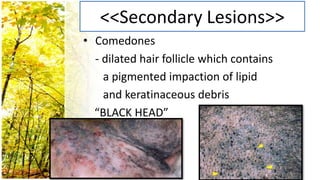
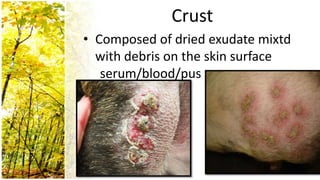
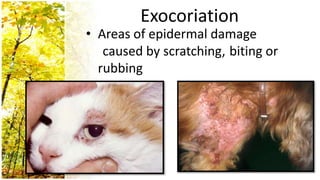
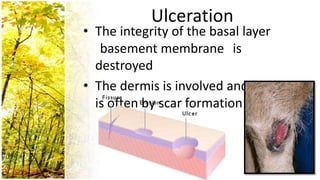
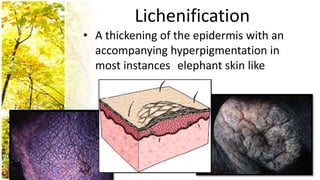
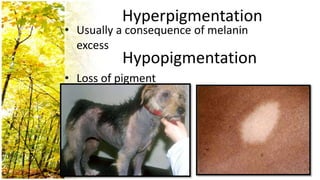
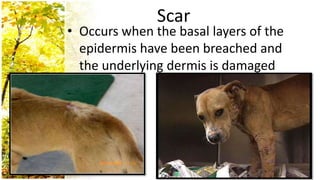
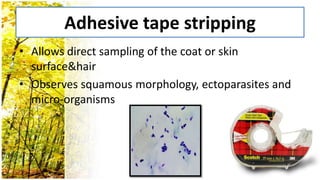
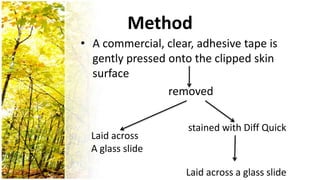
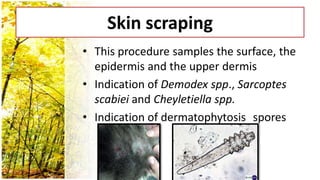
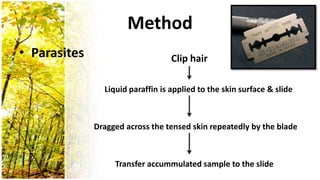
This document provides an overview of dermatological history taking, physical examination, diagnostic testing, and differential diagnosis of skin diseases in dogs. It discusses taking a patient history, performing a physical exam to identify primary and secondary skin lesions, and collecting samples via skin scrapings, trichograms, tape stripping, fungal culture and cytology. A range of parasitic, bacterial, viral, fungal and other infectious and non-infectious dermatological conditions are described. Diagnostic tests include Wood's lamp exam, skin biopsies and bacterial culture. Treatment may involve topical therapies, systemic drugs or surgery.