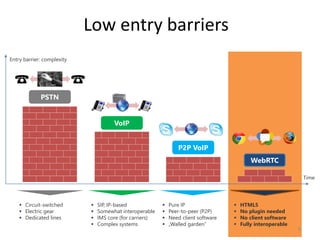
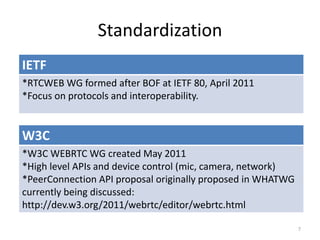
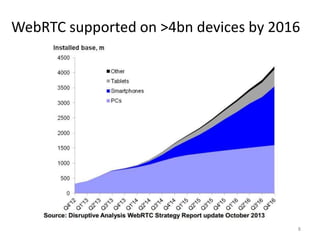
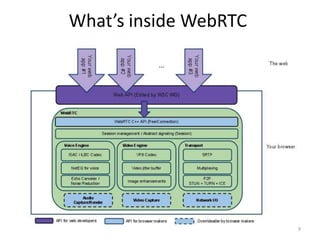
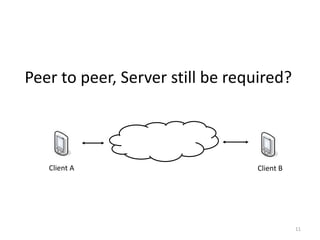
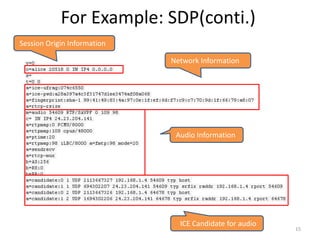
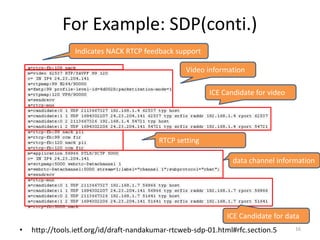
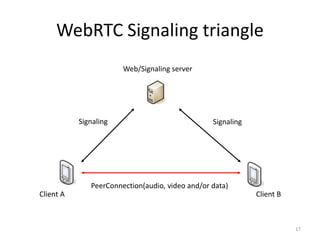
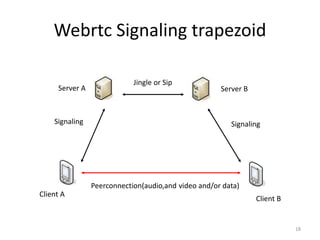
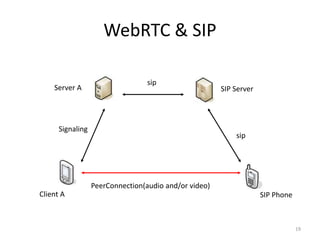
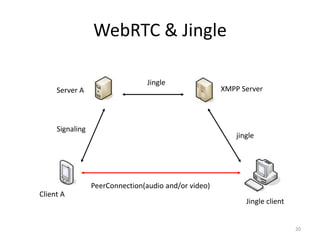
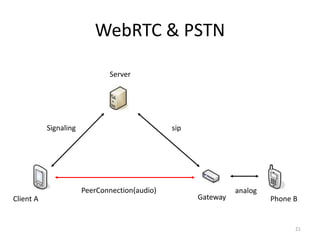
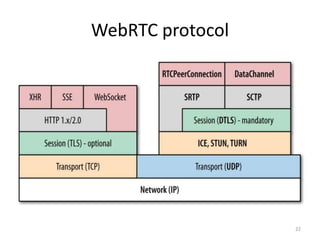
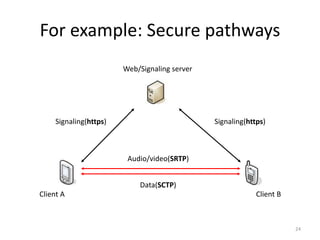
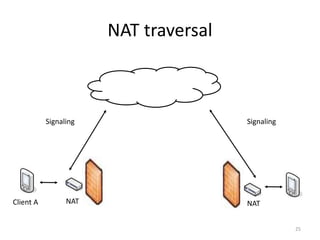
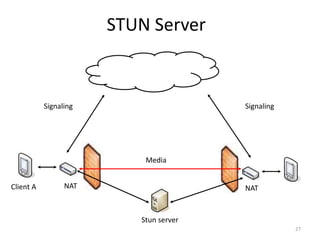
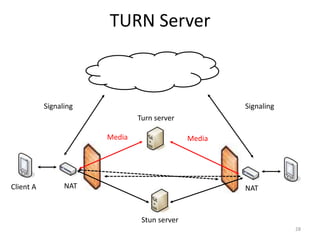
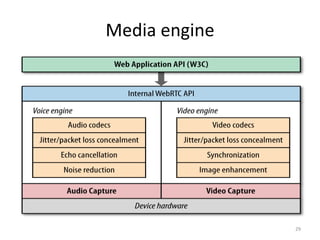
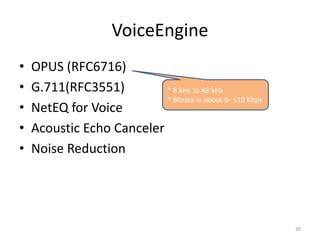
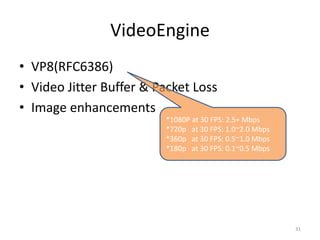
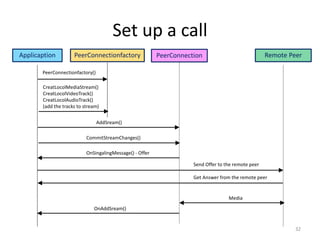
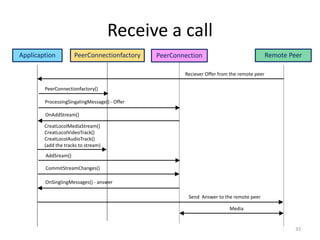
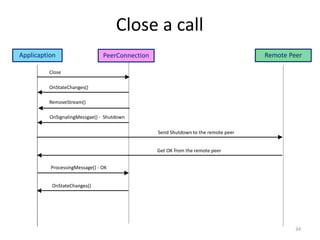
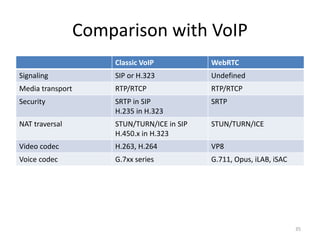
WebRTC allows for real-time communication through peer-to-peer connections for voice, video, and data directly in web browsers. It uses open standards and does not require any plugins. WebRTC uses protocols like STUN, TURN, and ICE for NAT traversal and uses SRTP for secure media transmission. Signaling is required to coordinate between peers, which can use protocols like SIP, XMPP, or WebSockets. Popular codecs used in WebRTC include VP8 for video and Opus for voice. WebRTC is supported on over 4 billion devices by 2016 and enables many applications including video calling, remote assistance, and game/desktop streaming directly in web browsers.