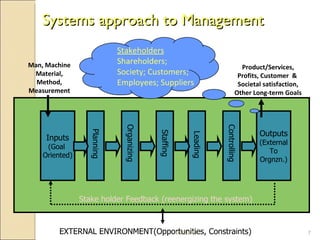
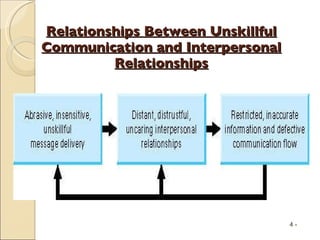
The document discusses several topics related to managing in today's changing world including:
1) The differences between traditional and modern business environments and the Pakistani work scenario.
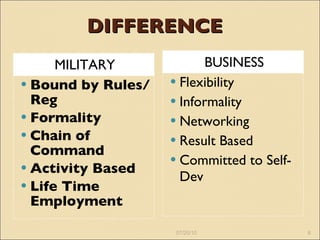
2) The differences between military and business management approaches in terms of rules, formality, and goals.
3) Key skills needed for management including technical, human, and conceptual skills.
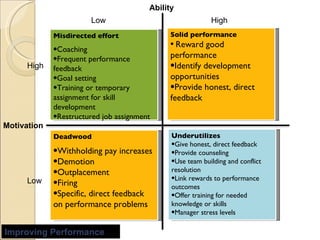
4) The importance of human resource management and empowering employees to improve organizational performance and productivity.