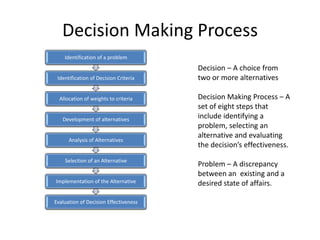
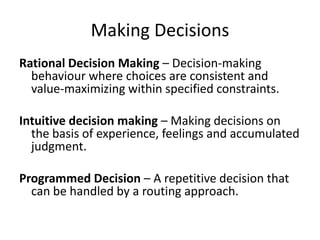
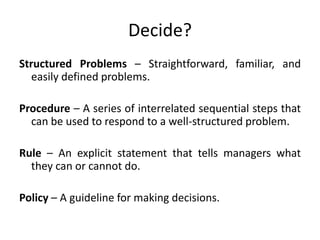
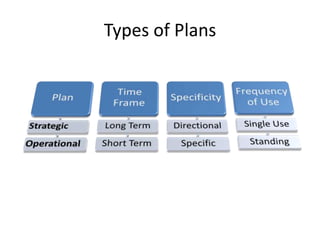
The document discusses the decision making process which includes identifying a problem, criteria for making a decision, developing alternatives, analyzing options, selecting an alternative, implementing it, and evaluating the results. It also covers types of decisions, conditions for decision making, common decision making errors, and different types of plans used in organizations.