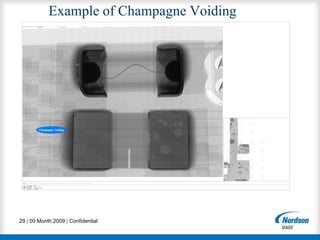
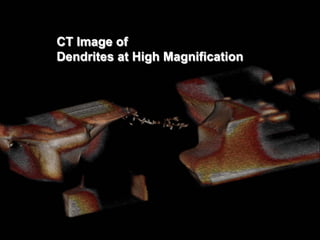
This document summarizes an X-ray inspection workshop that covered common defects seen in electronics manufacturing and how to identify them using X-ray imaging. The workshop discussed why X-ray inspection is used, suggested requirements for X-ray systems, and provided examples of defects like BGA opens, voids, cracks, and dendrites. Attendees were taught inspection procedures and criteria to evaluate components like BGAs, QFNs, and through-hole joints using X-ray imaging.