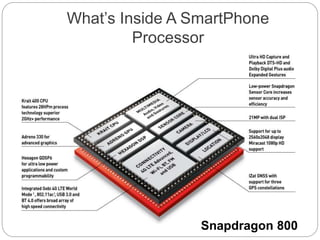
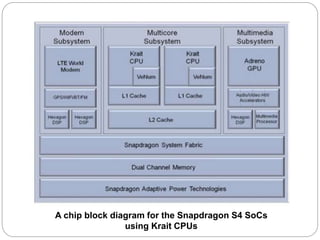
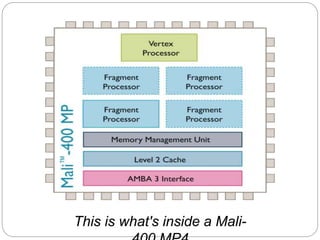
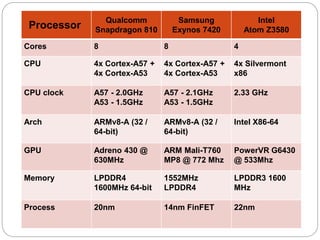
This document provides an introduction to system on chip (SoC) based smartphone processors, their working, and architecture. It defines an SoC as an integrated circuit that combines all components of an electronic system into a single chip, including digital, analog and radio frequency functions. SoCs are used in smartphones to minimize size and power consumption by integrating components like the CPU, memory, timing sources and peripherals onto one chip. Popular smartphone SoCs include Qualcomm's Snapdragon and Samsung's Exynos, which are based on ARM architecture and include CPU cores, GPU, and cellular radios. Key aspects of SoC processors discussed include cores, clock speed, multi-threading, and why Qualcomm Snapdragon processors are