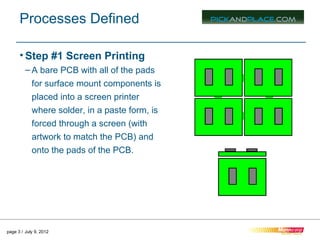
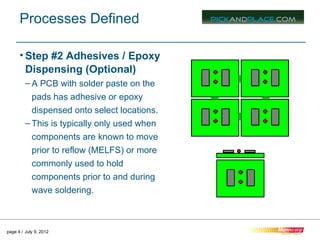
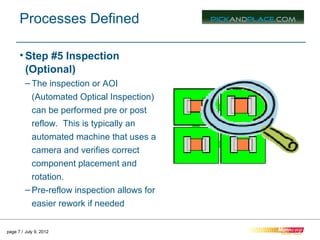
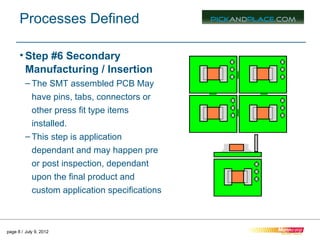
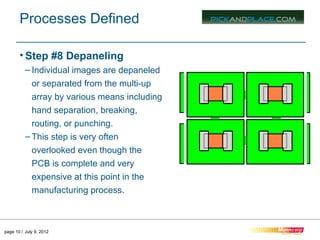
This document outlines the typical 12 step surface mount manufacturing process for printed circuit boards. It describes each step in detail, including screen printing solder paste, component pick and place, reflow soldering, inspection, secondary assembly, cleaning, depaneling, product assembly, testing, packaging and shipping. The key steps are screen printing to apply solder paste, pick and place to position components, reflow soldering to bond components, inspection to check placement, and depaneling individual circuit boards.