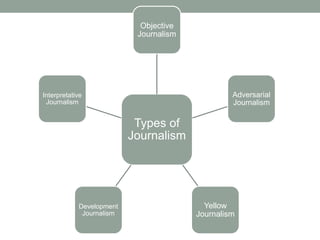
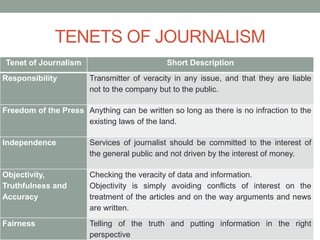
Carl Patrick S. Tadeo provides an overview of journalism. He defines journalism as the collection and dissemination of news through print and electronic media, which involves reporting, writing, editing, photographing, broadcasting, or cablecasting news items. Tadeo outlines the different types of journalism, including objective journalism, interpretative journalism, adversarial journalism, development journalism, and yellow journalism. He also discusses key tenets of journalism like responsibility, freedom of the press, independence, objectivity, truthfulness, accuracy, and fairness.