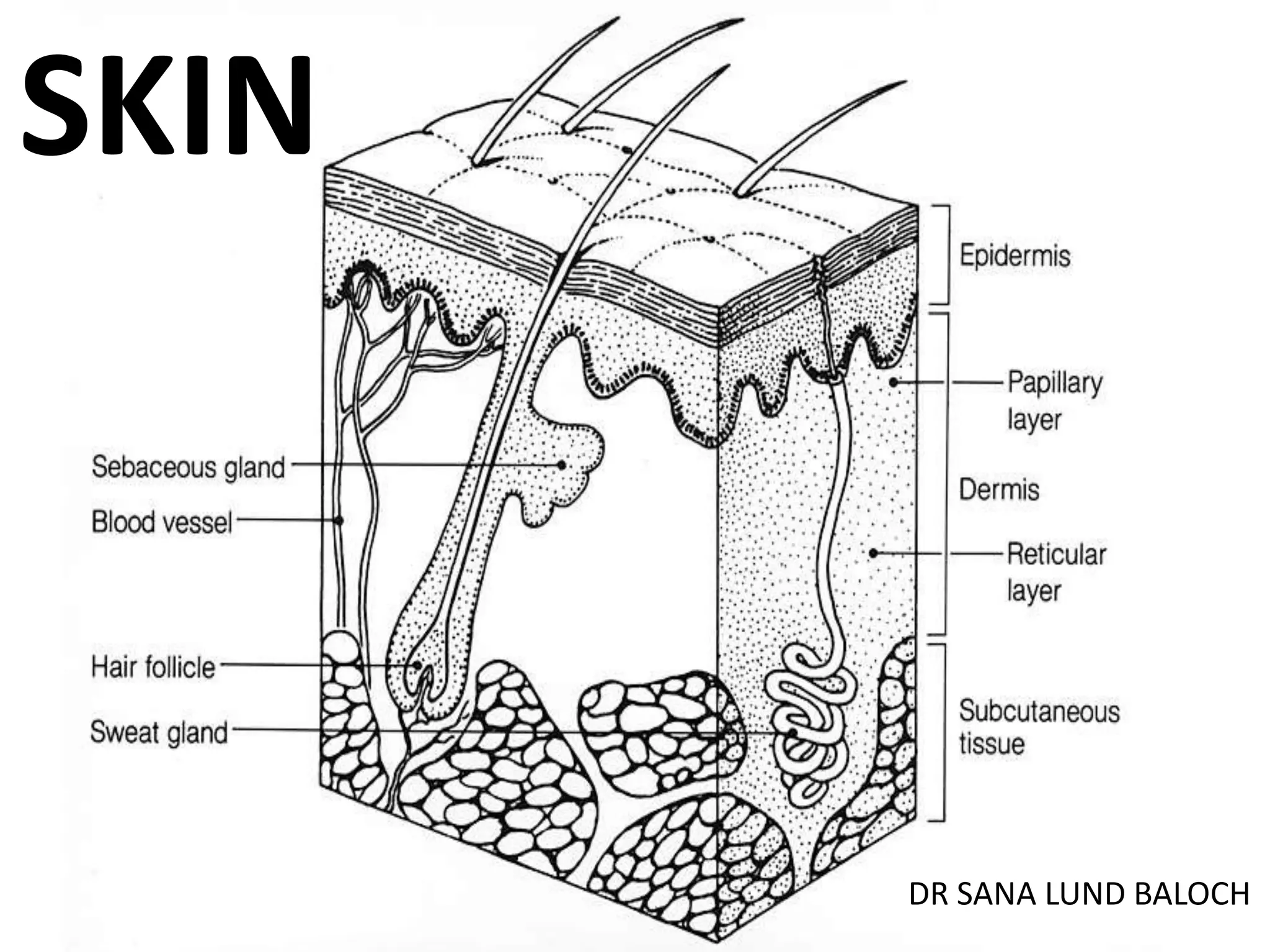
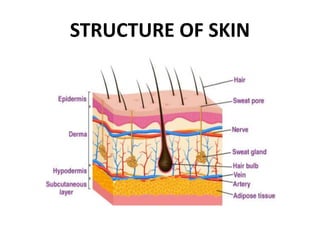
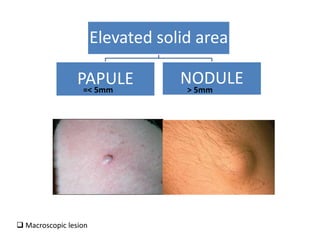
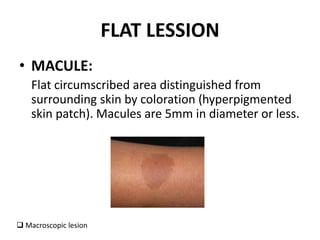
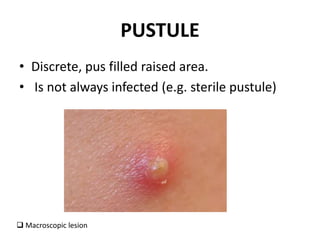
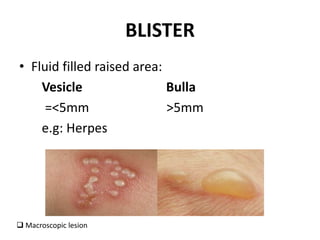
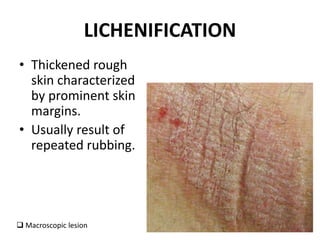
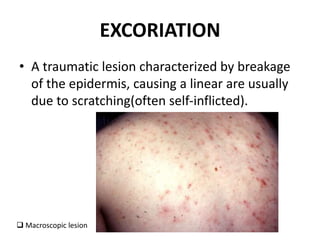
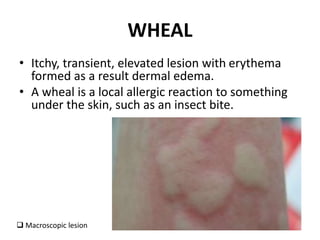
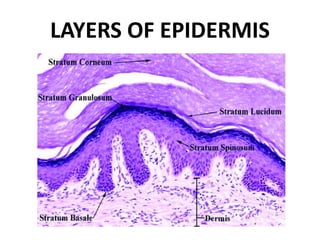
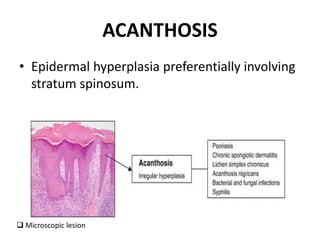
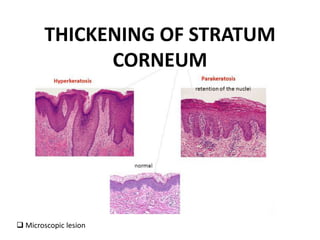
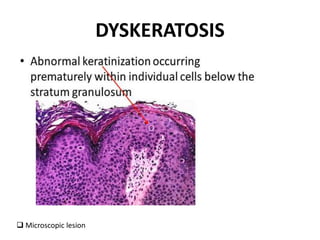
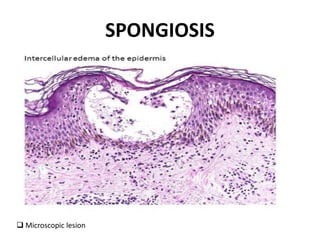
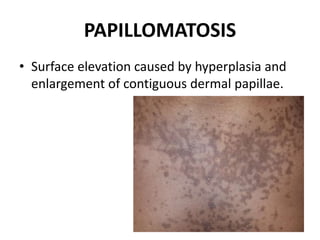
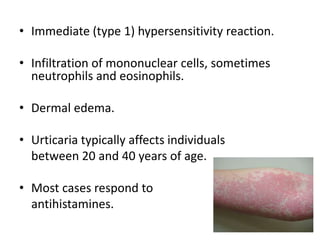
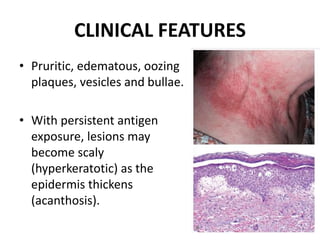
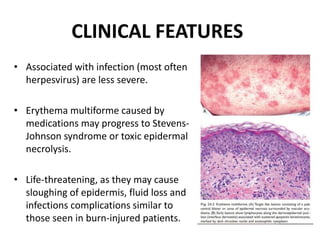
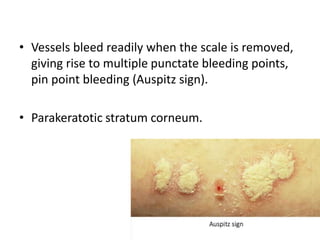
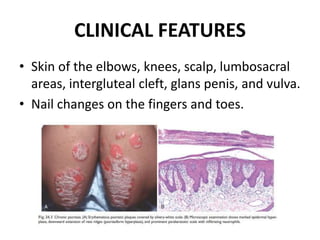
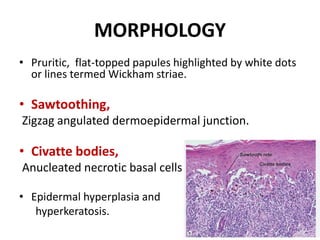
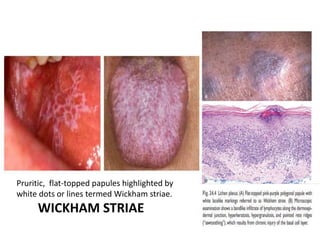
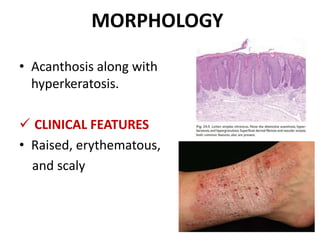
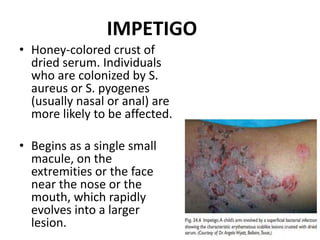
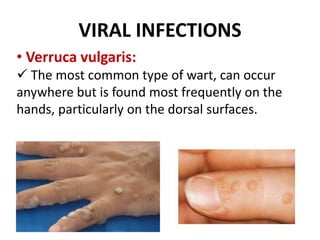
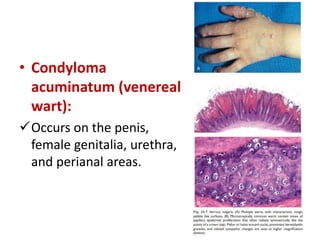
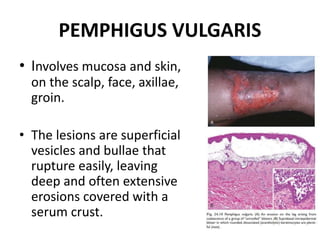
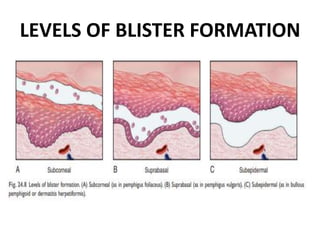
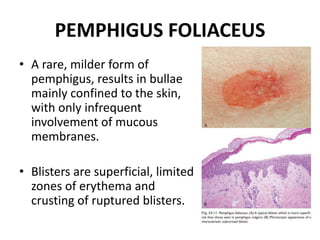
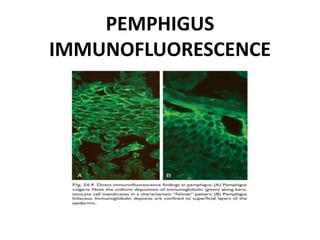
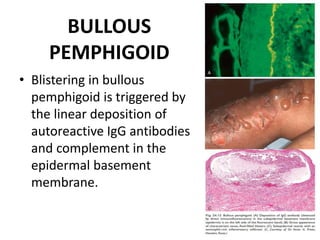
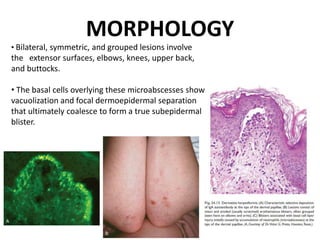
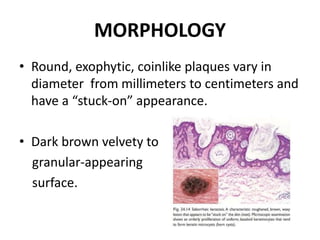
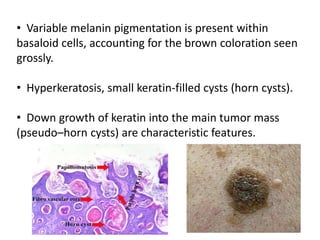
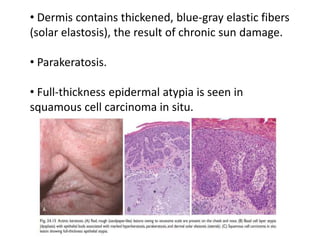
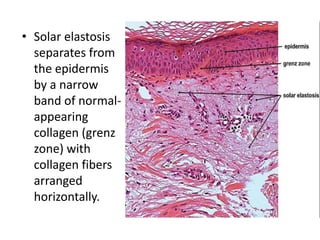
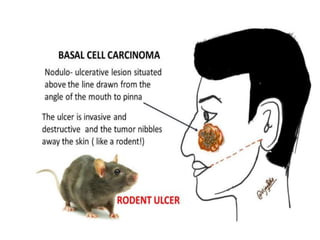
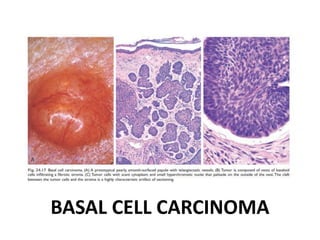
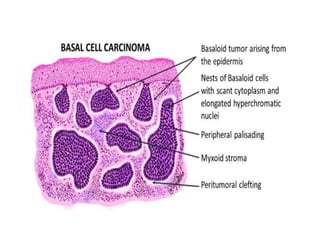
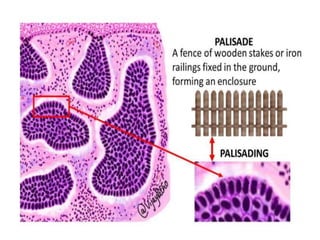
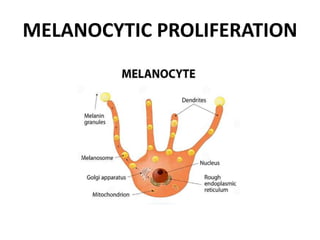
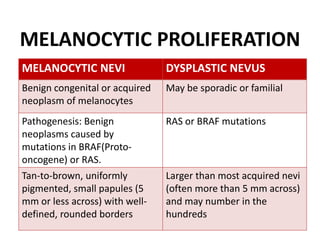
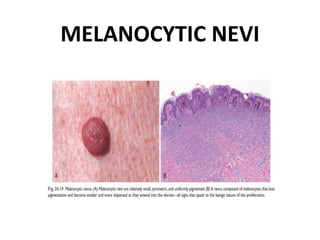
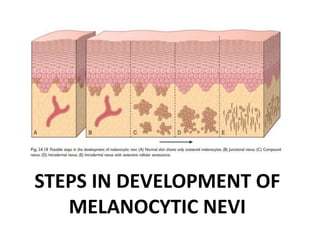
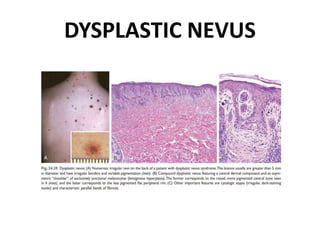
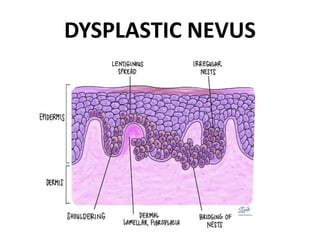
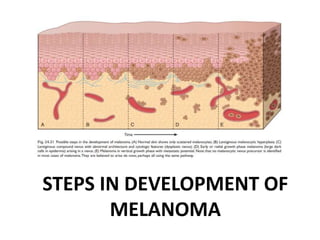
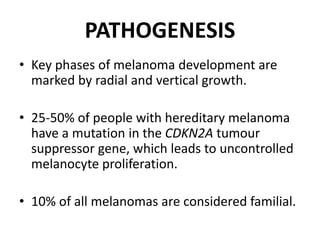
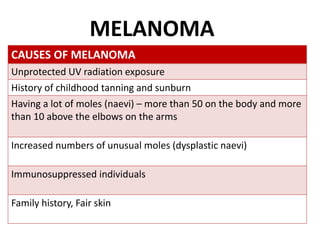
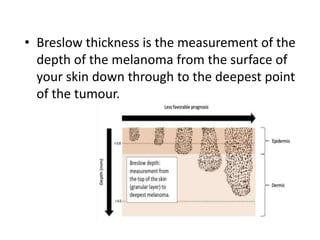
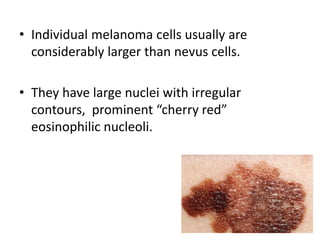
This document discusses the structure and functions of skin. It provides details on the layers of the epidermis and dermis. Various skin appendages like hair follicles and sebaceous glands are also mentioned. The document then discusses several common dermatological conditions like psoriasis, lichen planus, bacterial and fungal infections, blistering disorders, and tumors of the skin. Macroscopic and microscopic features of these conditions are described along with their pathogenesis and clinical presentation. Common benign tumors of the skin like seborrheic keratosis and premalignant lesions like actinic keratosis are also summarized.