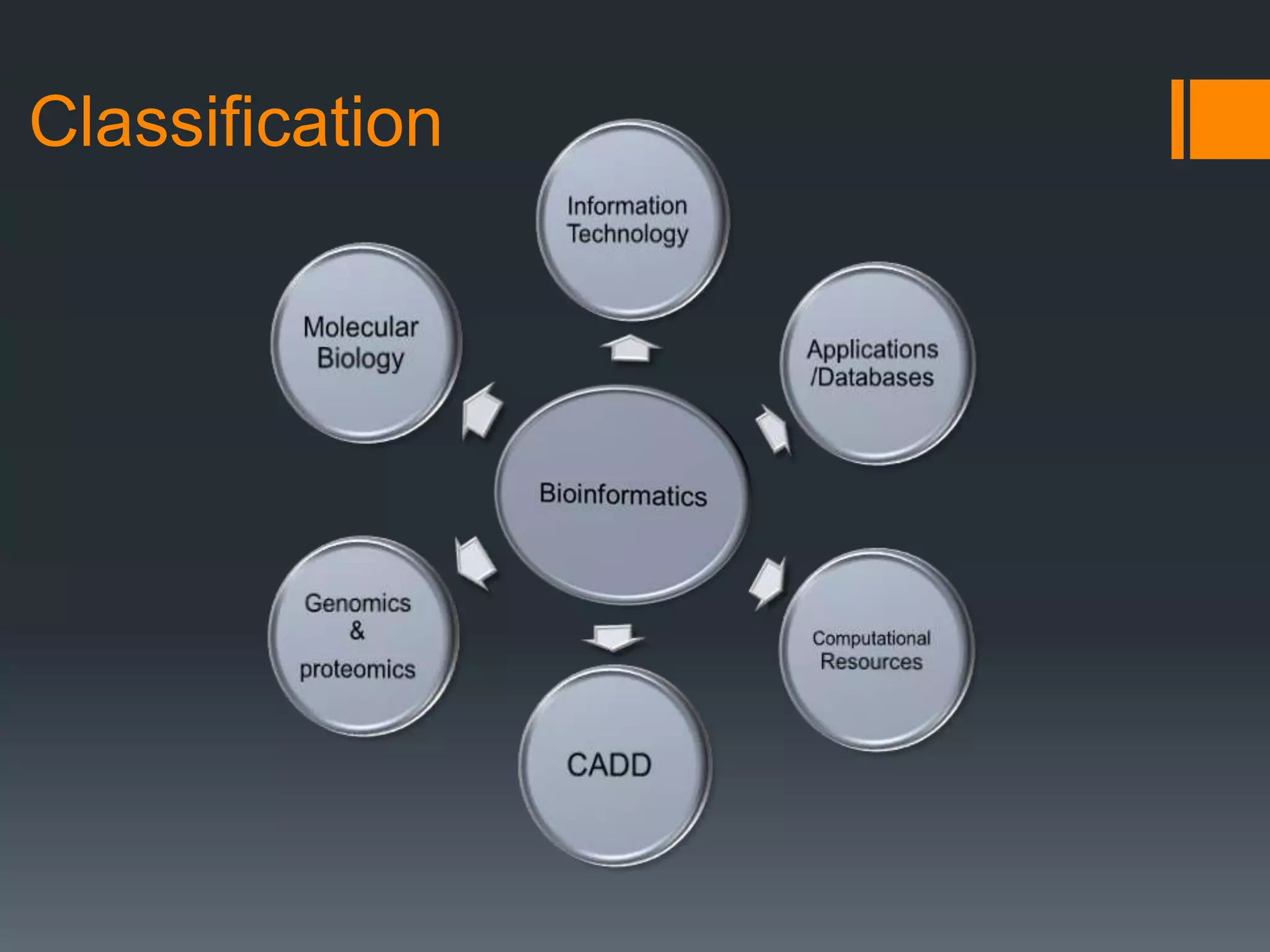
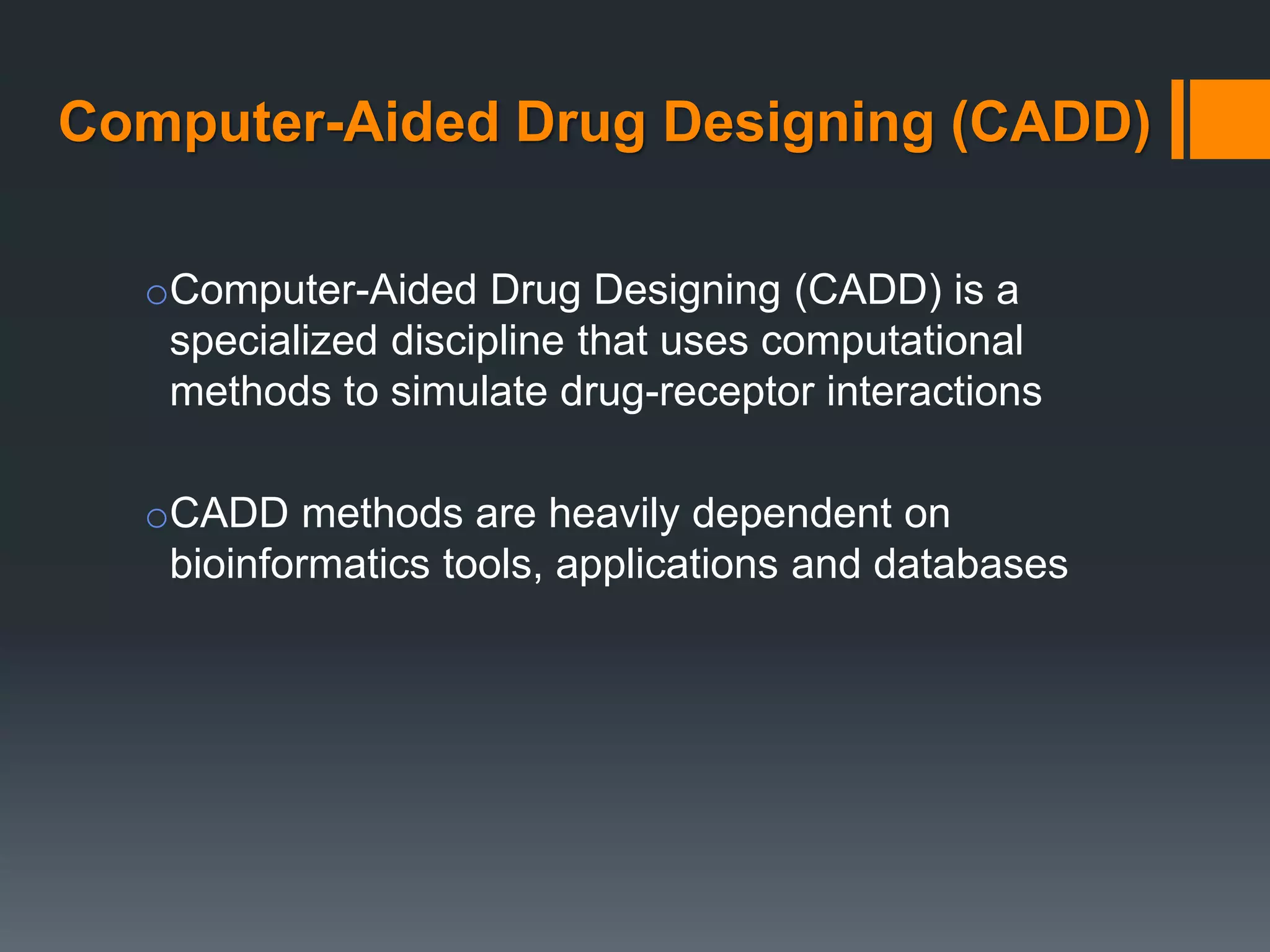
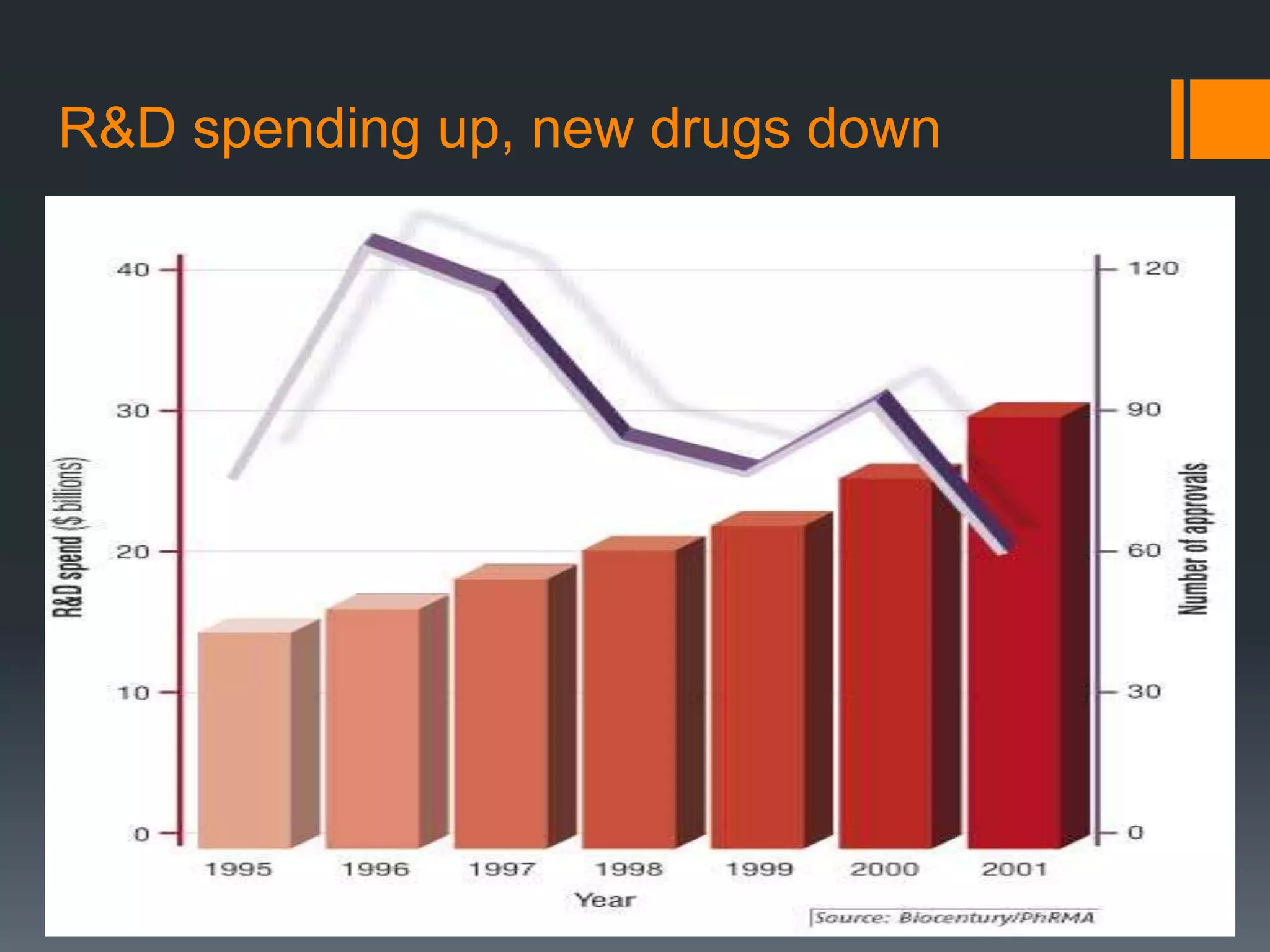
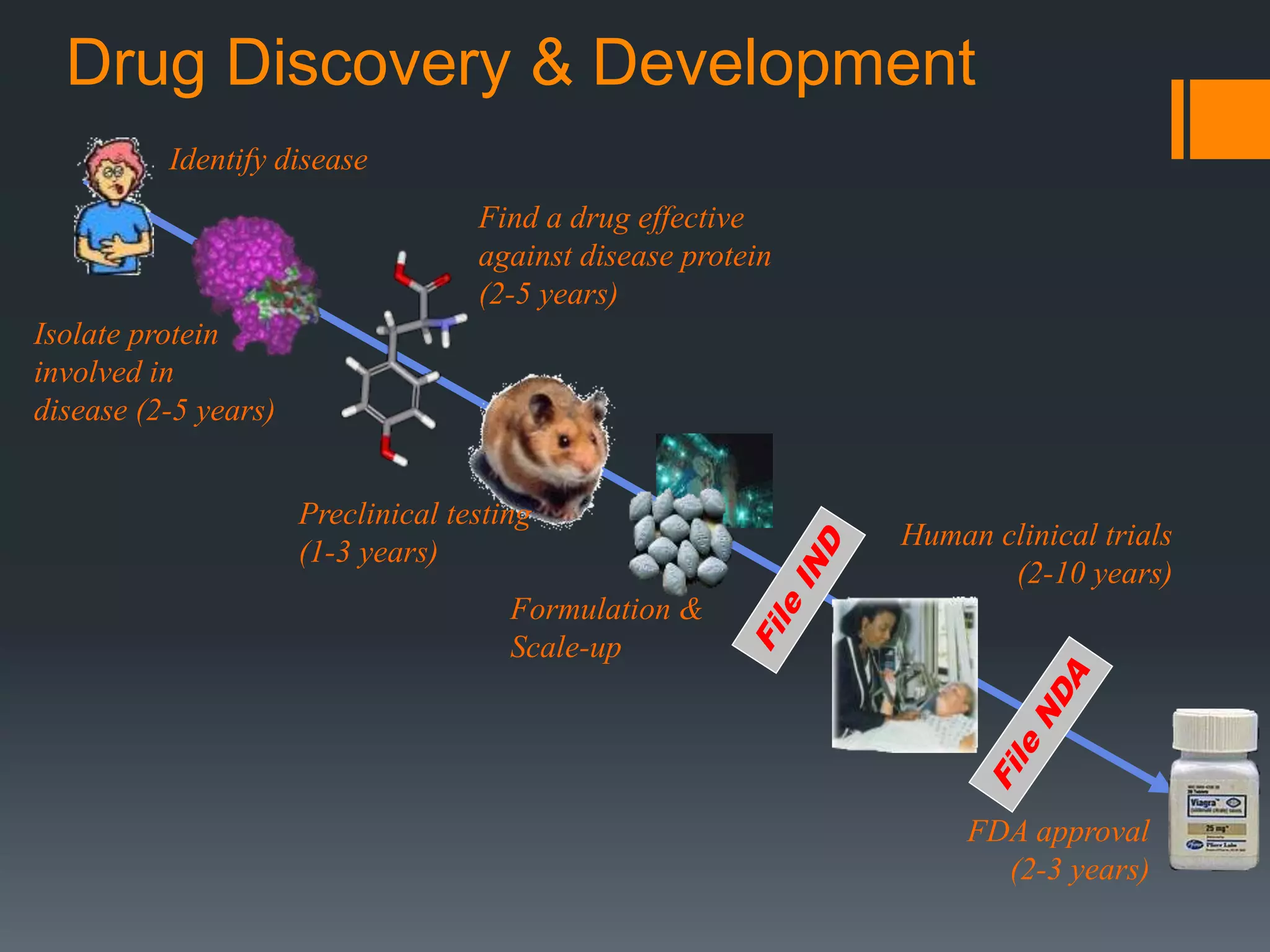
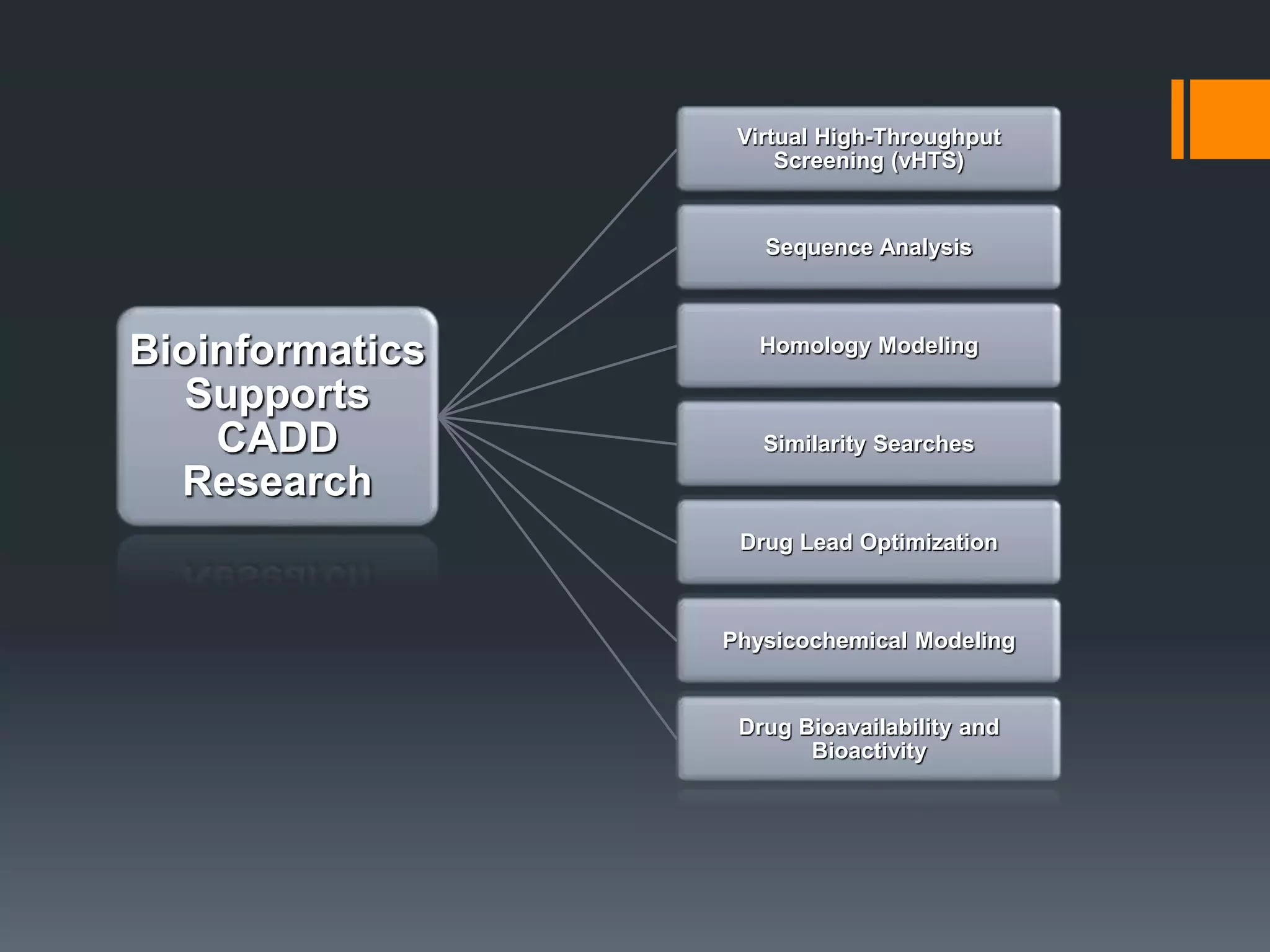
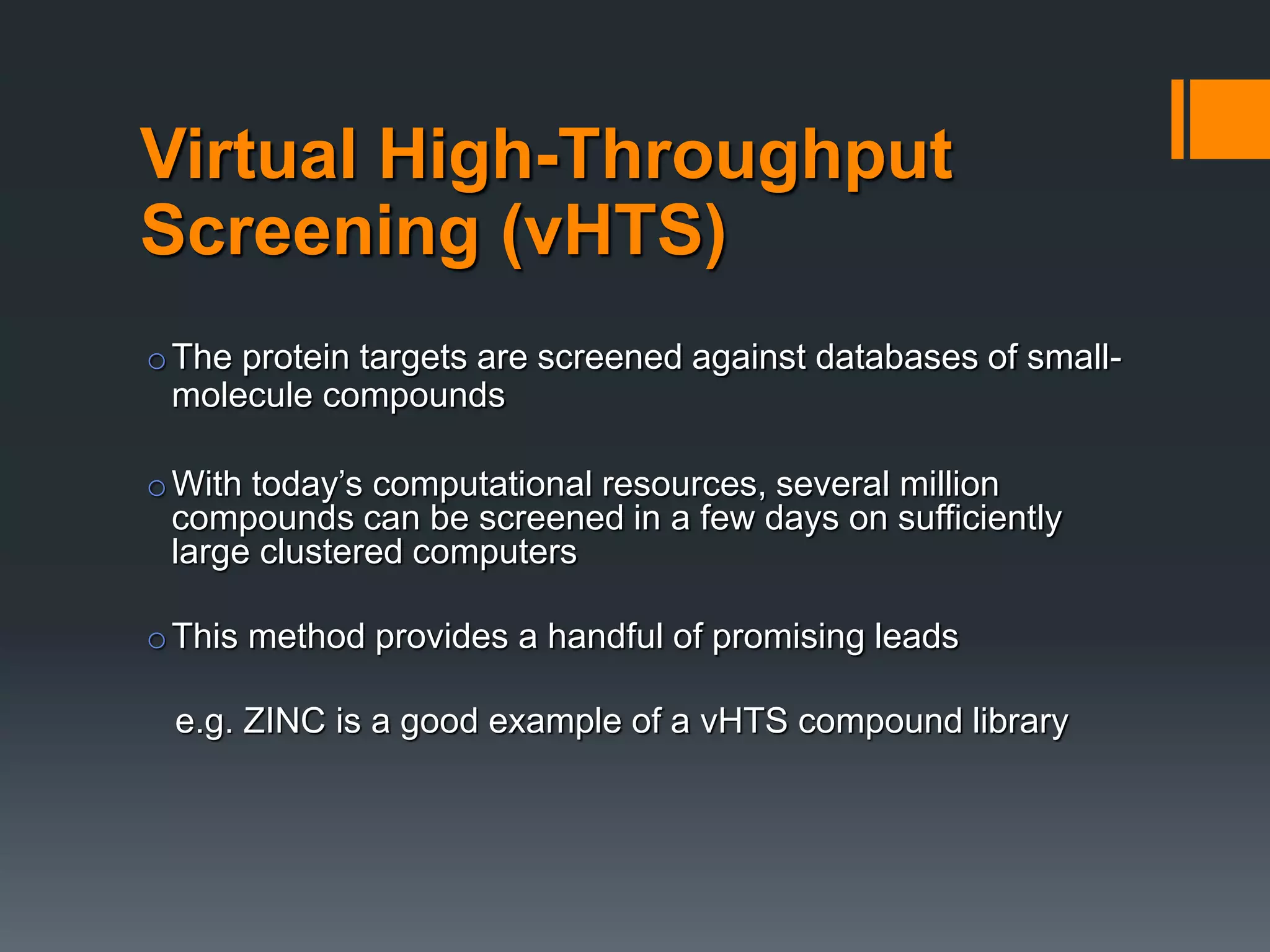
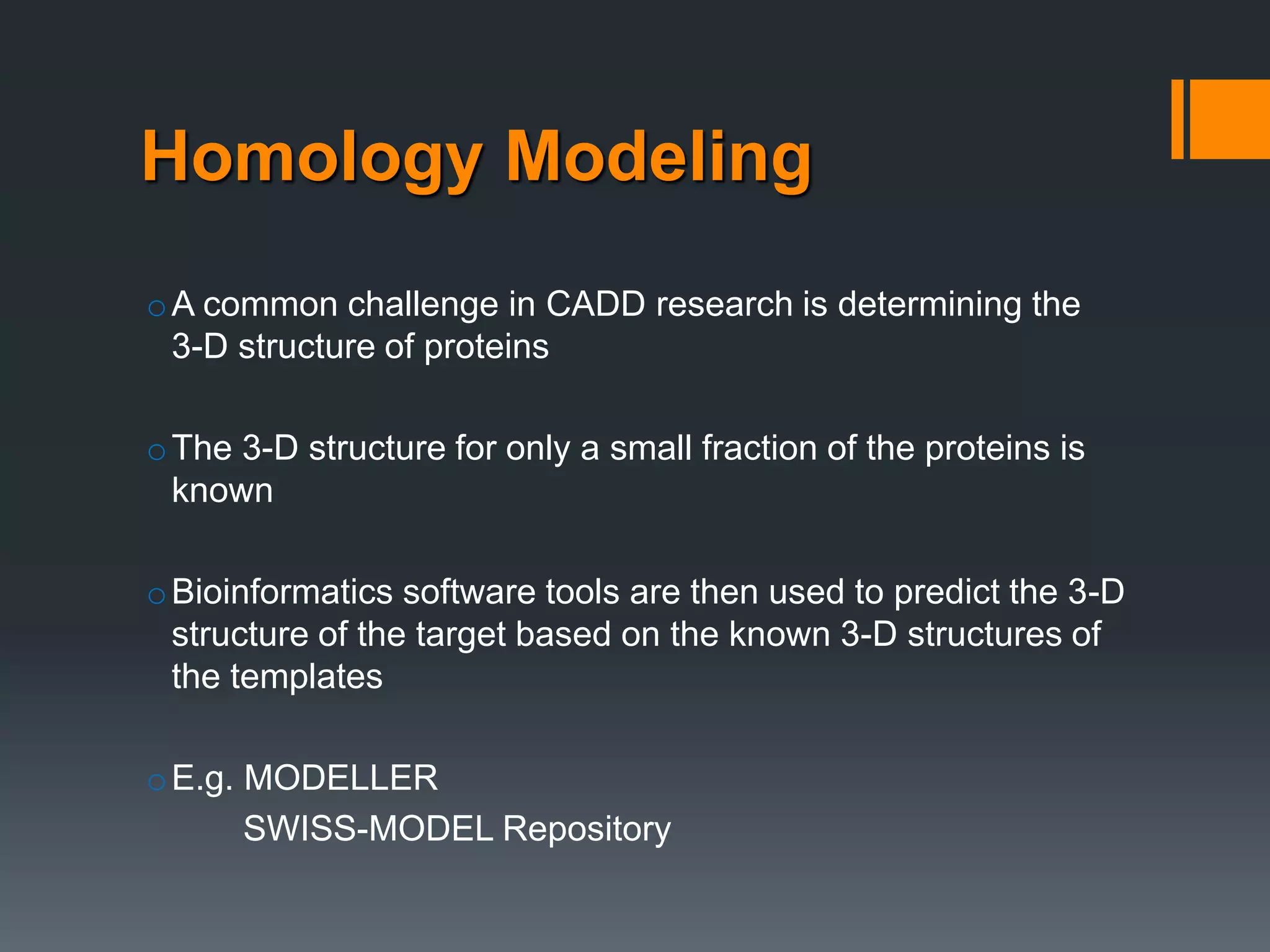
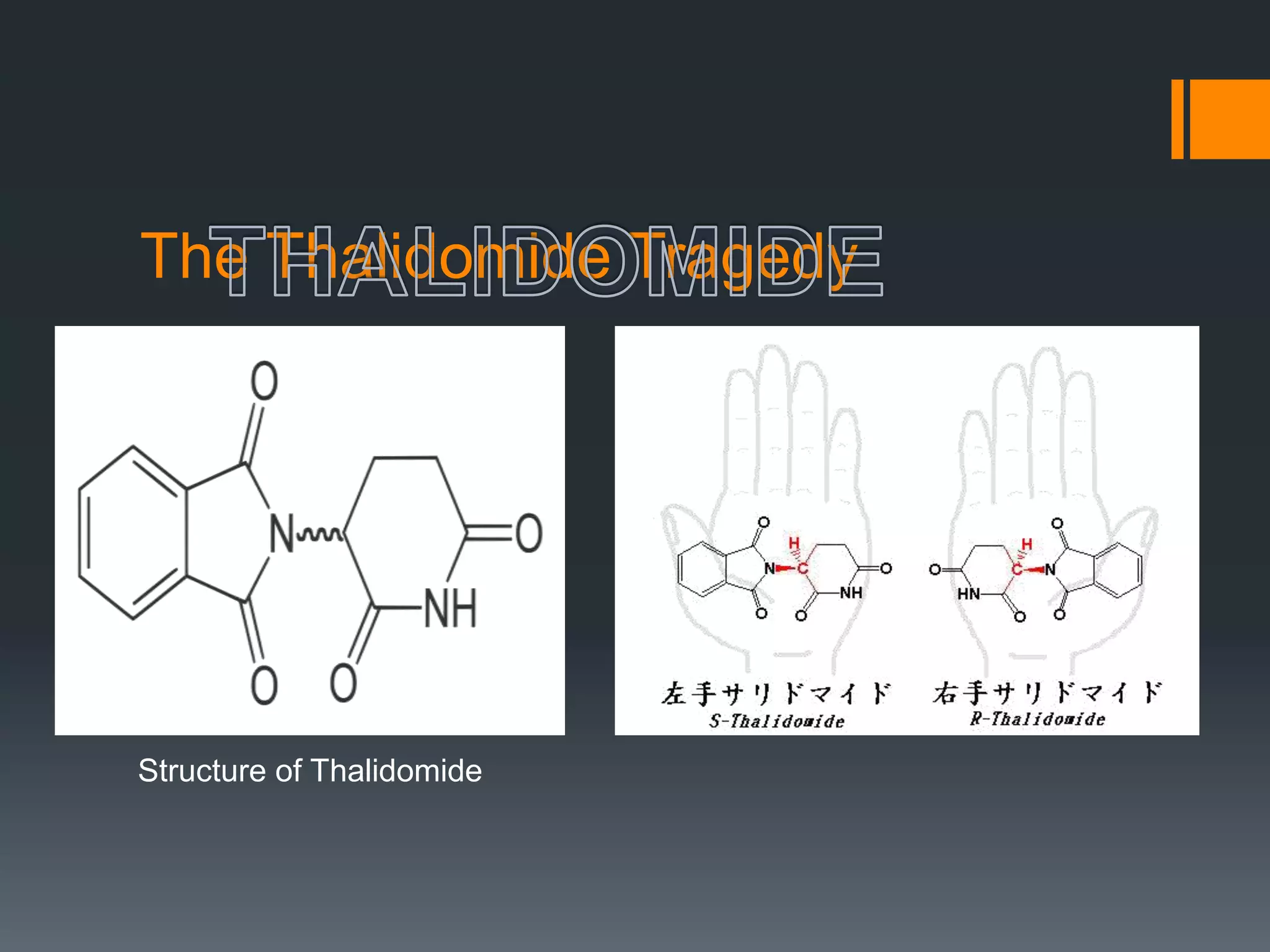
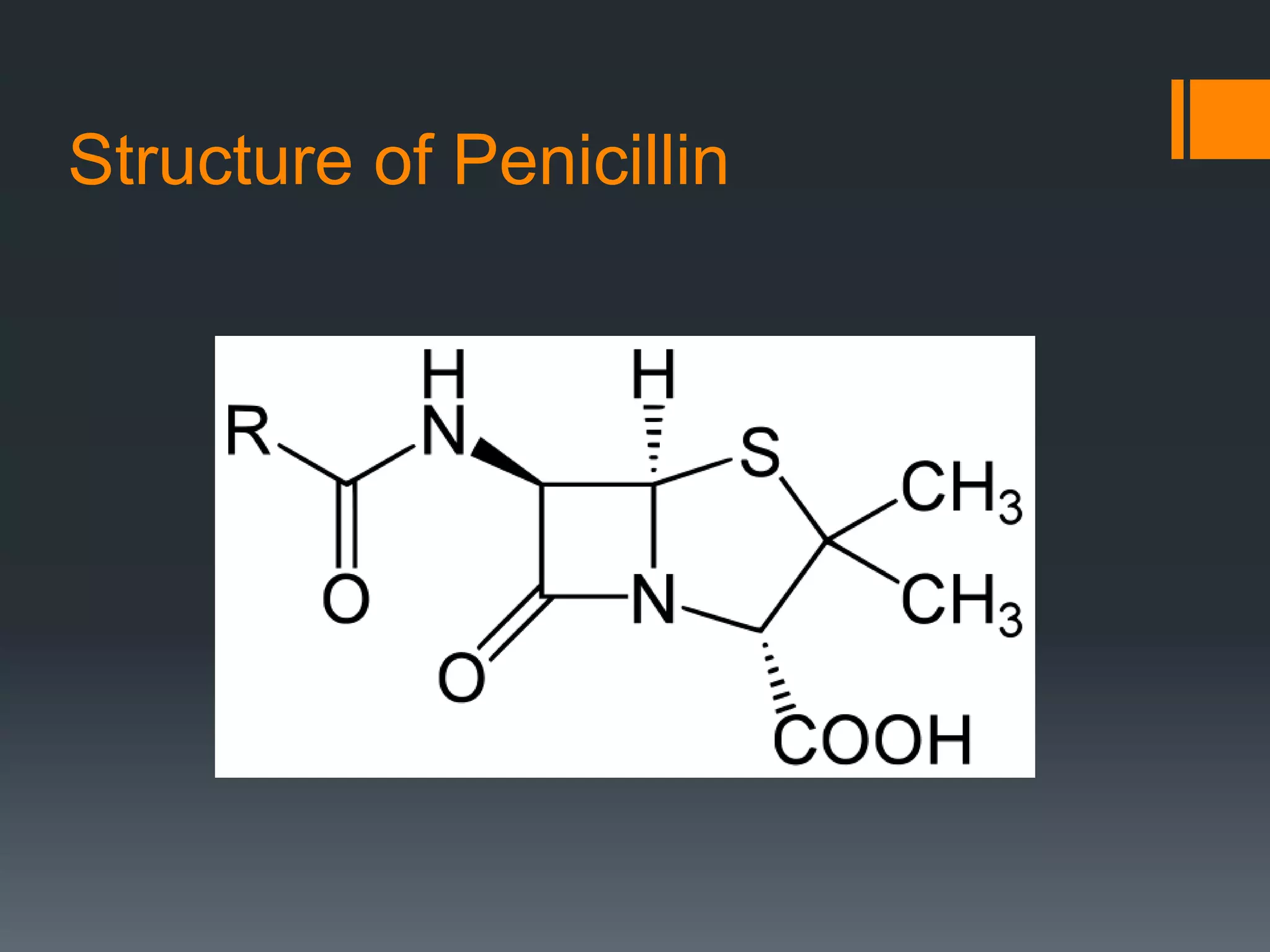
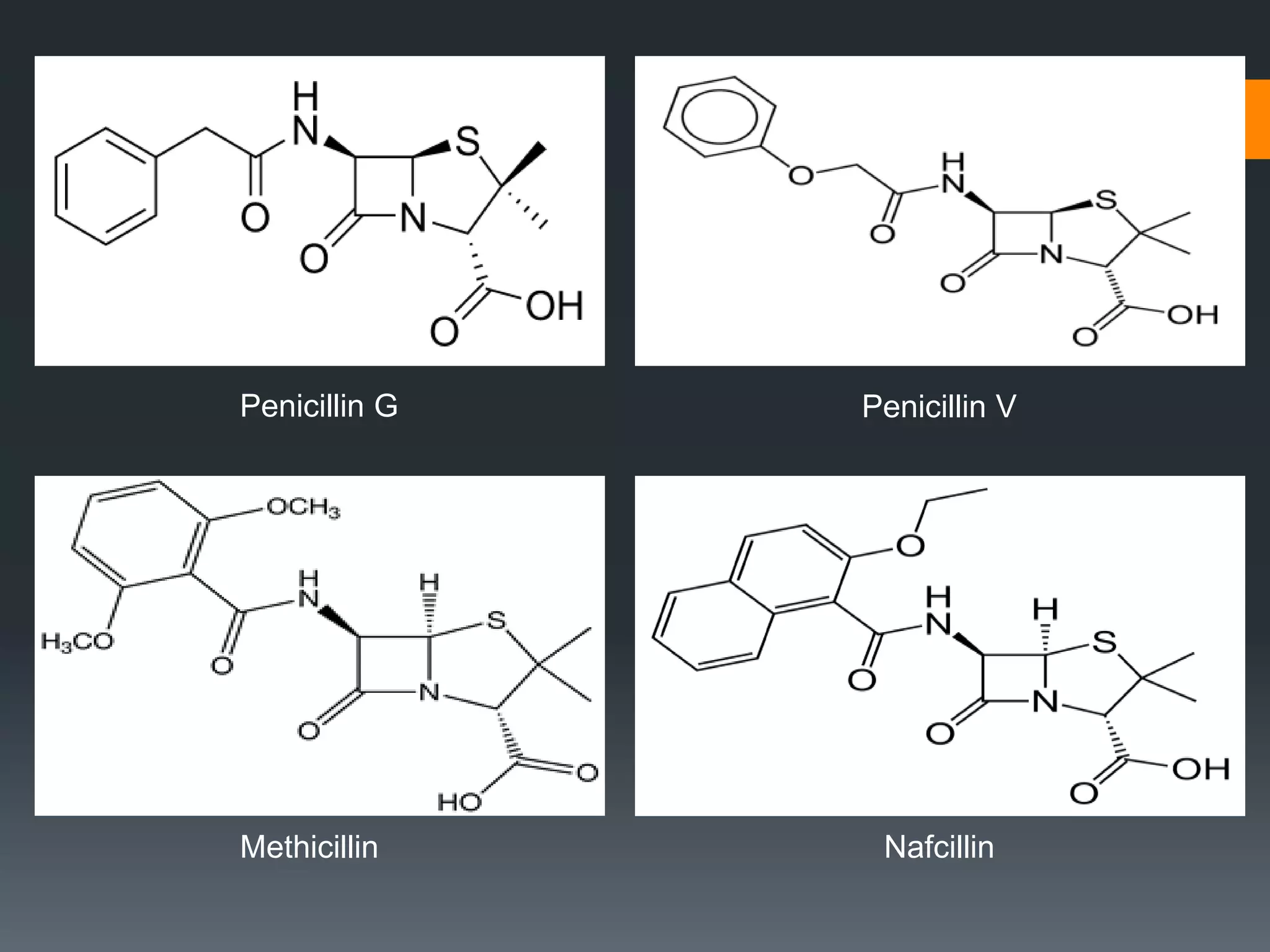
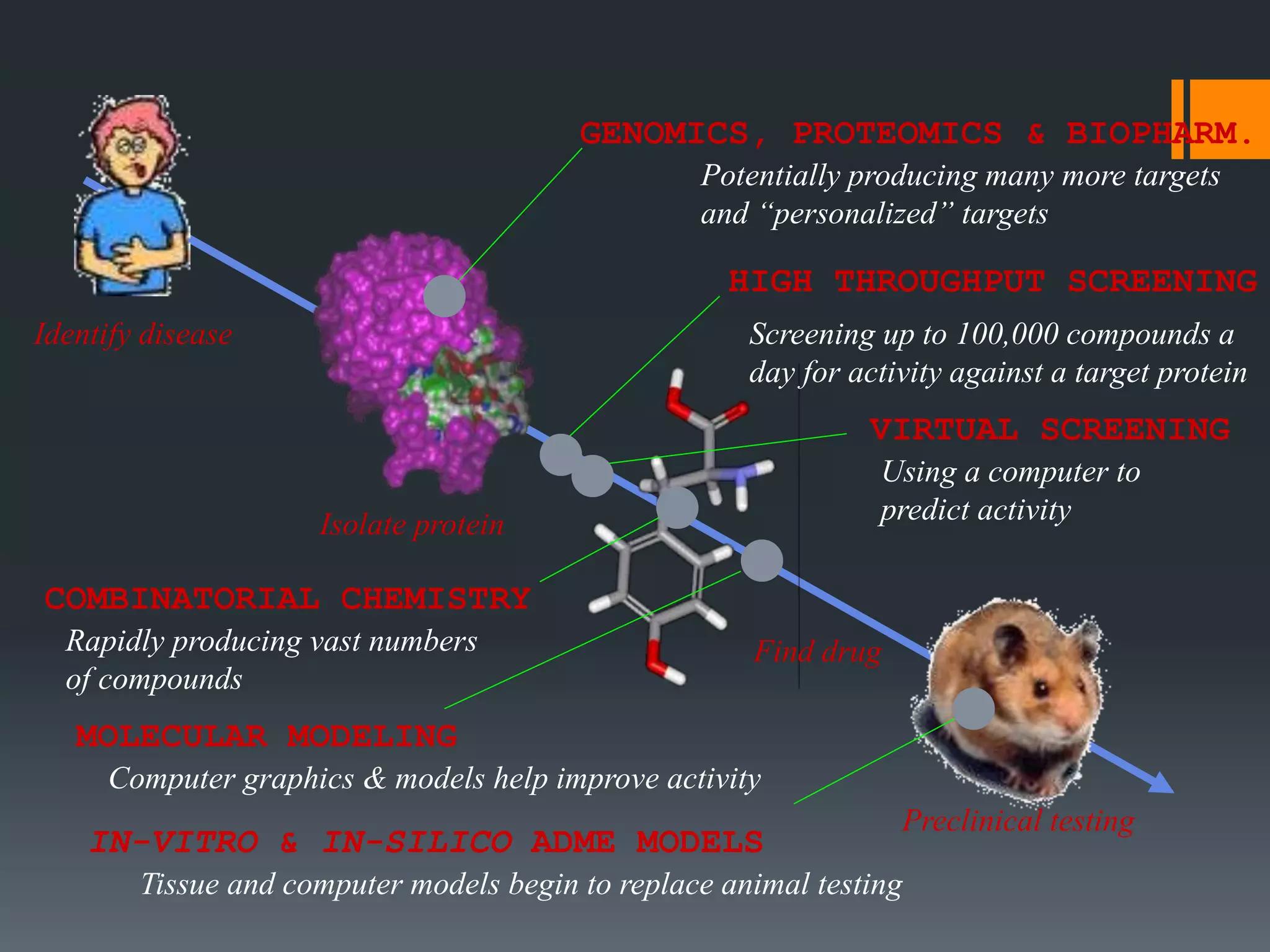
The document discusses computer-aided drug design (CADD) and its integration with bioinformatics to enhance drug discovery and development processes. It highlights the challenges, methodologies, and benefits of CADD, including virtual high-throughput screening, sequence analysis, and homology modeling, which help identify potential drug candidates more efficiently. The use of computational methods in drug discovery can significantly reduce costs and time-to-market while providing deeper insights into drug-receptor interactions.