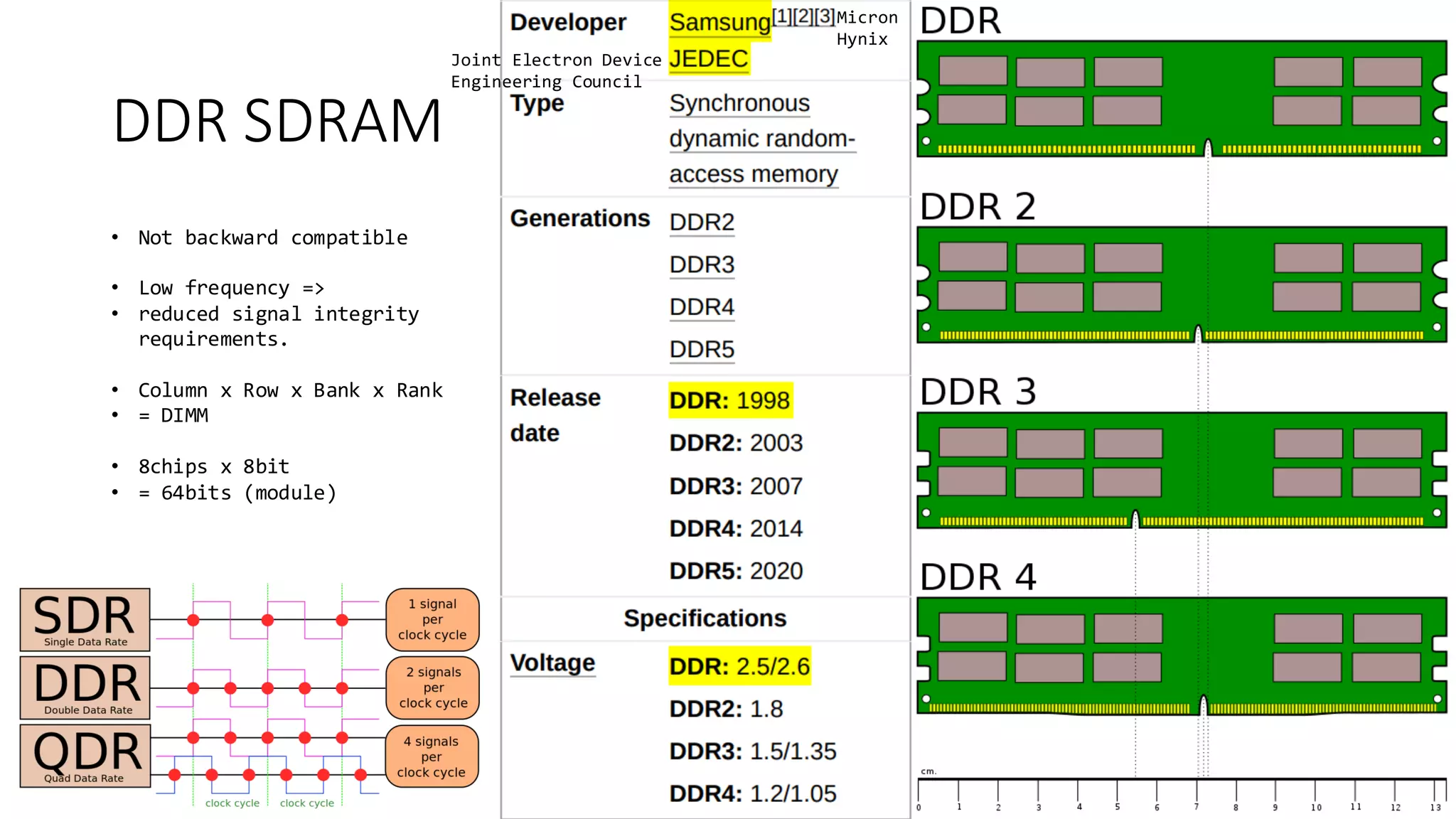
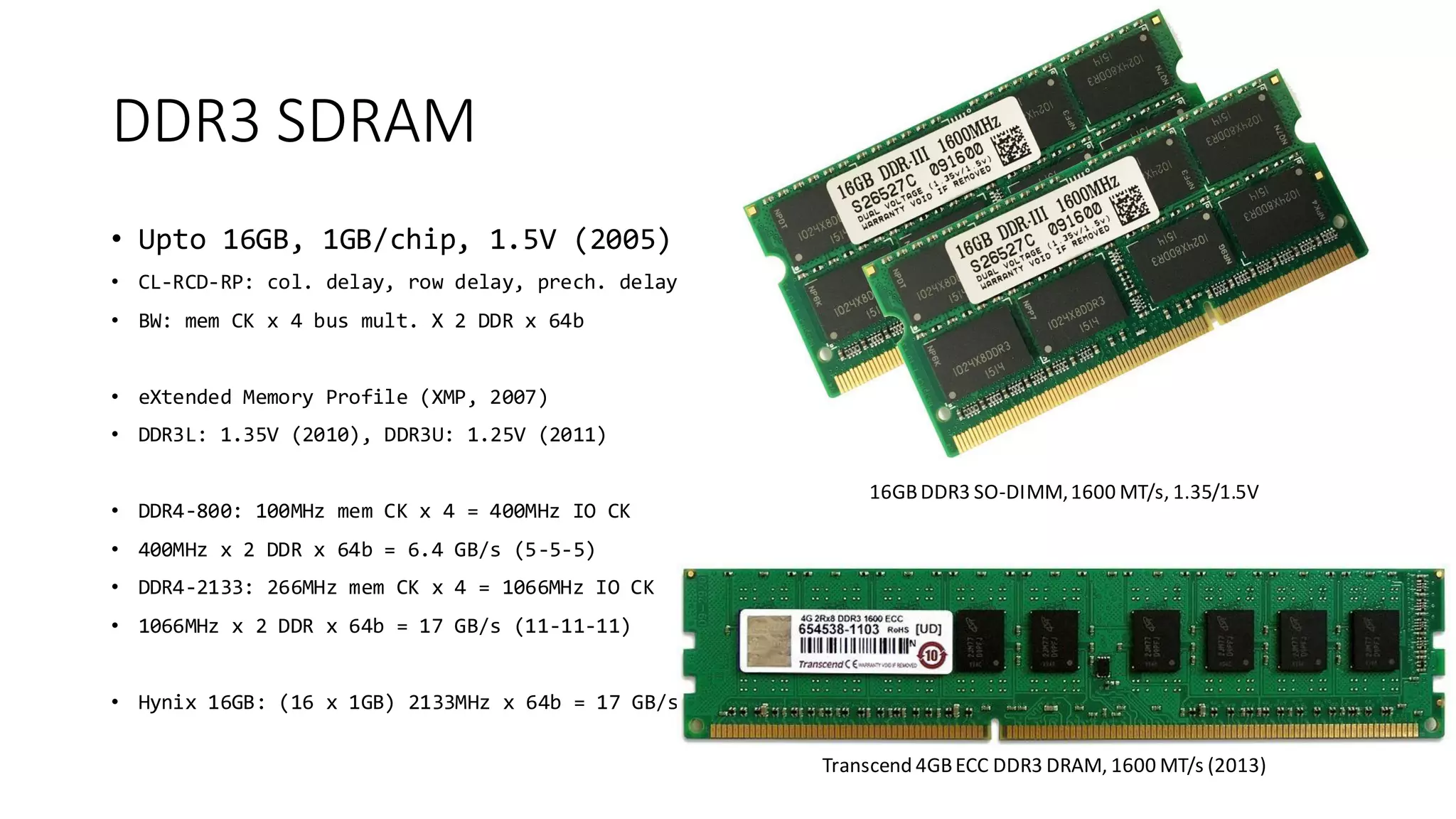
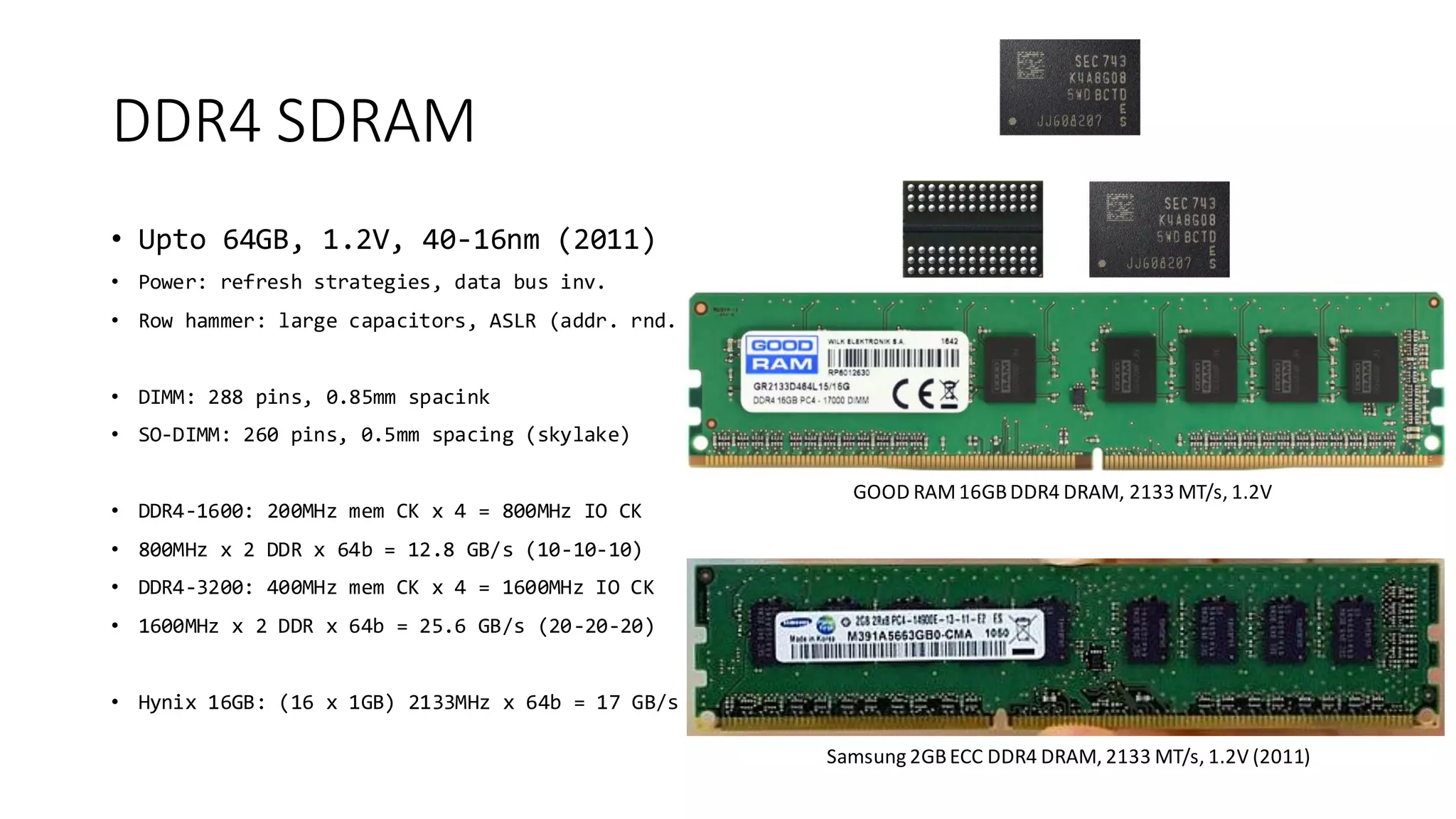
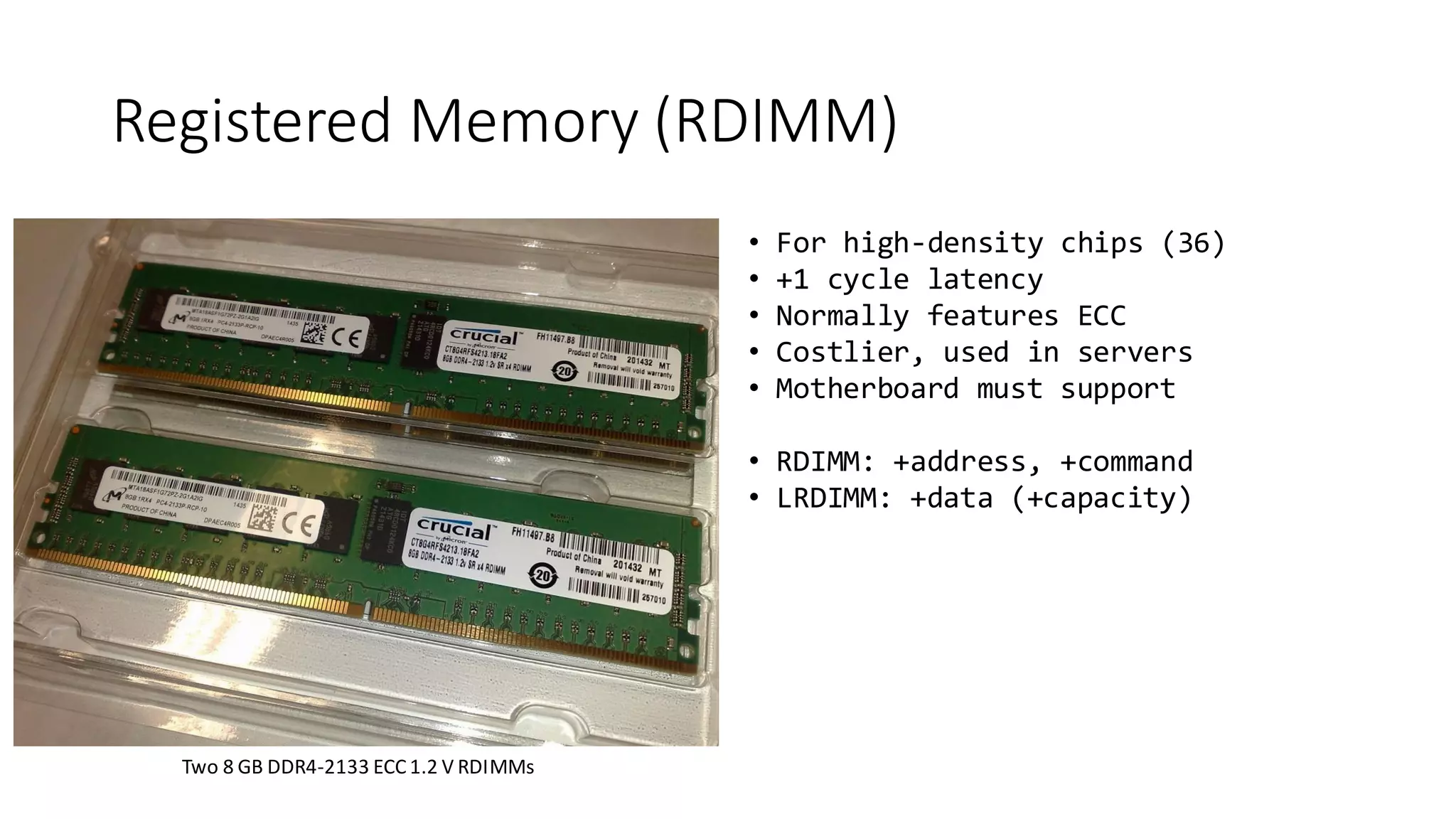
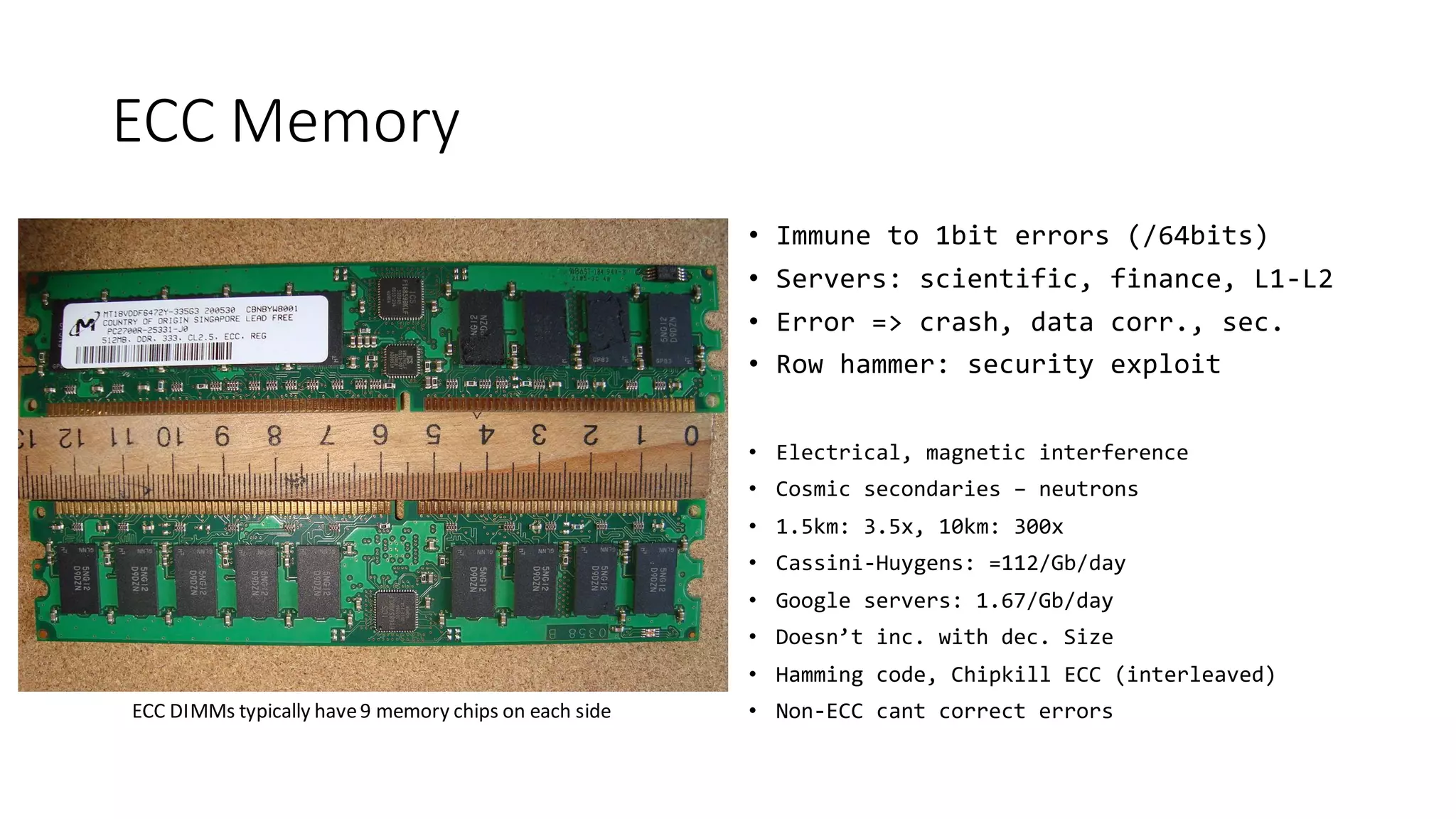
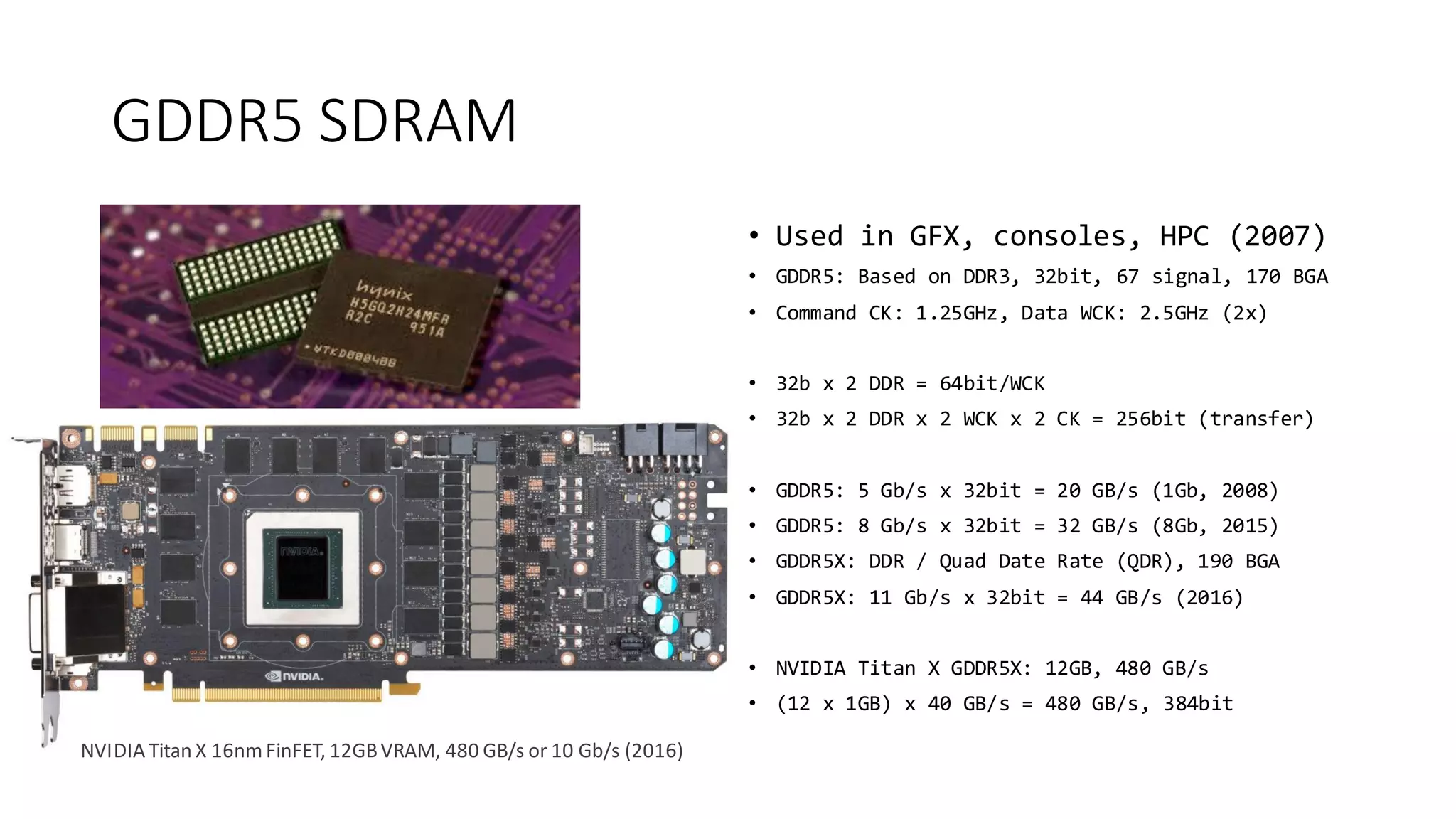
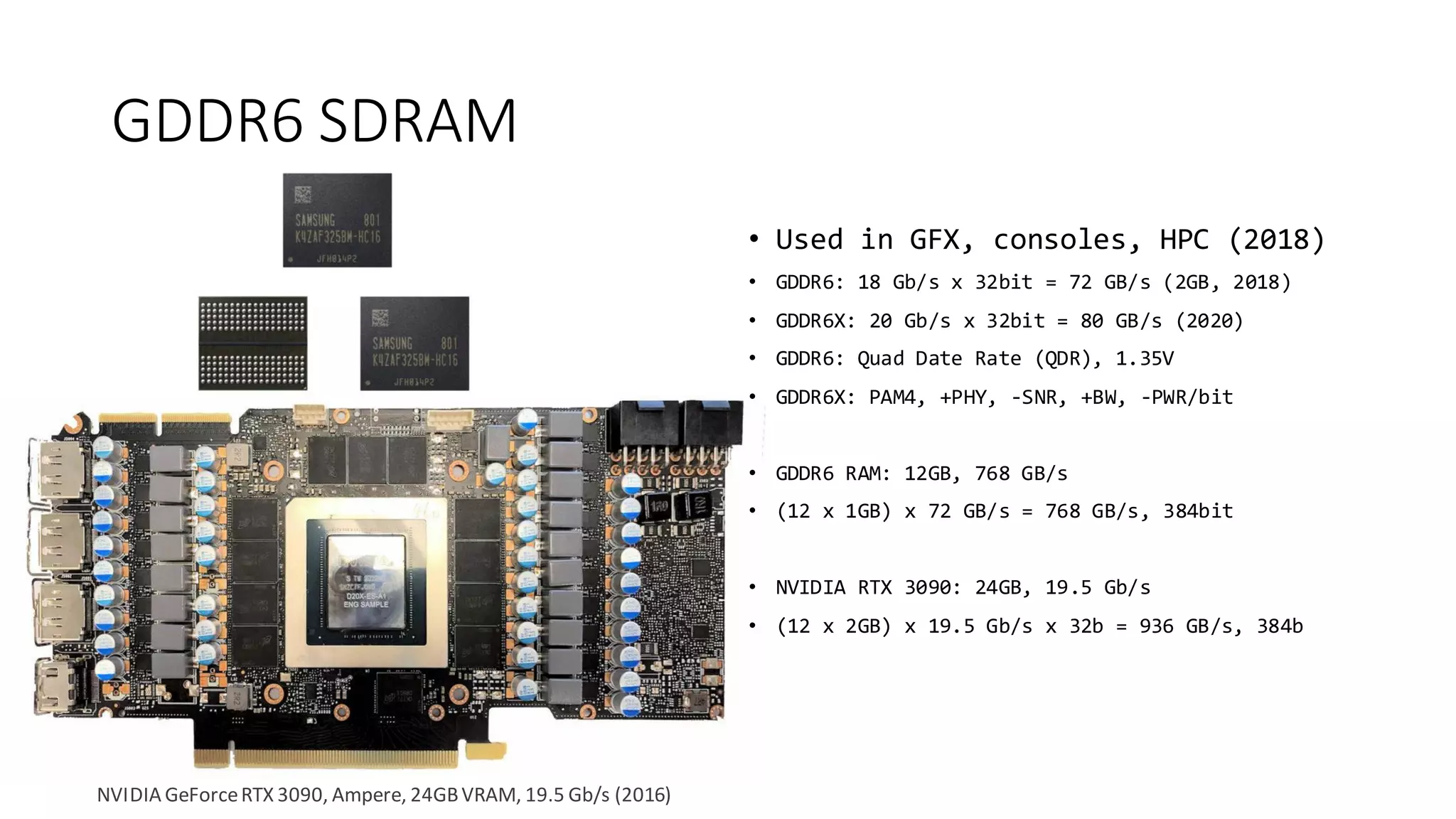
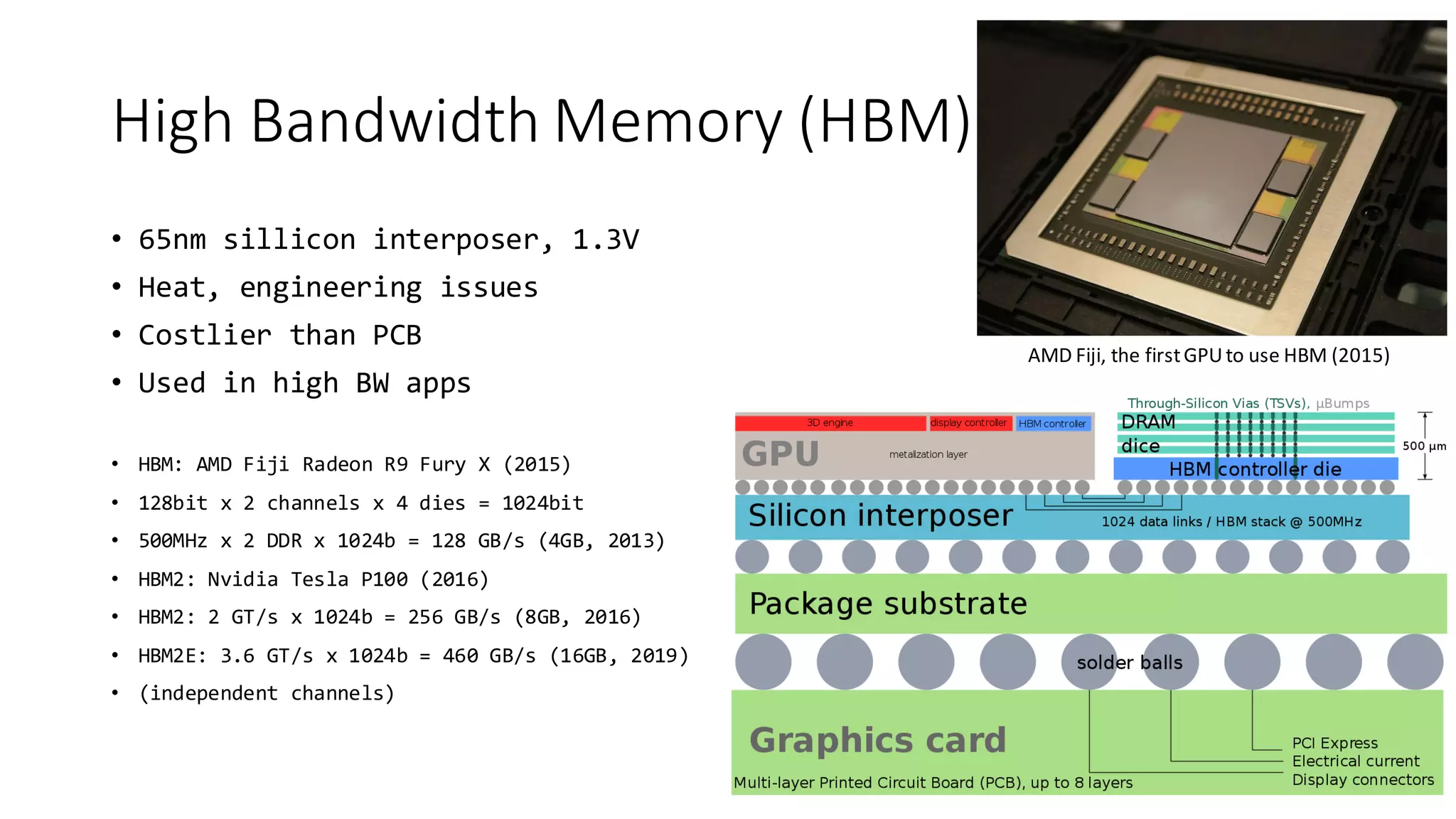
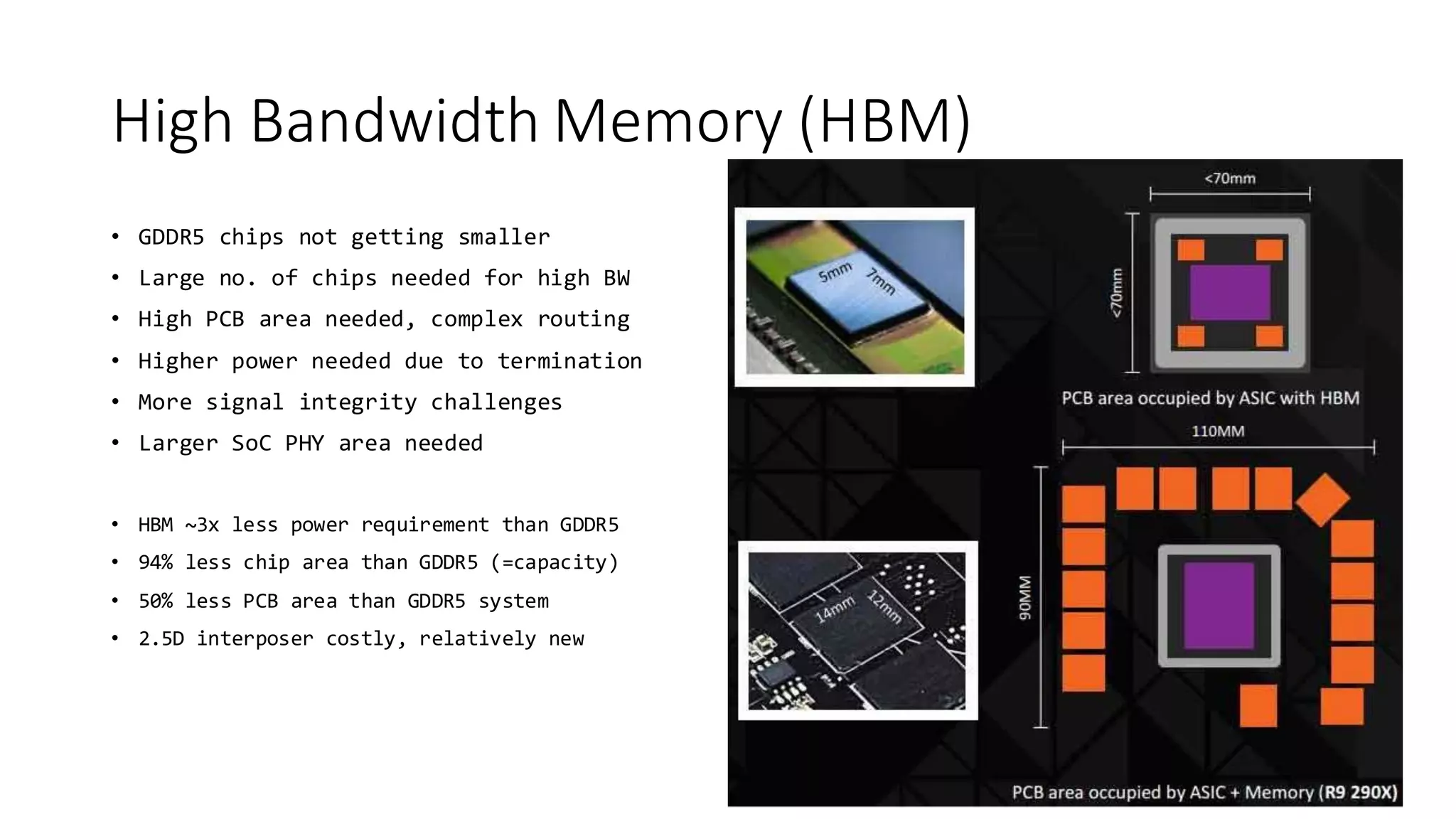
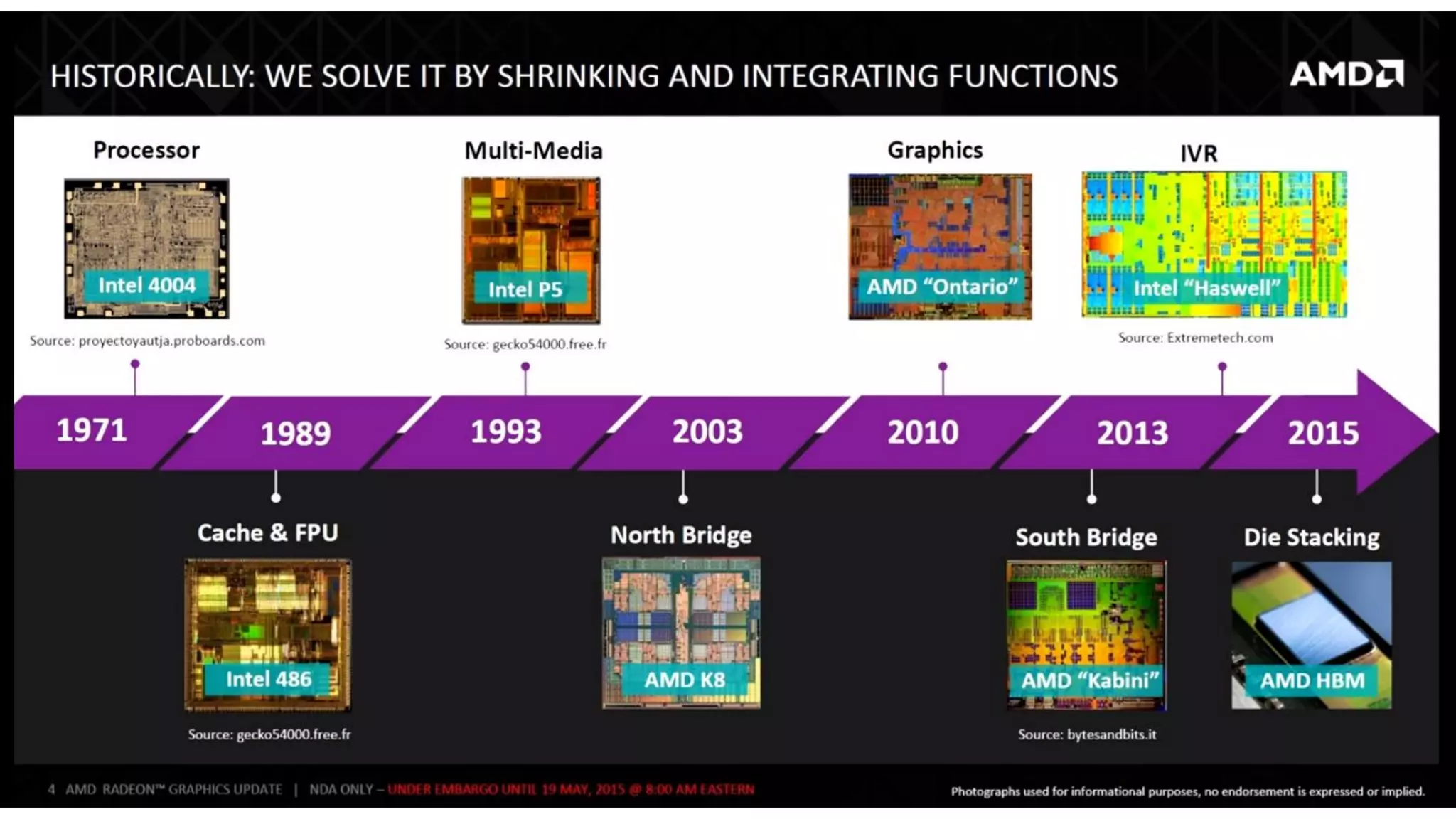
The document provides a detailed overview of various types of DDR SDRAM technologies, including DDR3, DDR4, GDDR, and High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), highlighting key specifications such as voltages, capacities, and speeds. It also discusses memory-related technologies such as error correction codes (ECC), memory dimensions, and the significance of specific memory features in different applications, particularly in servers and graphics. Furthermore, it mentions the evolution of memory interface technologies and the increasing demand for higher bandwidth and lower power consumption.