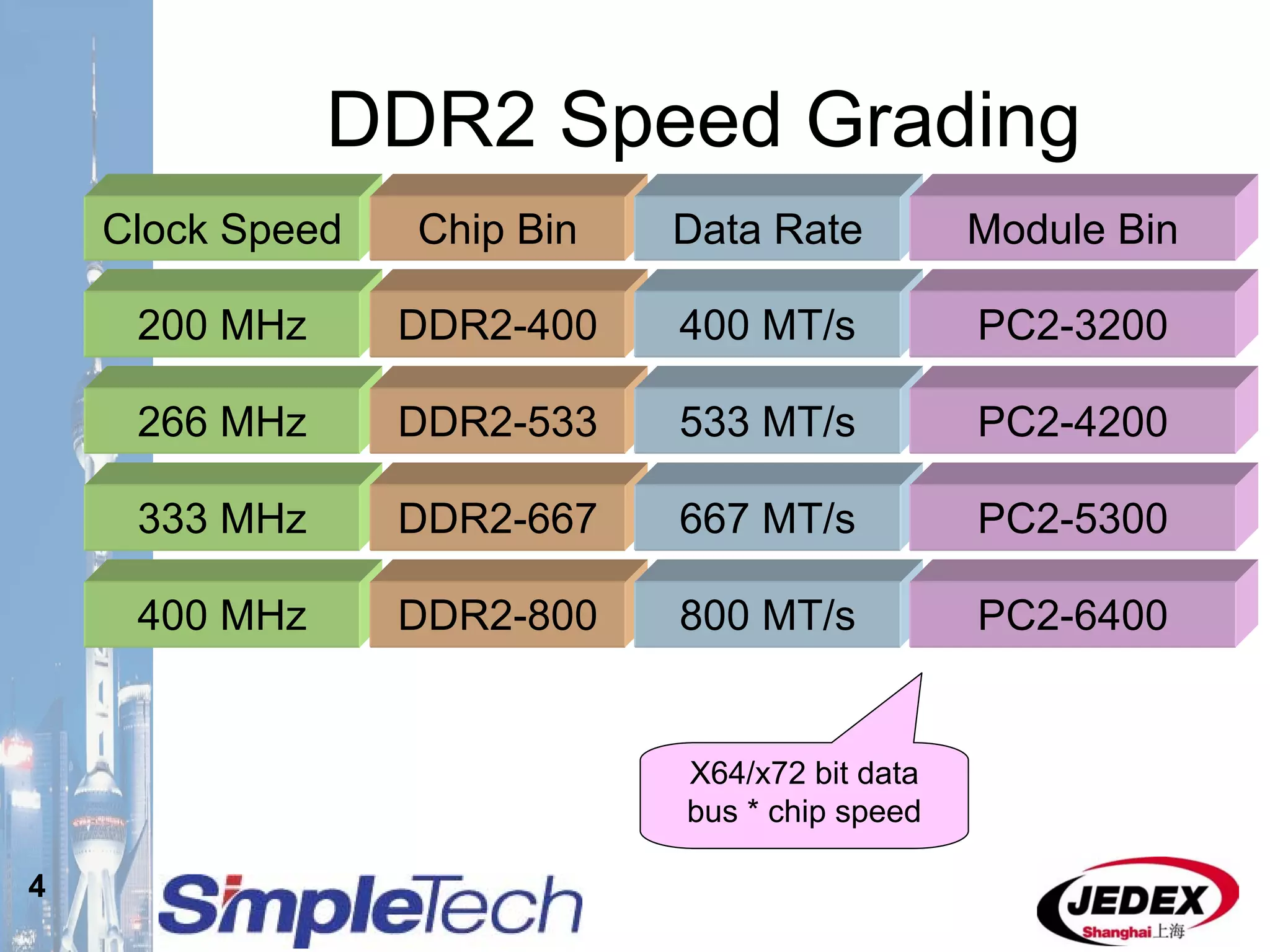
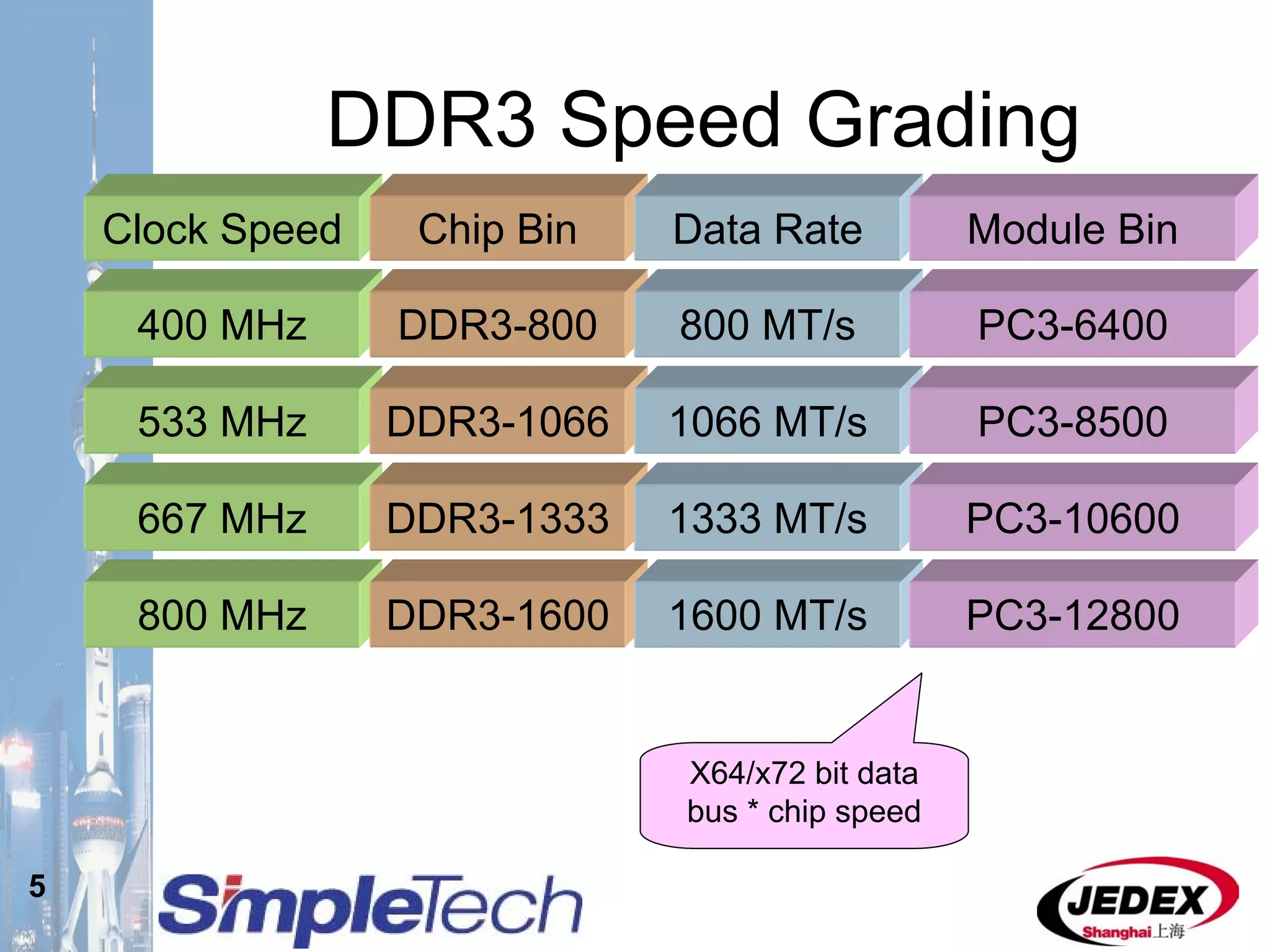
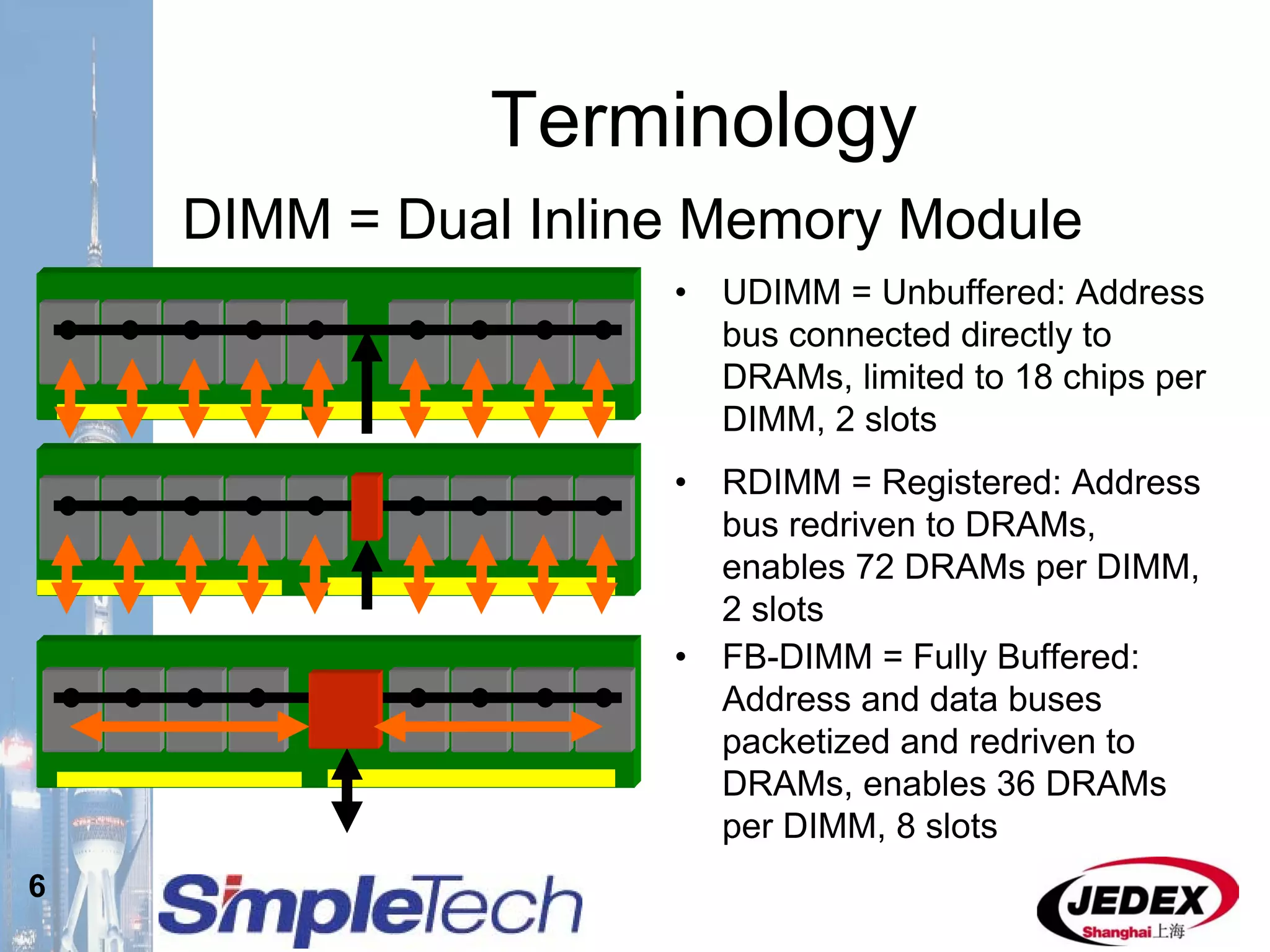
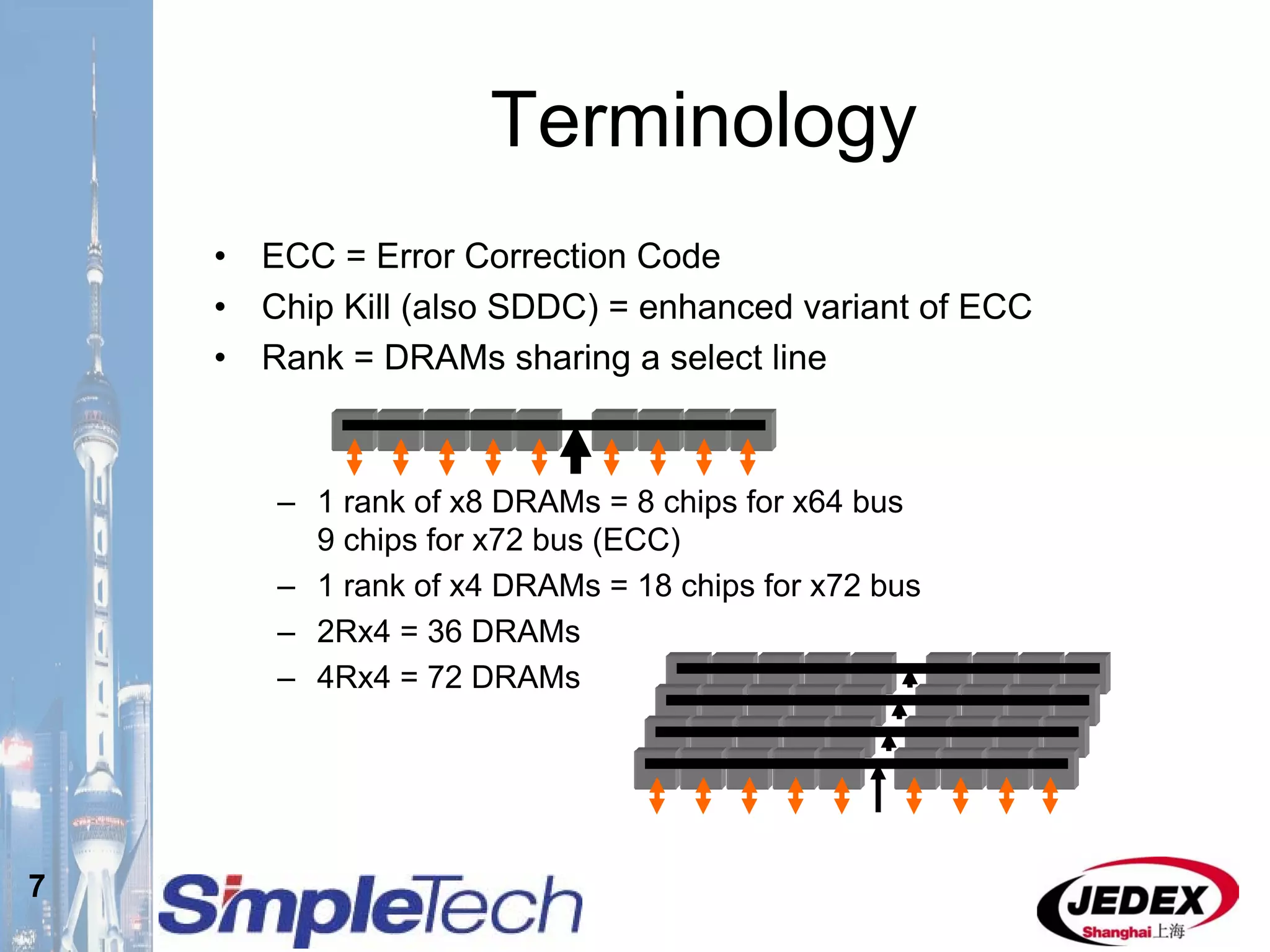
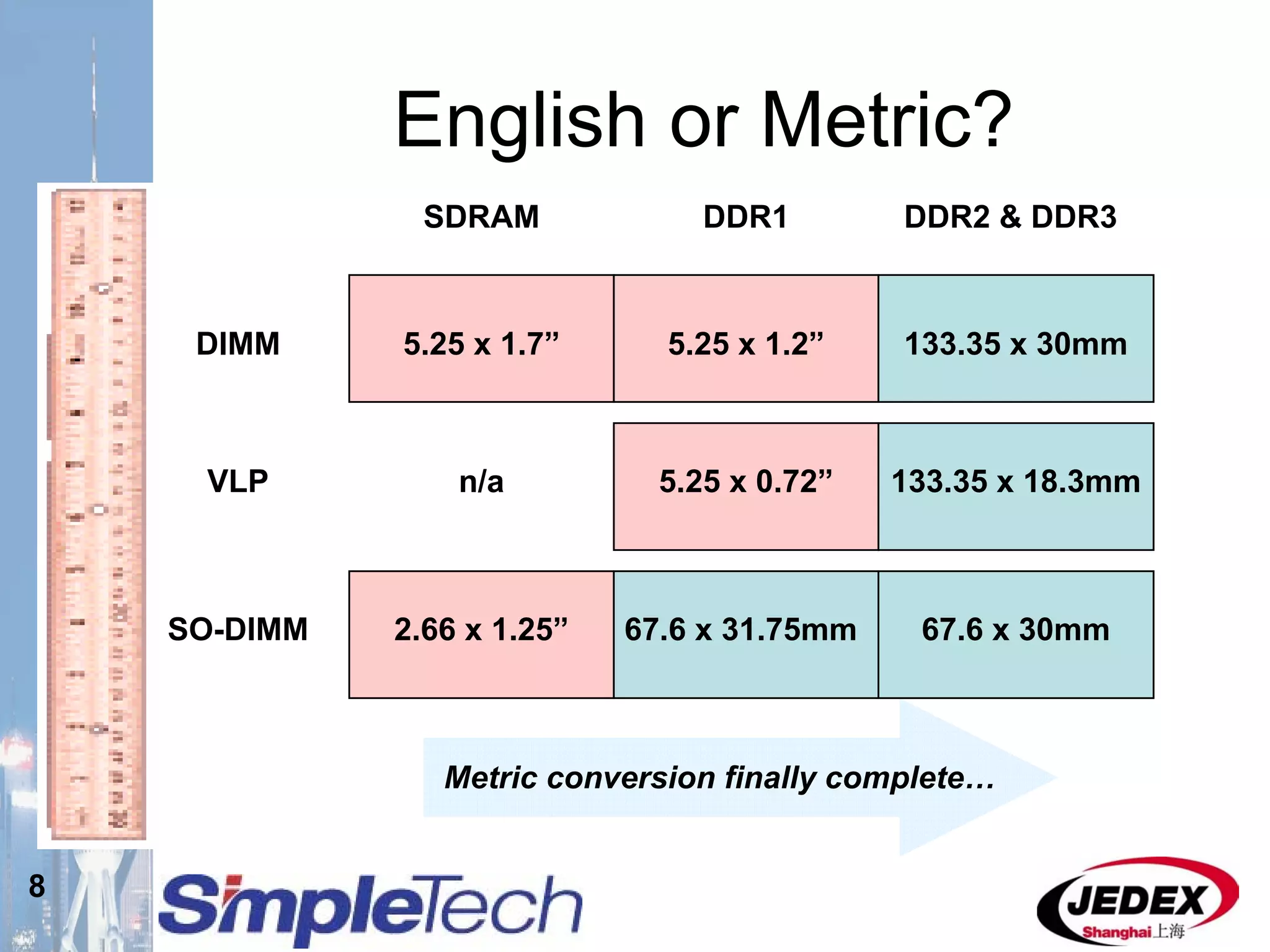
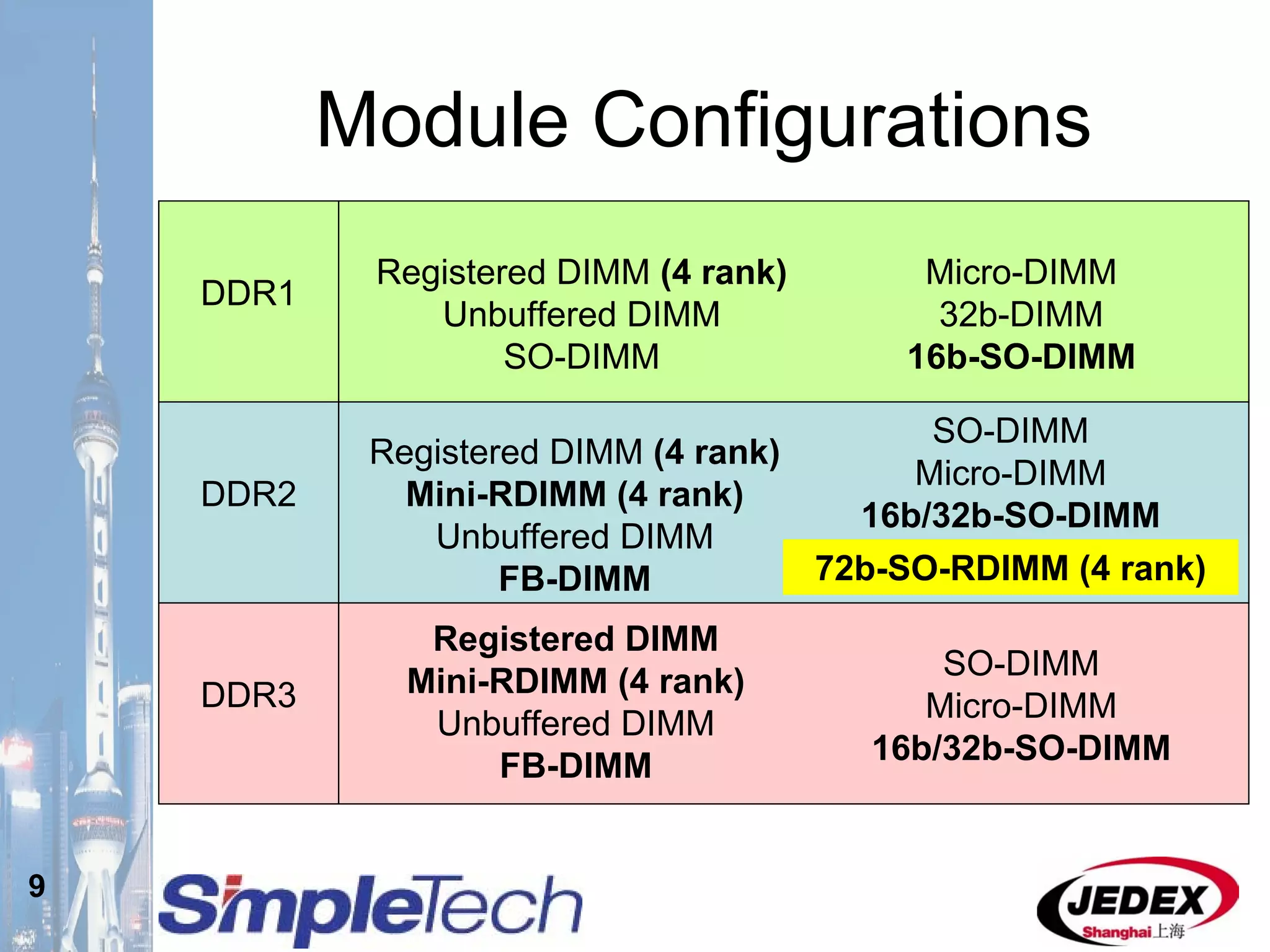
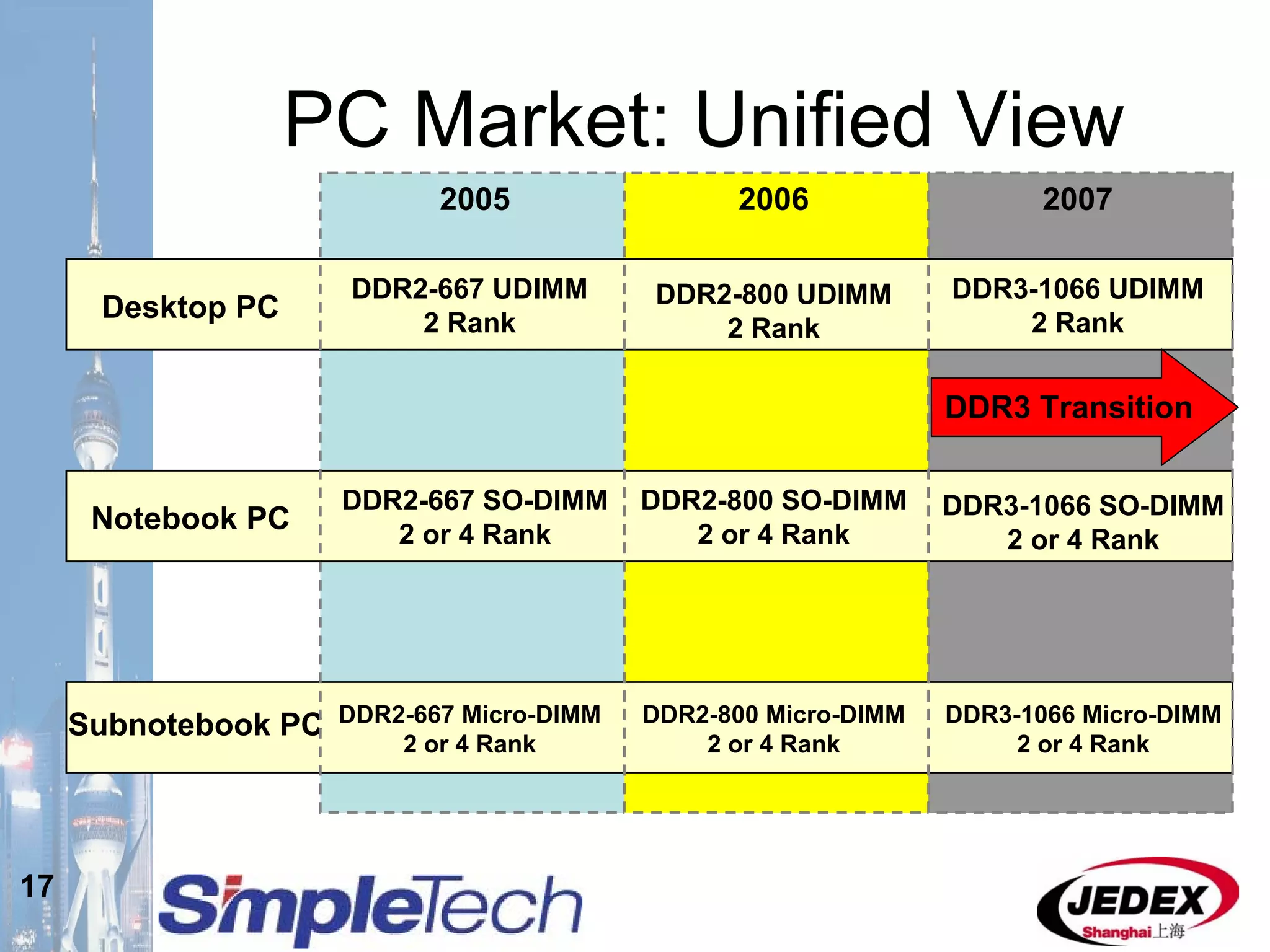
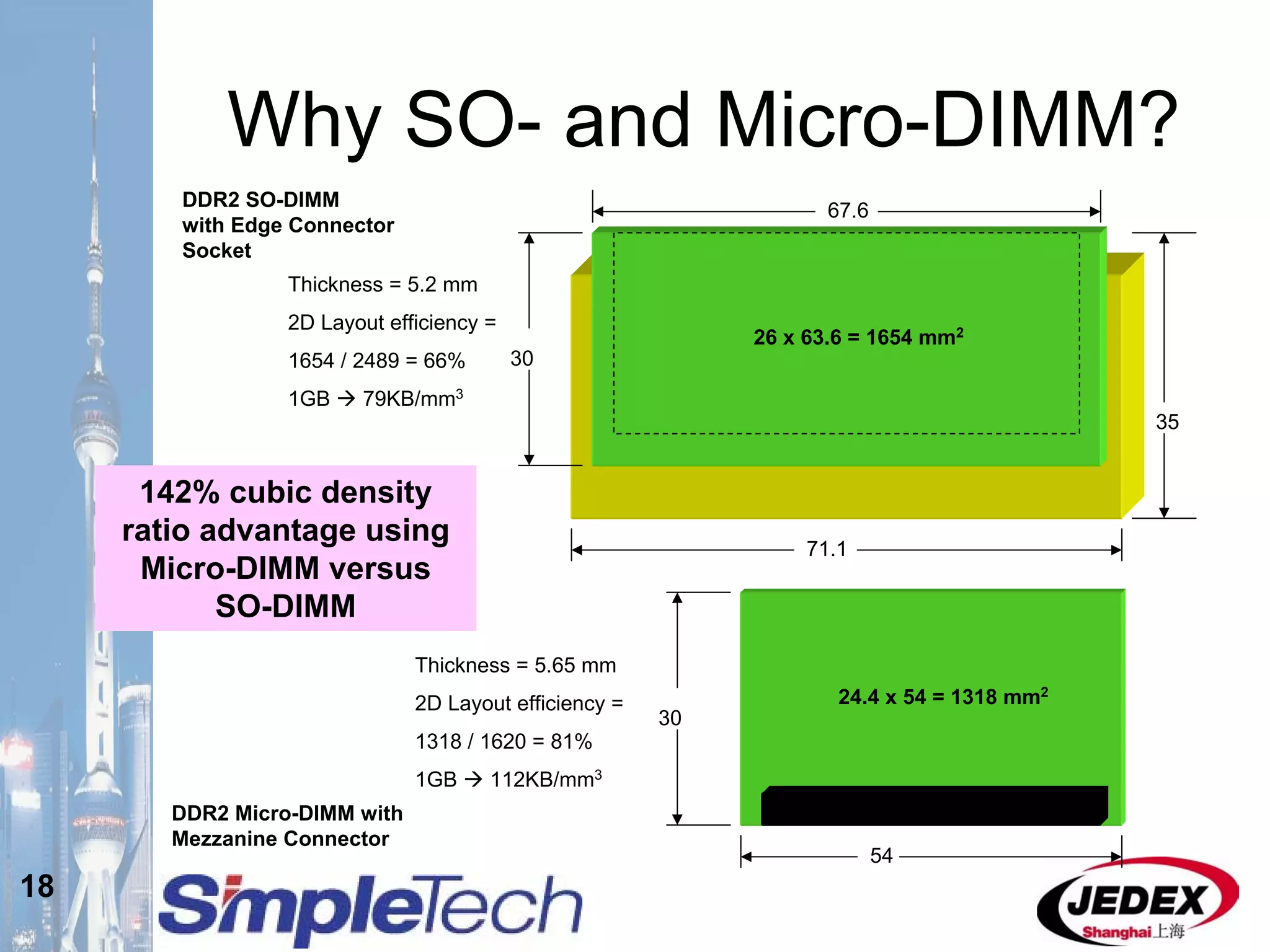
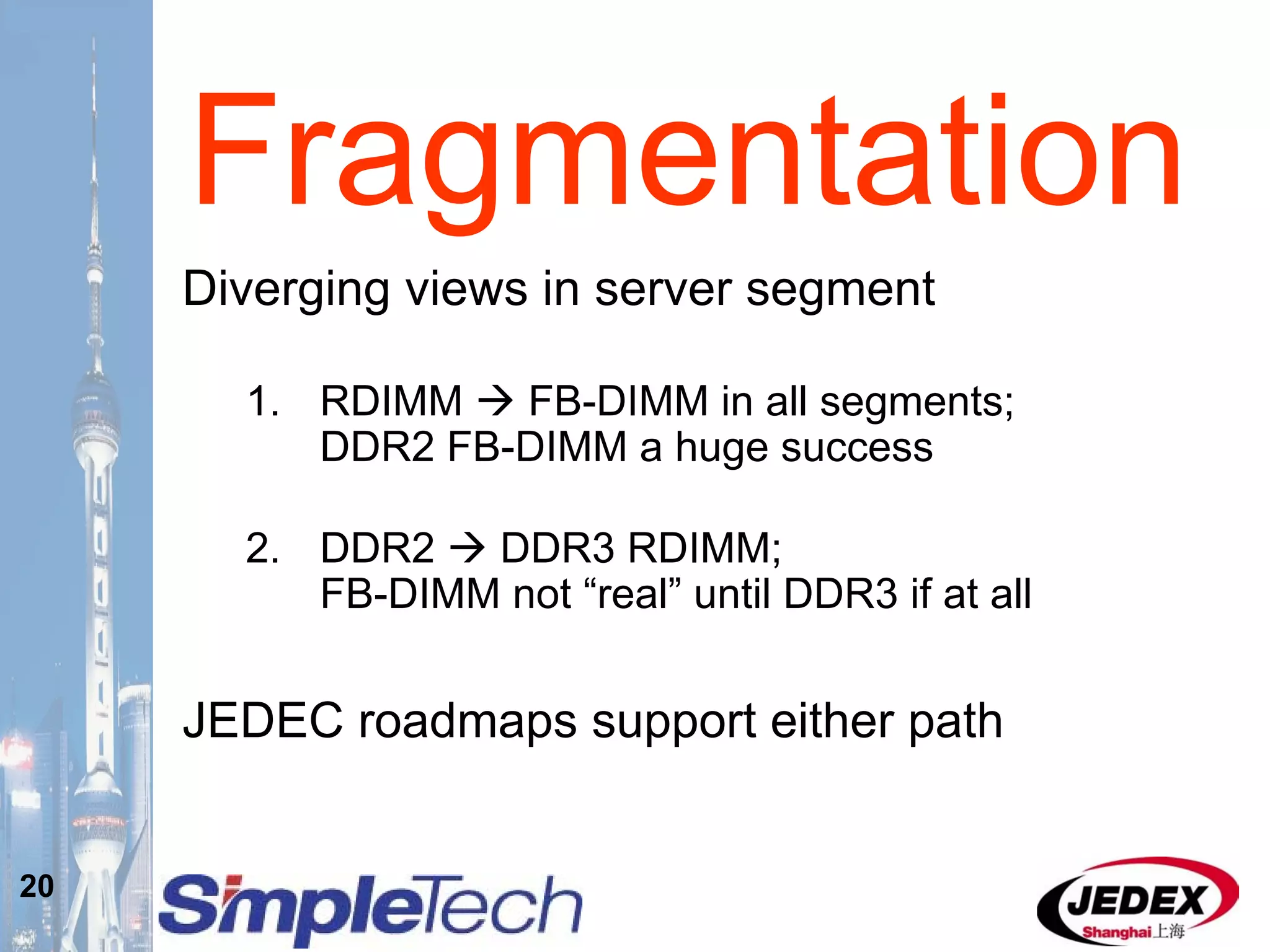
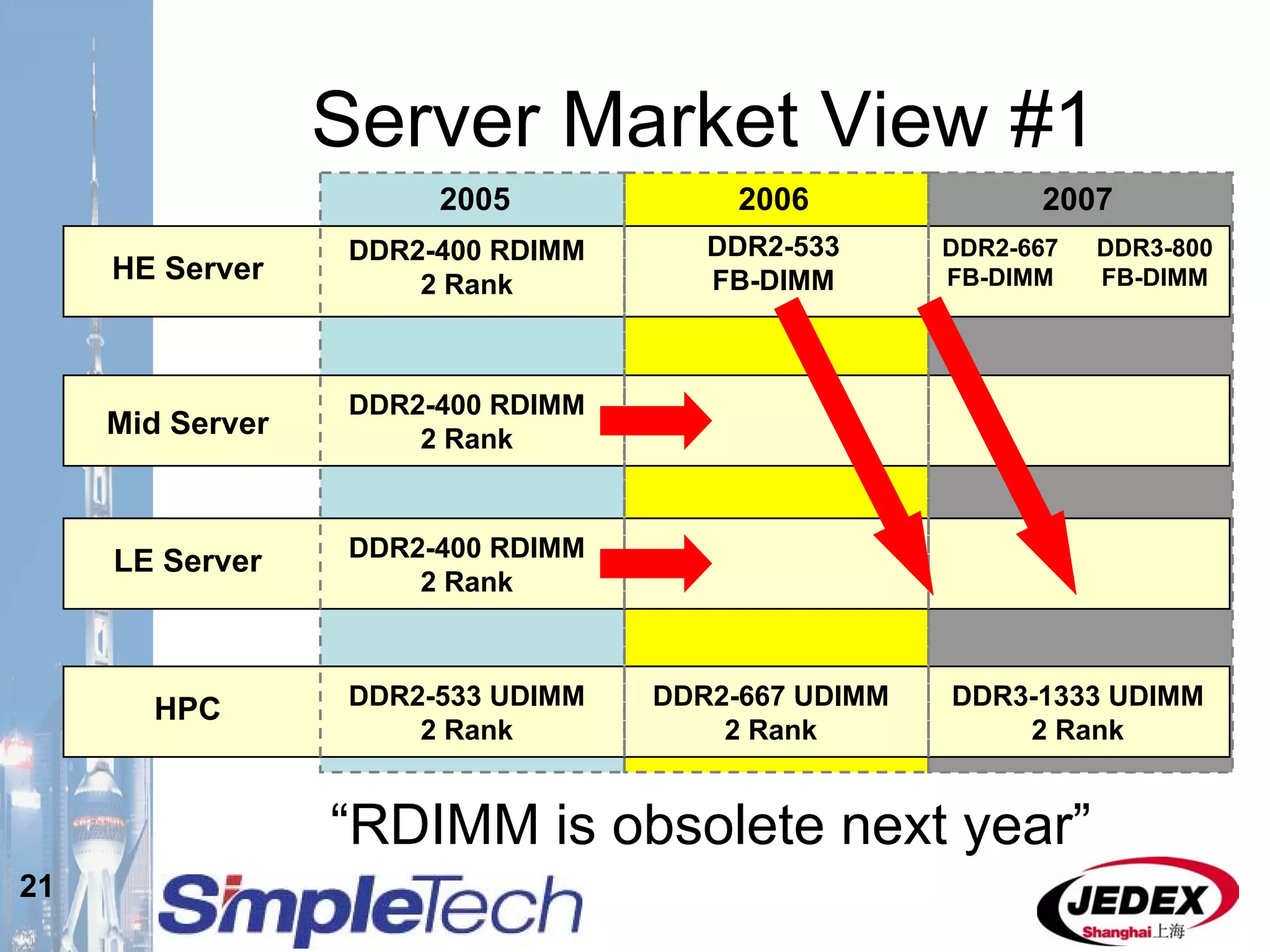
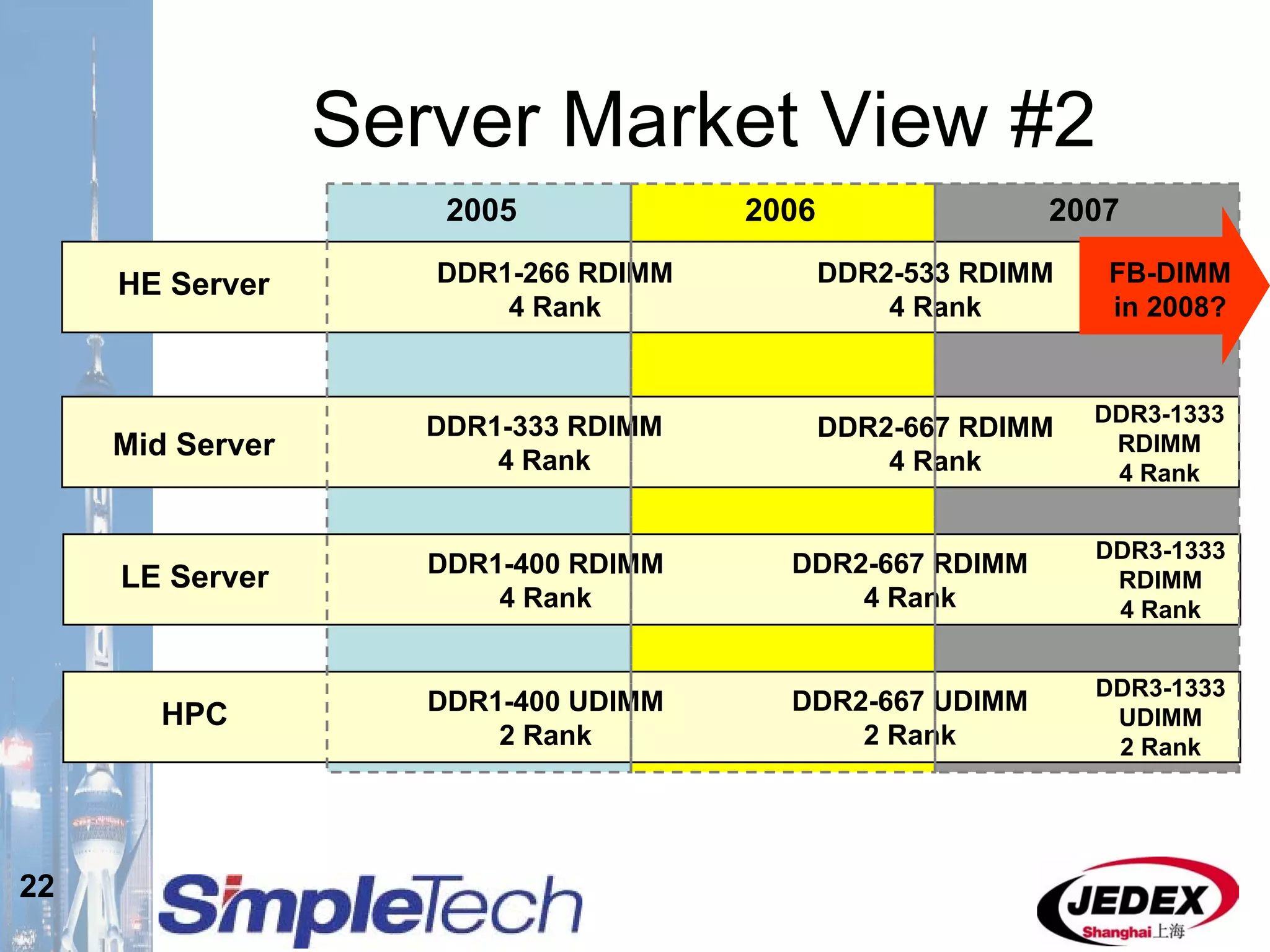
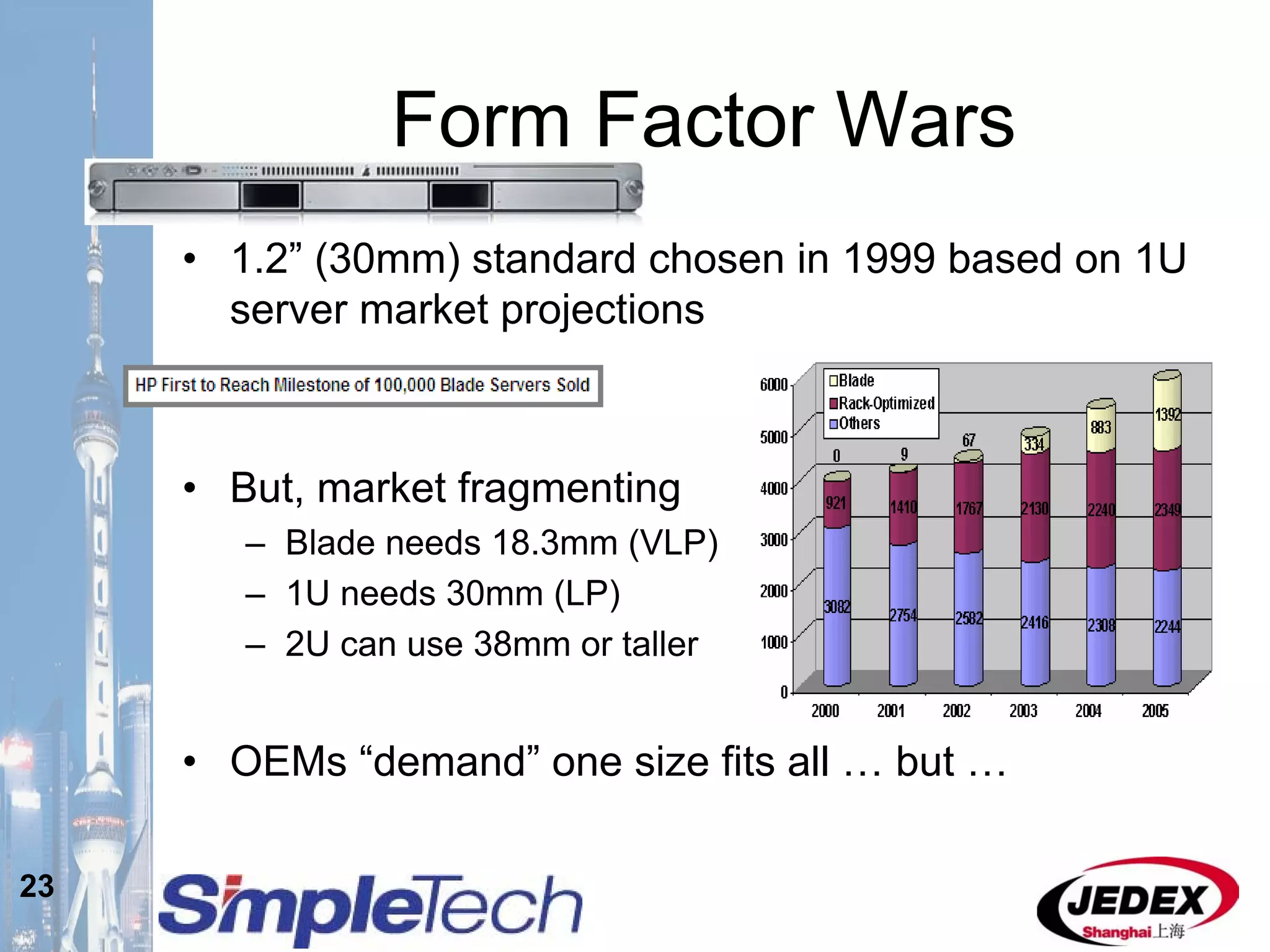
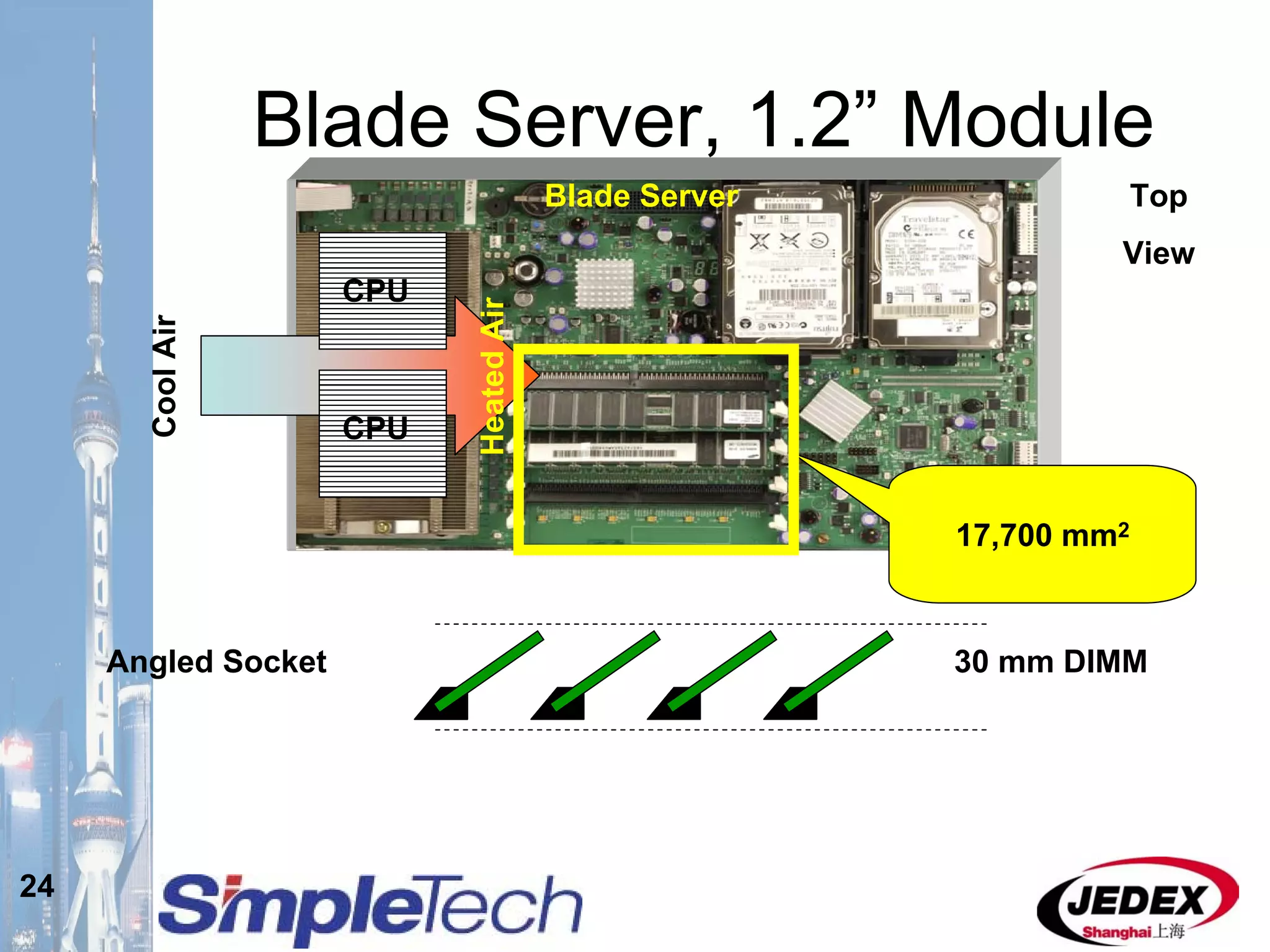
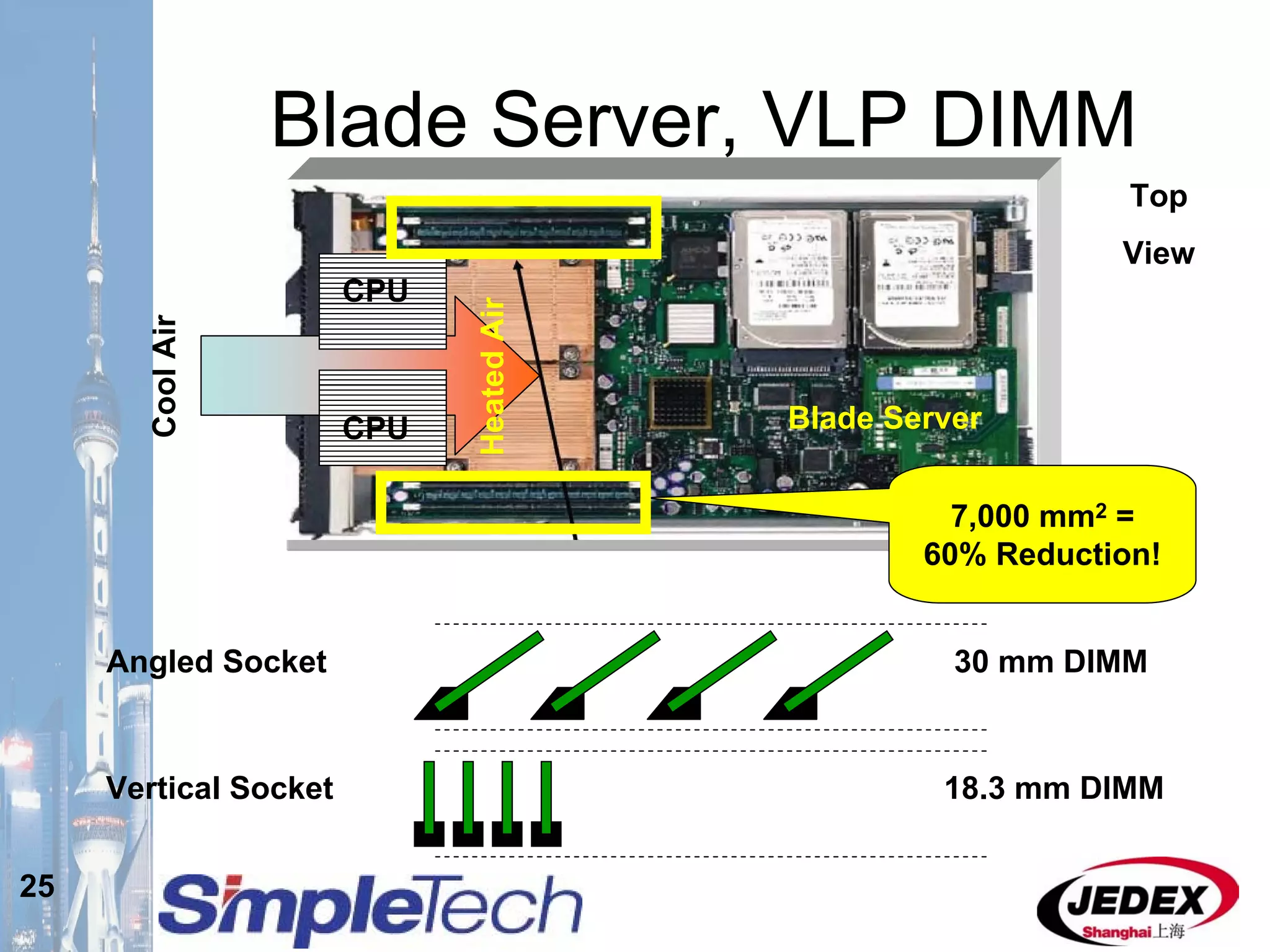
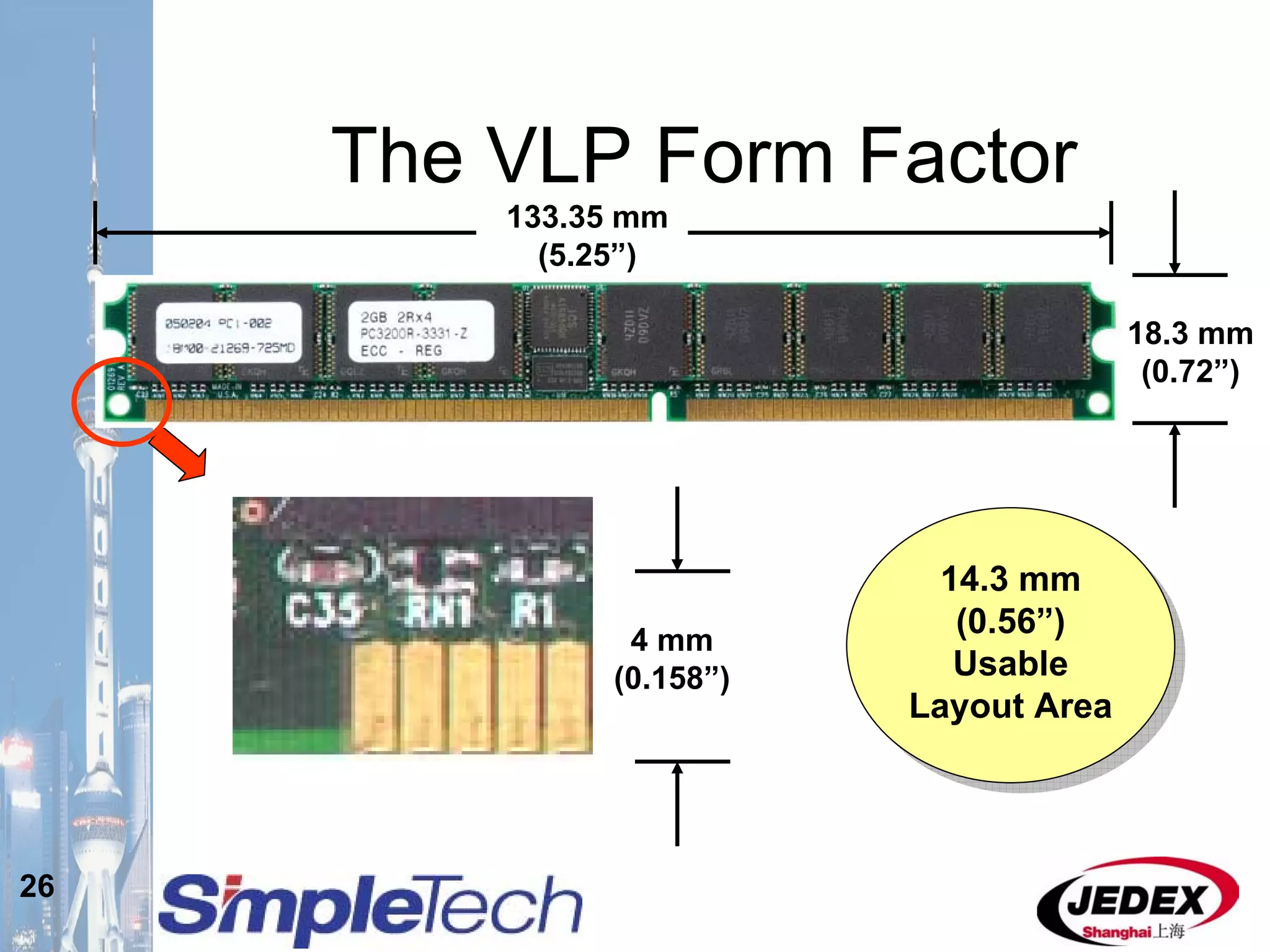
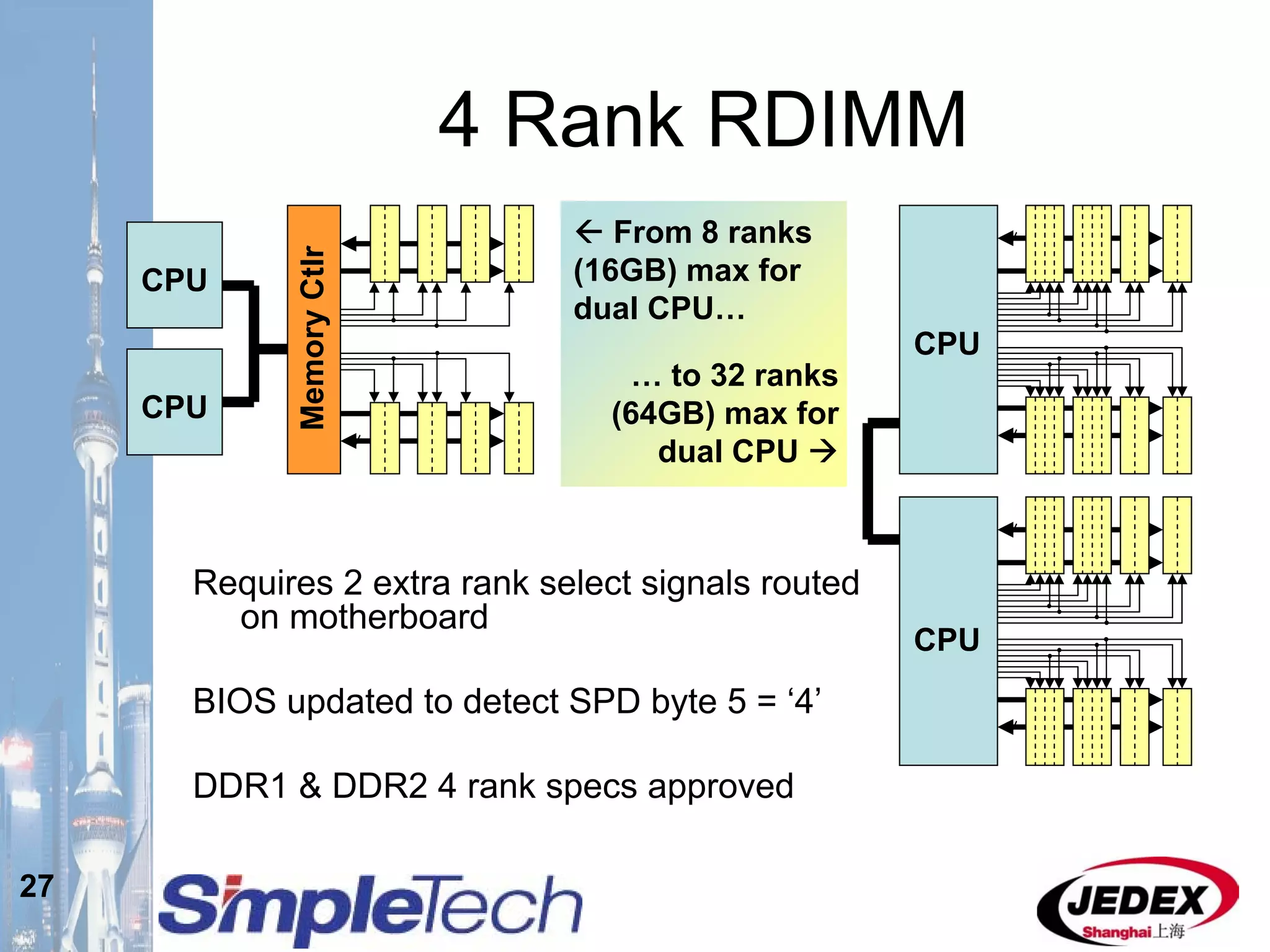
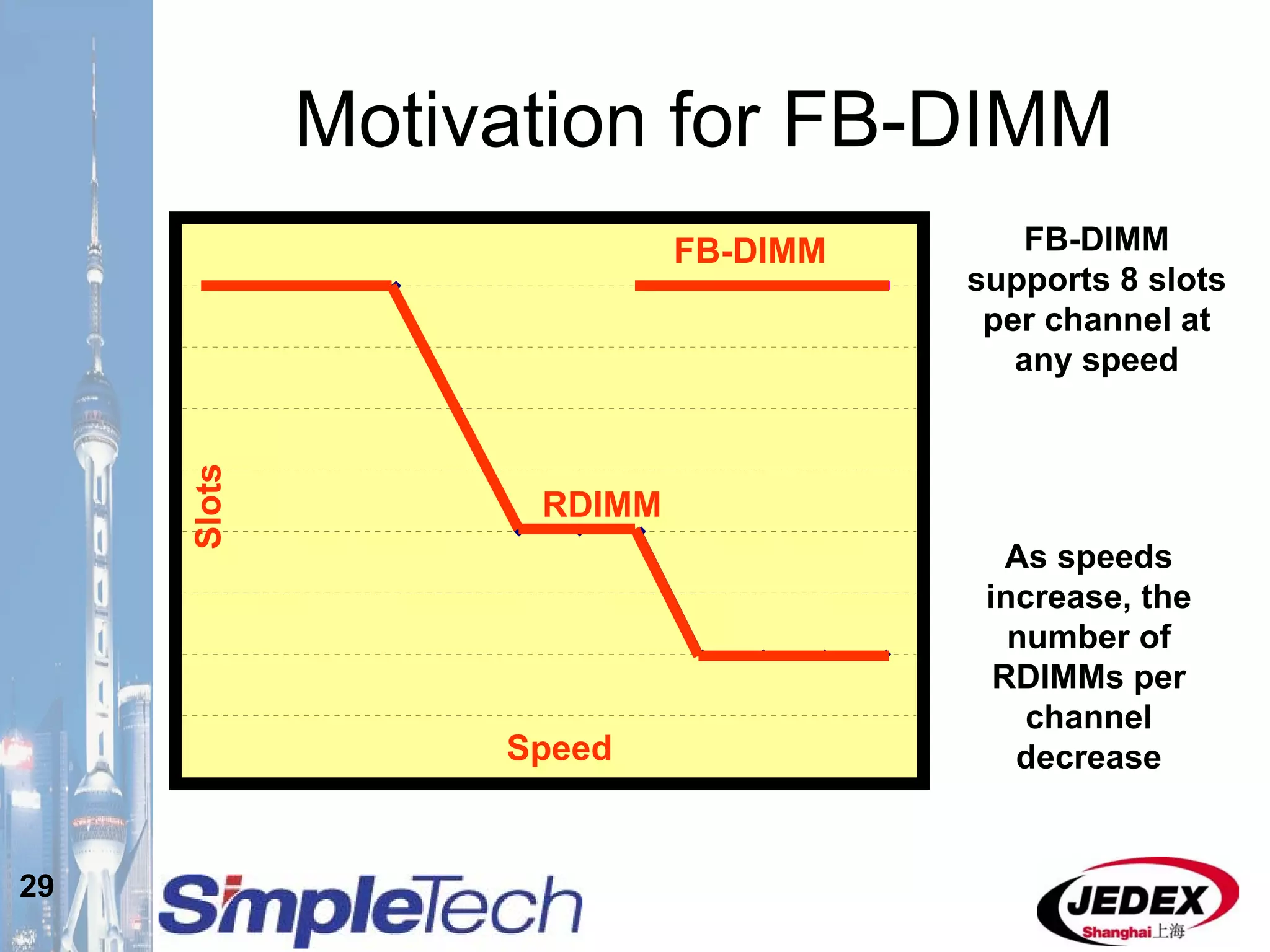
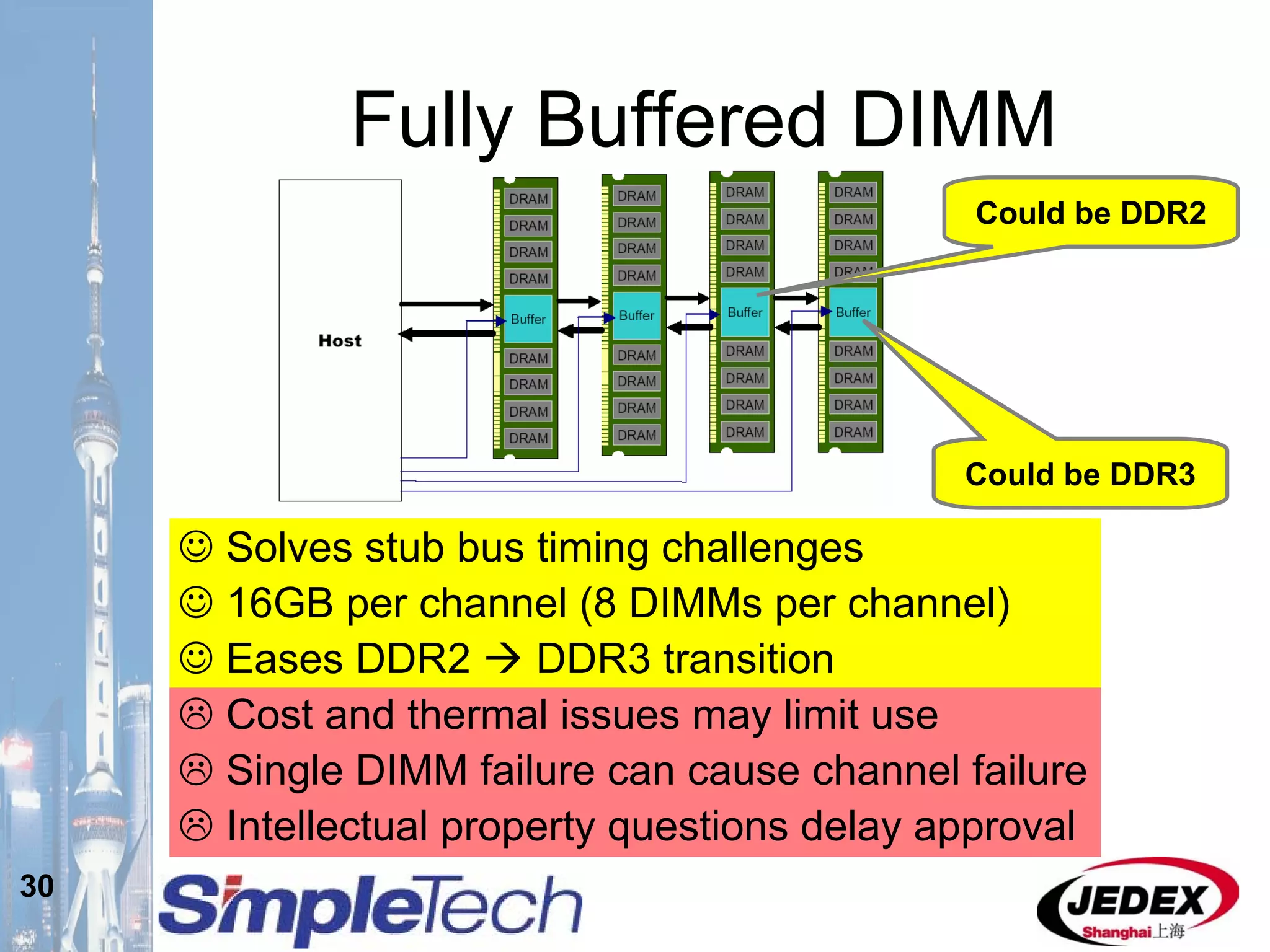
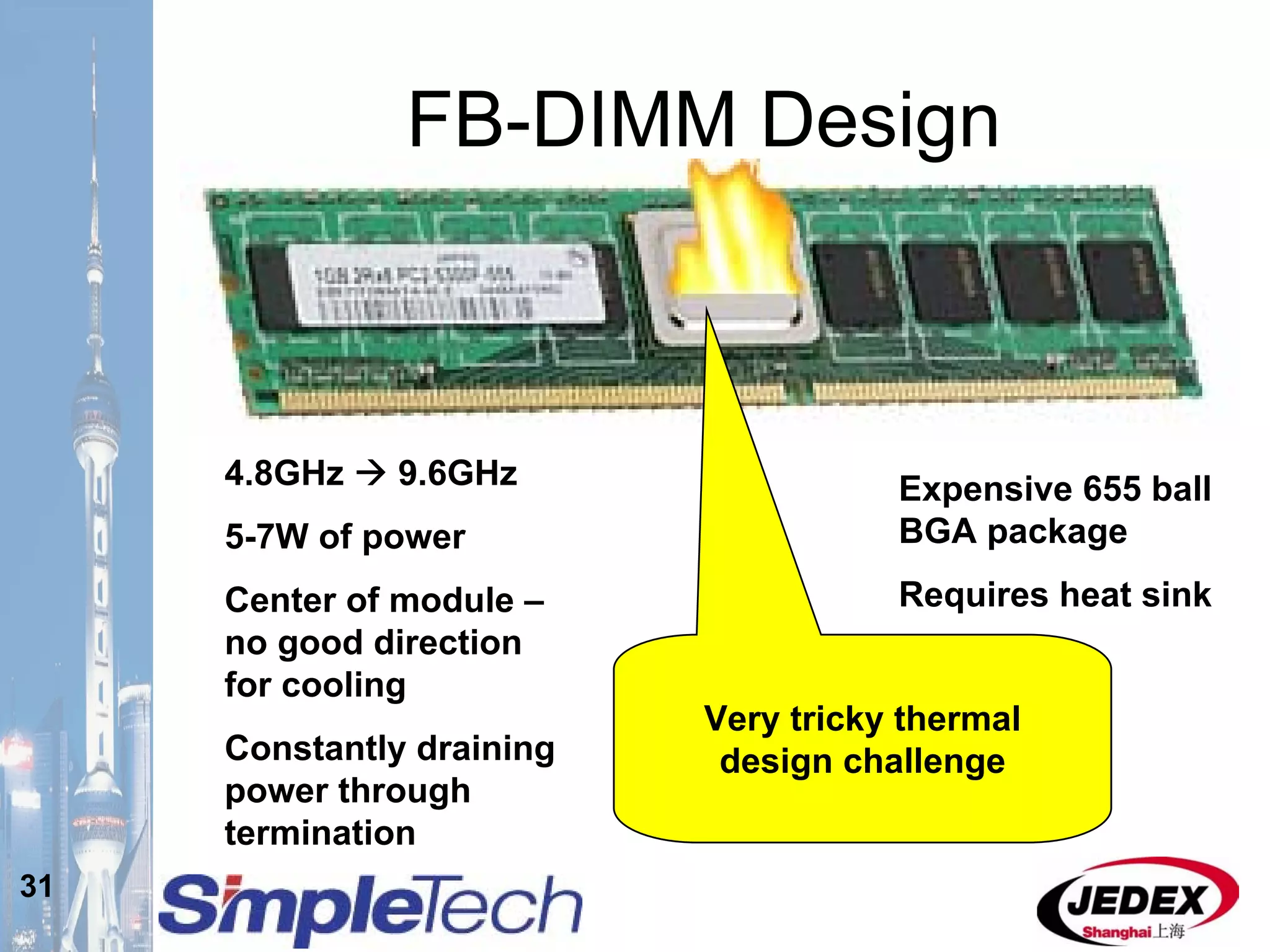
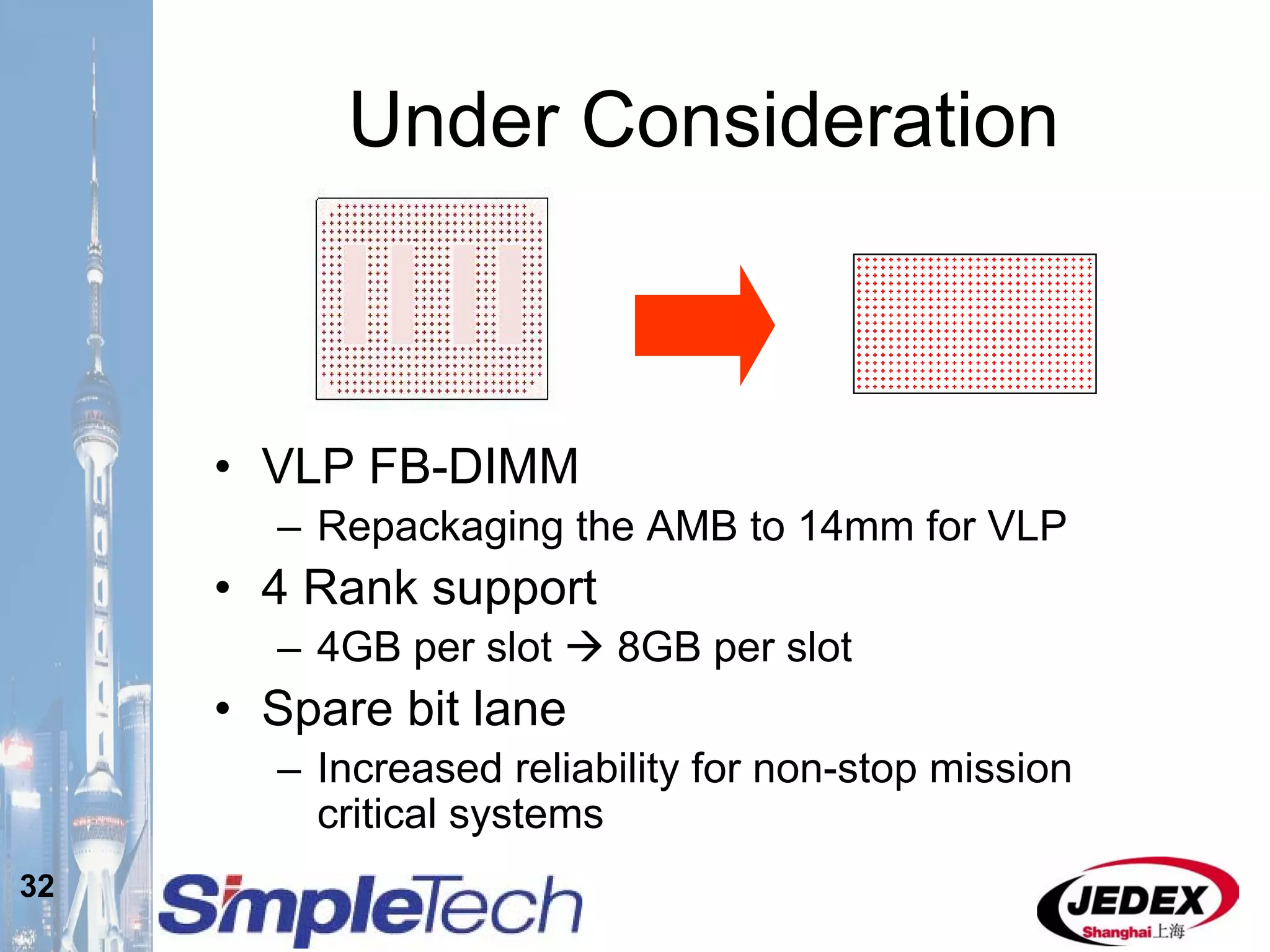
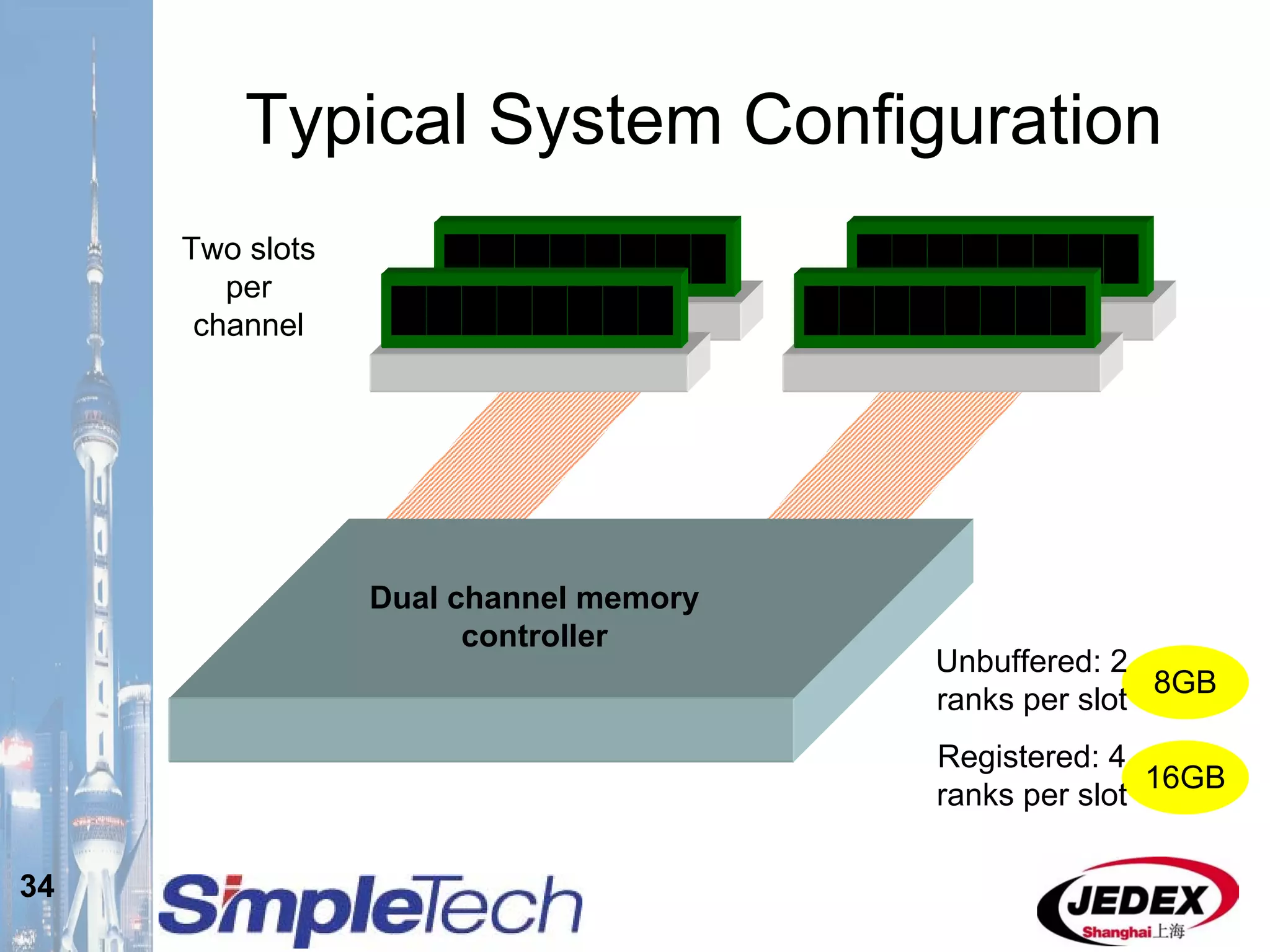
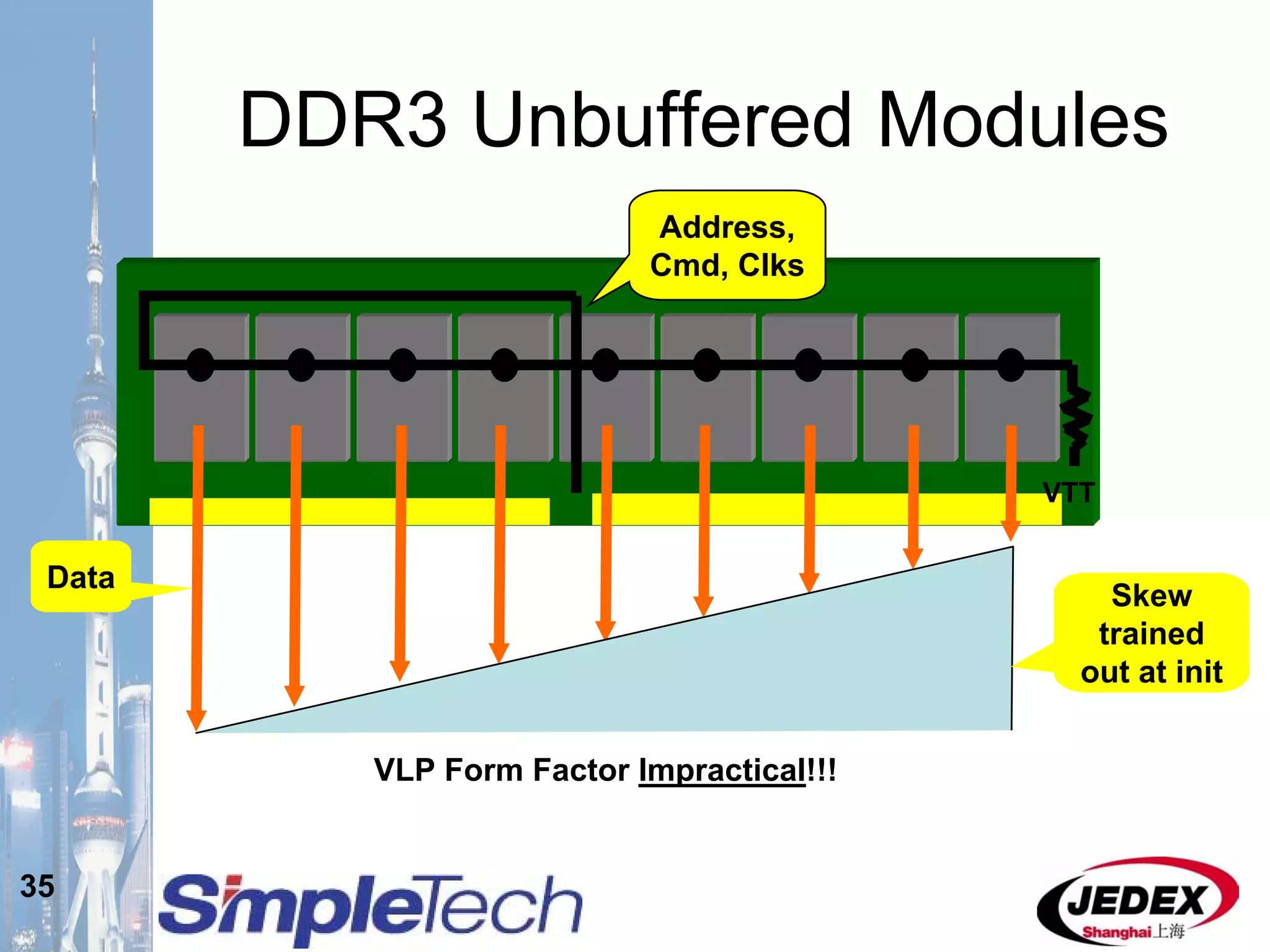
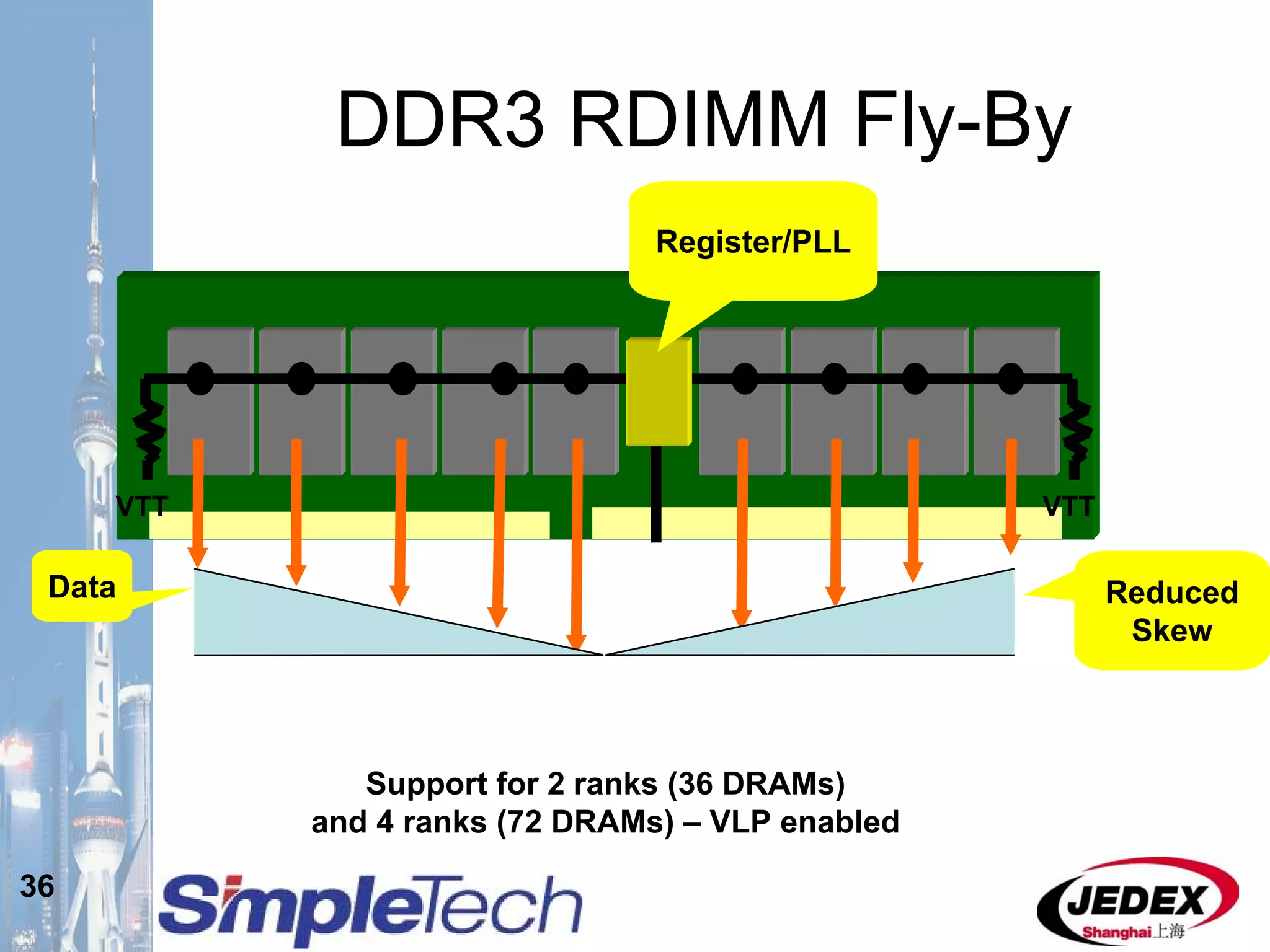
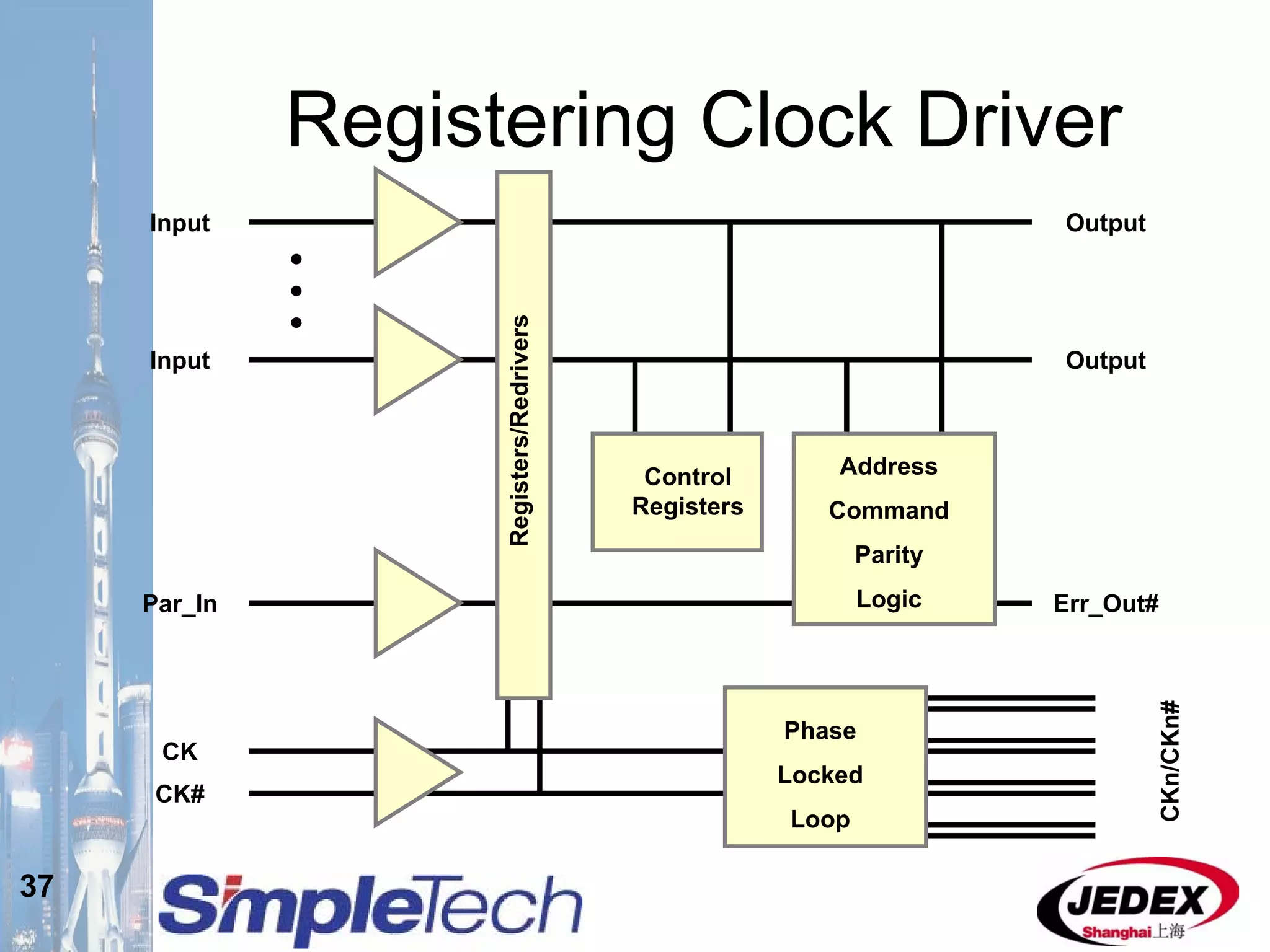
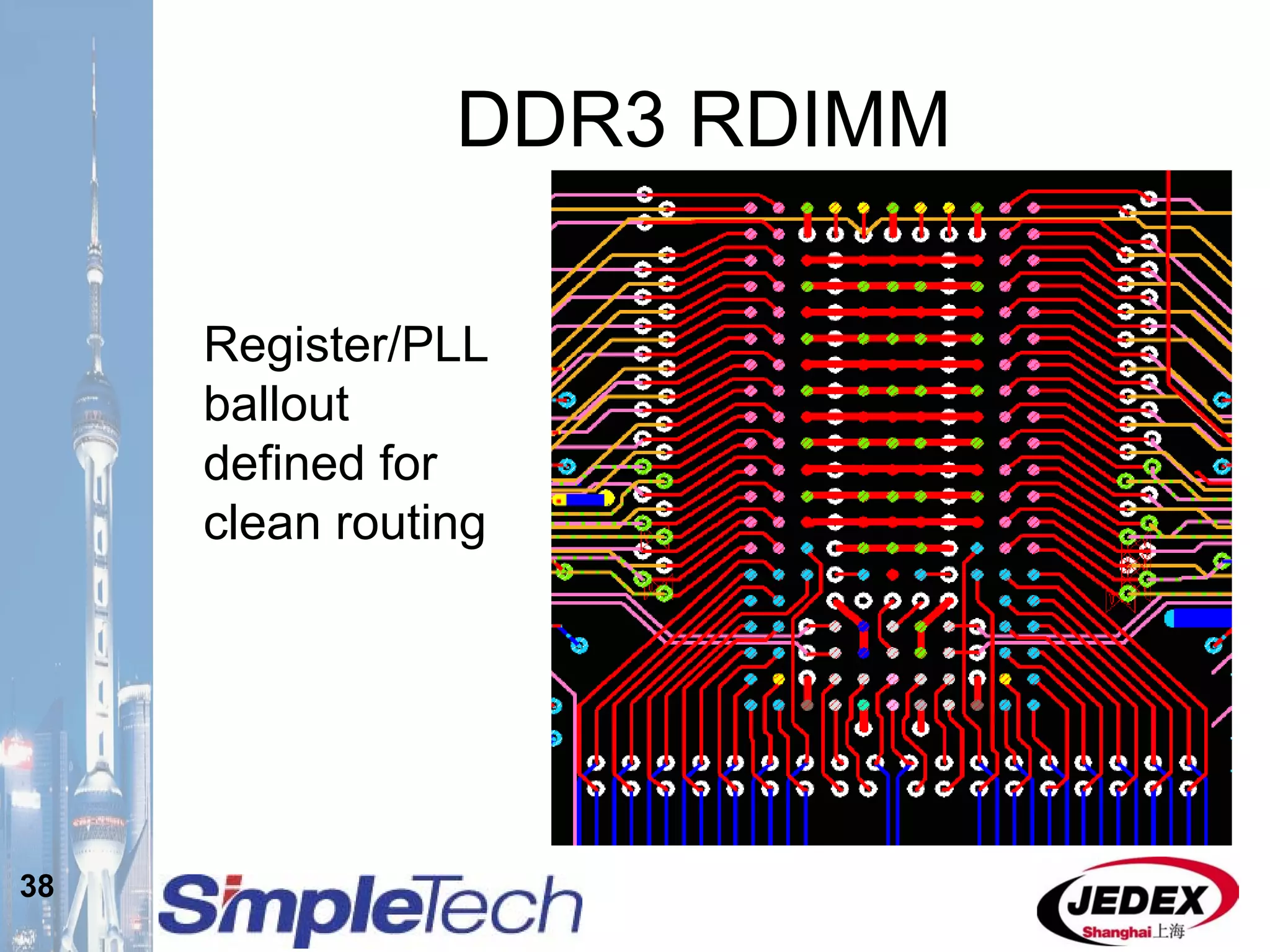
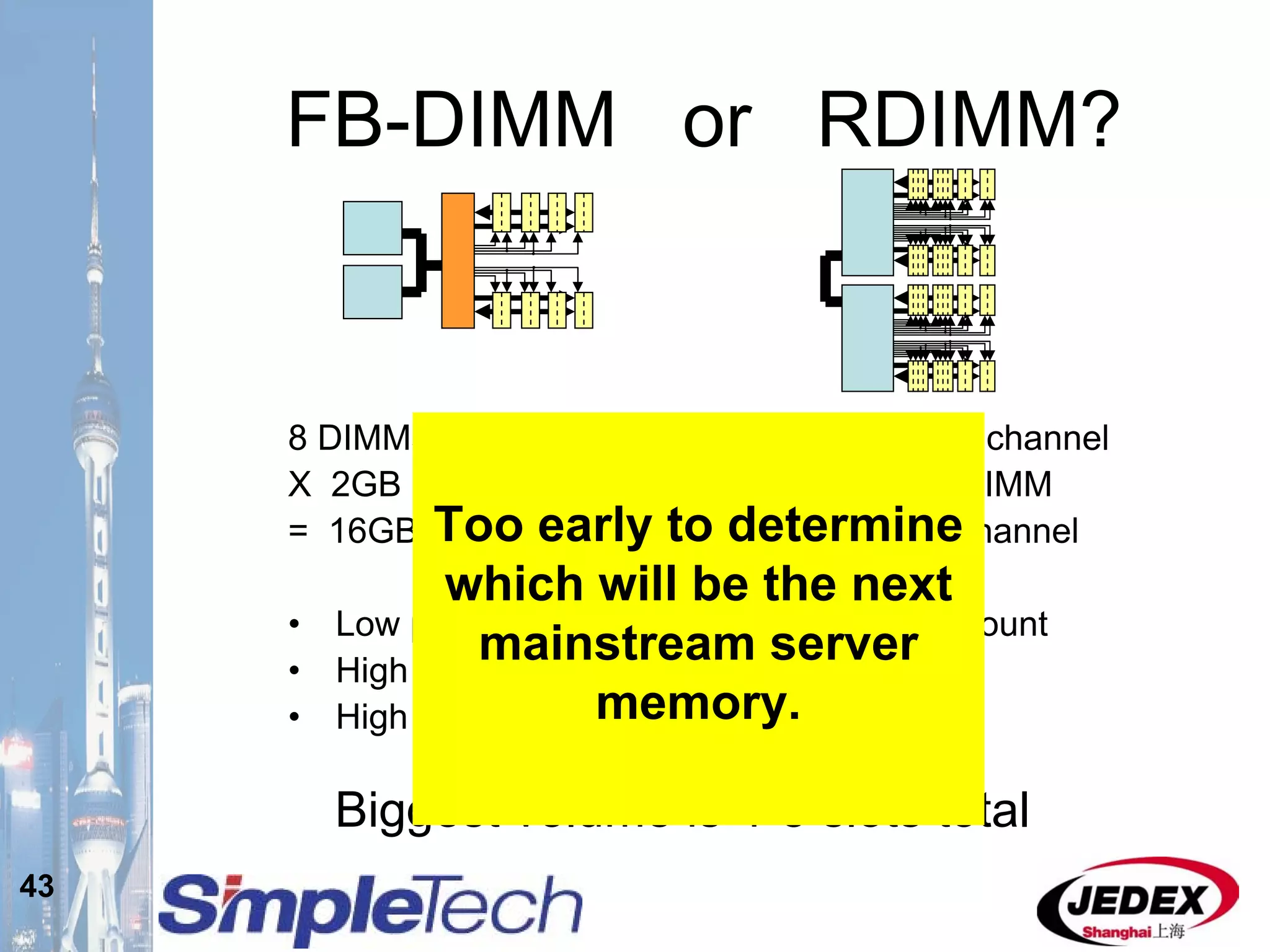
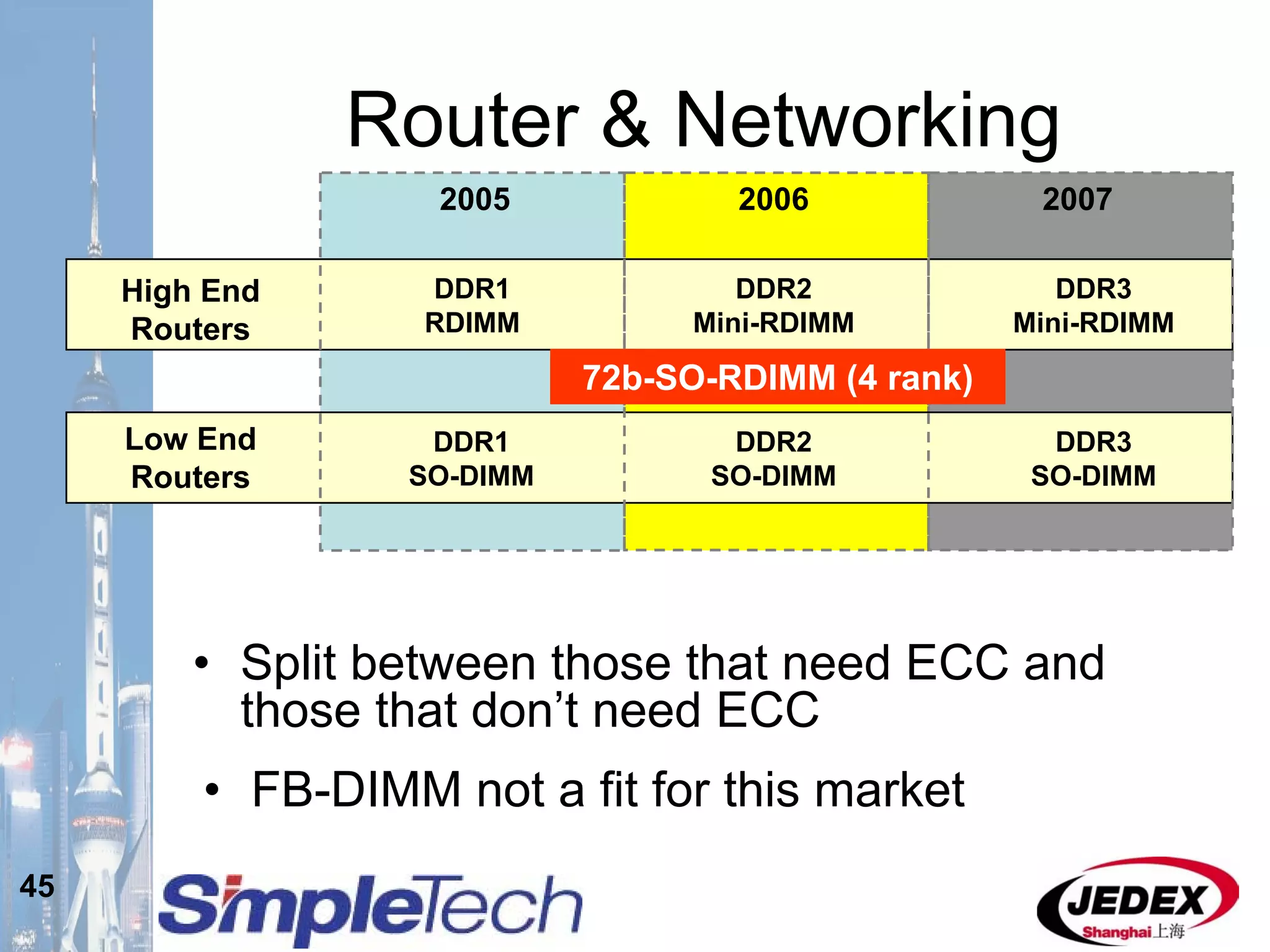
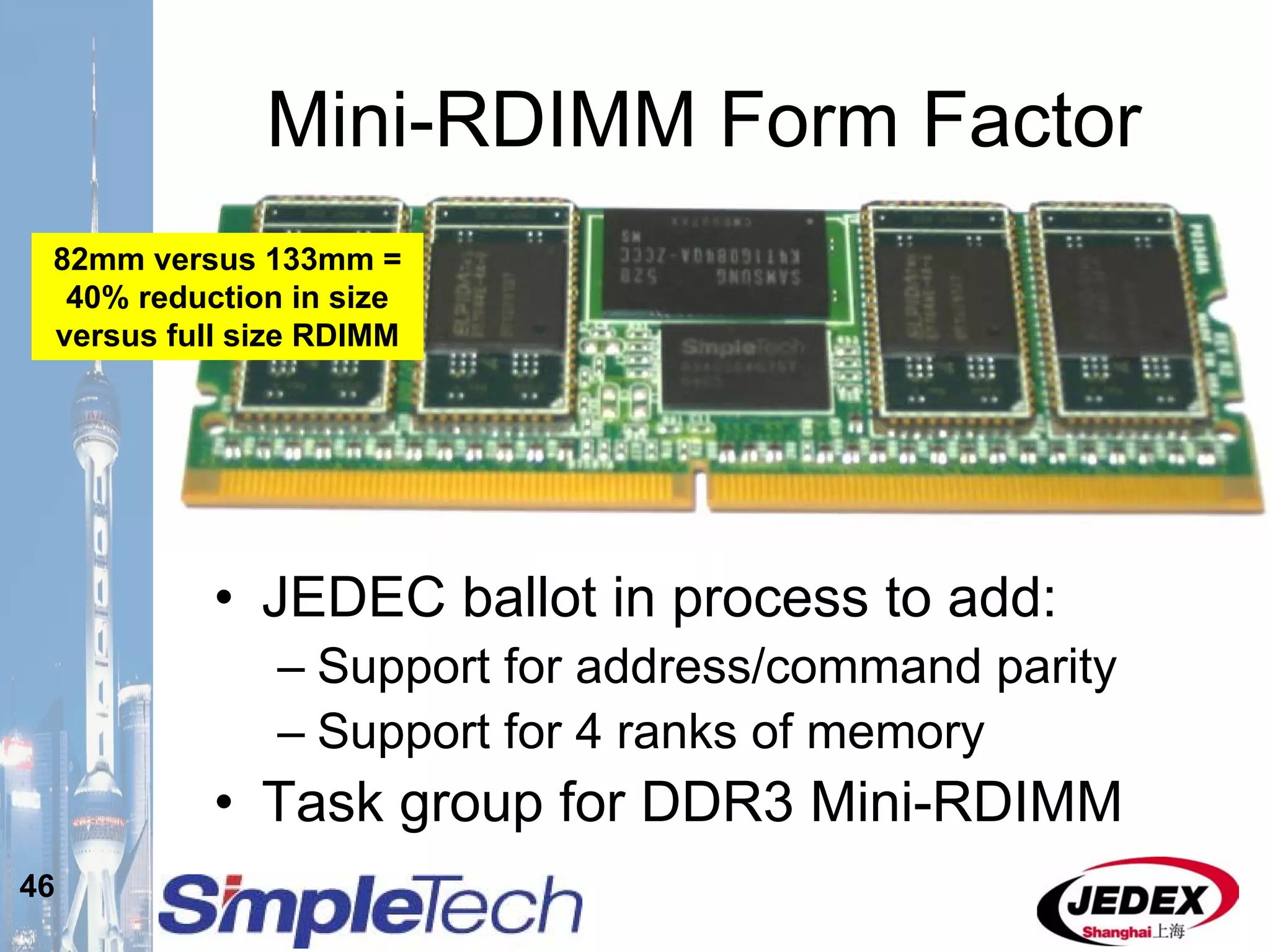
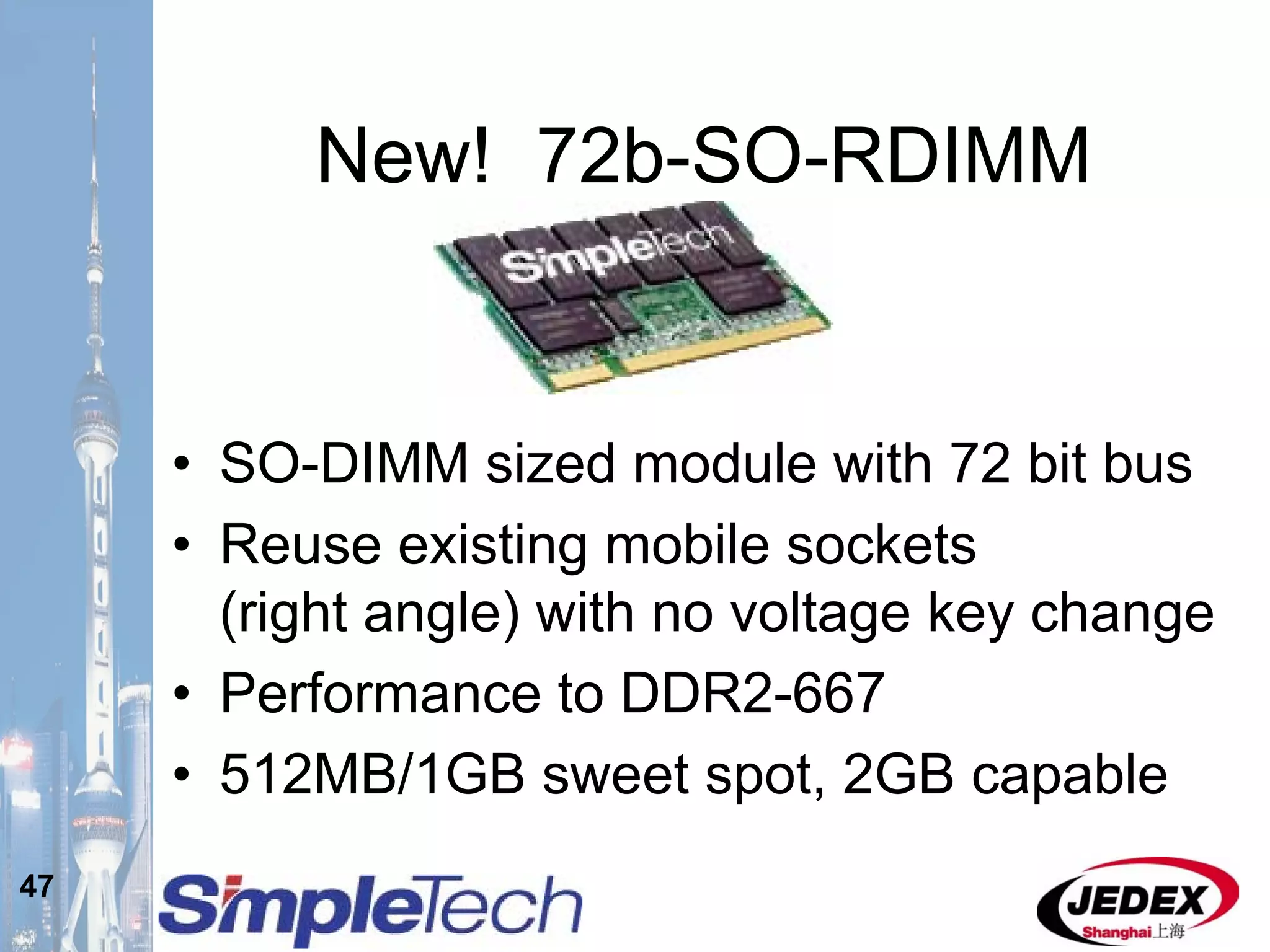
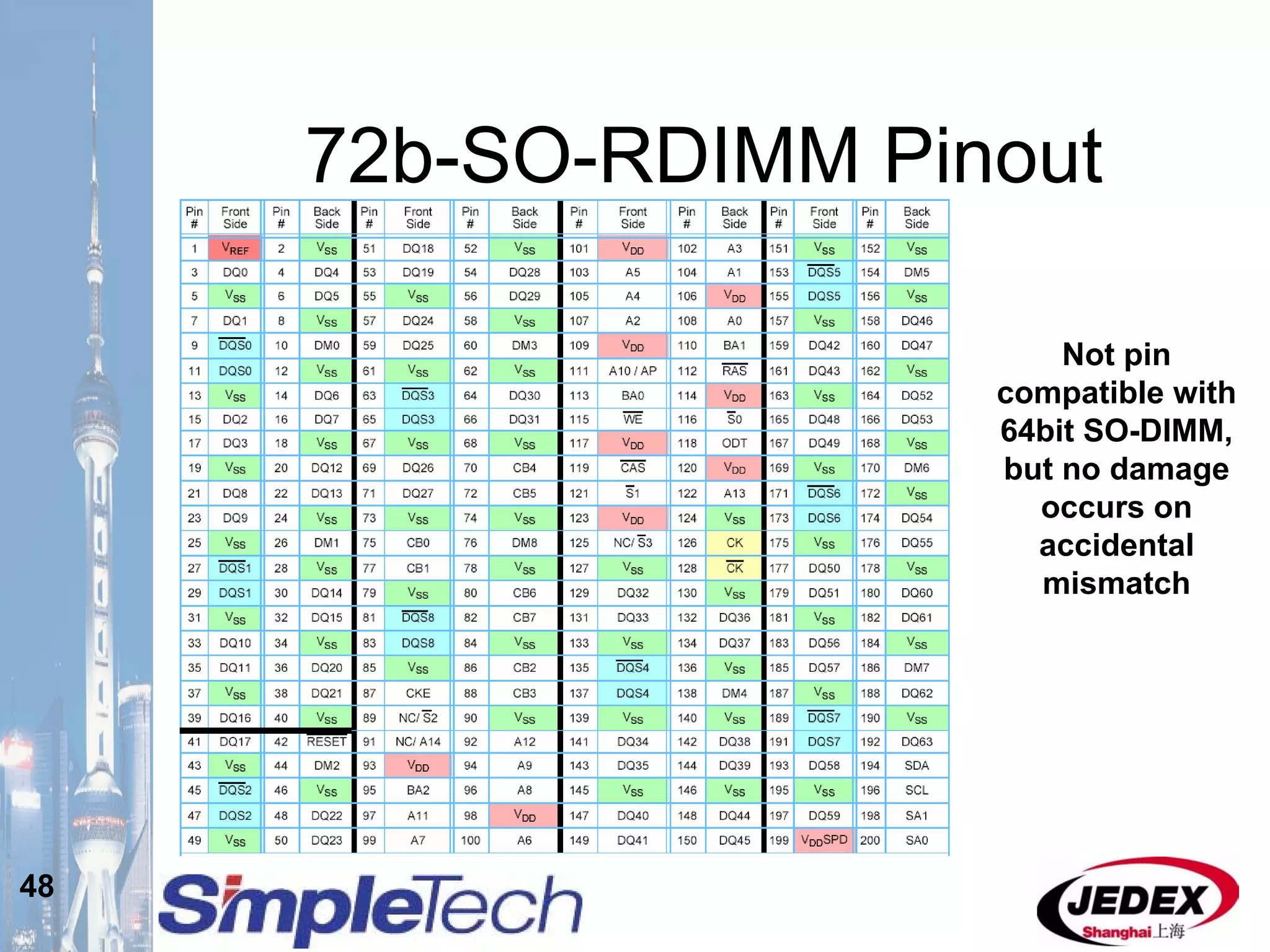
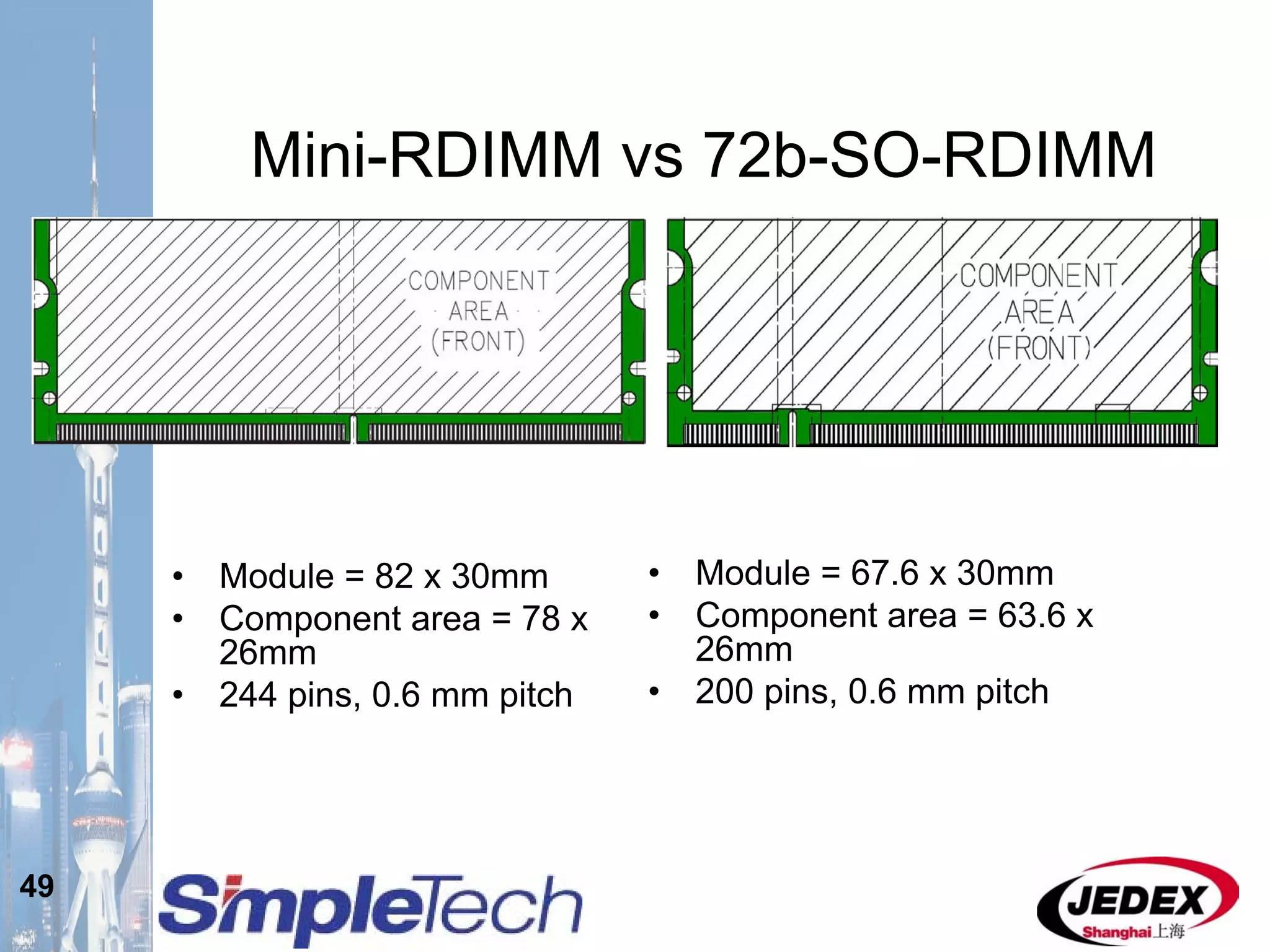
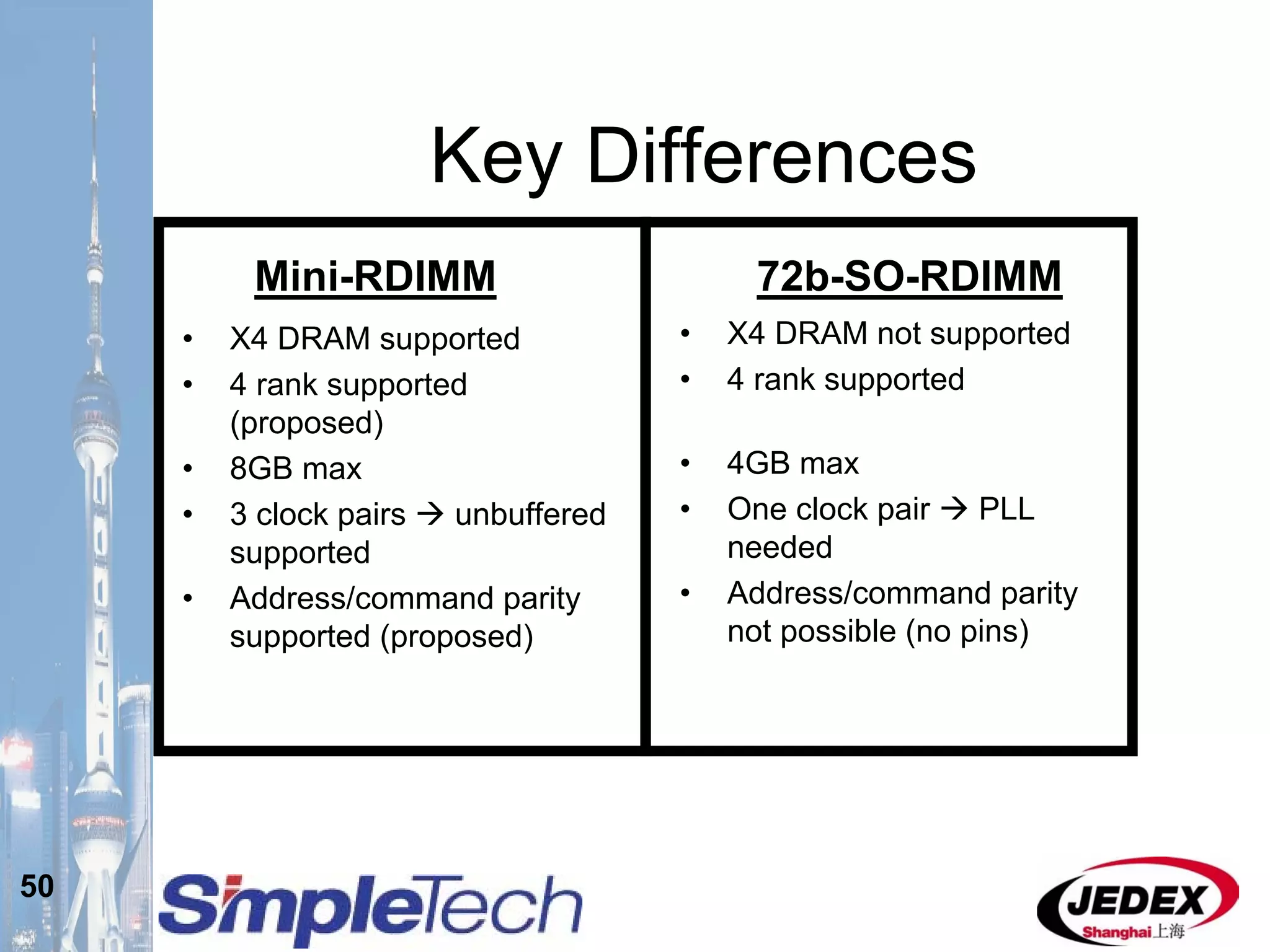
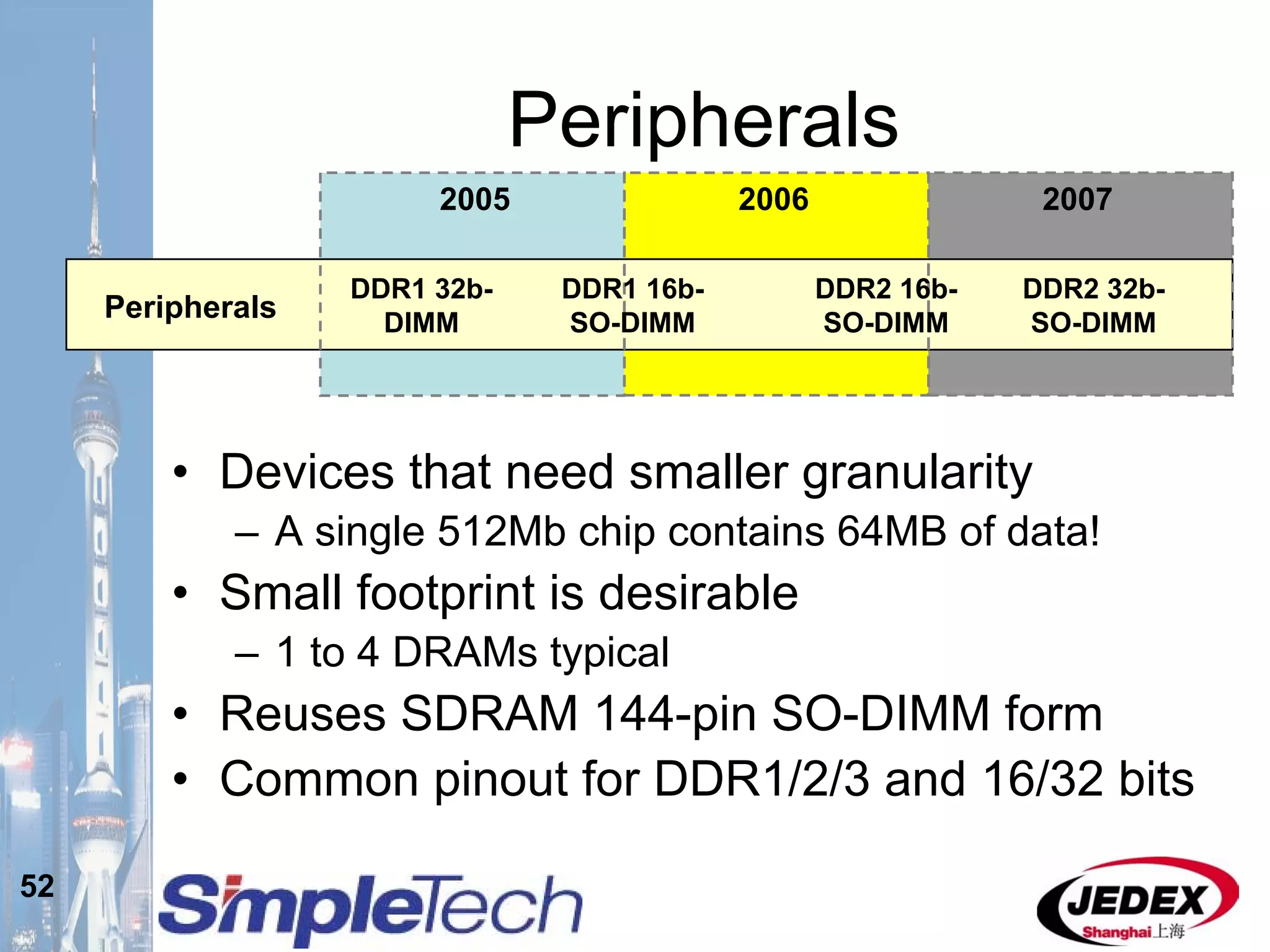
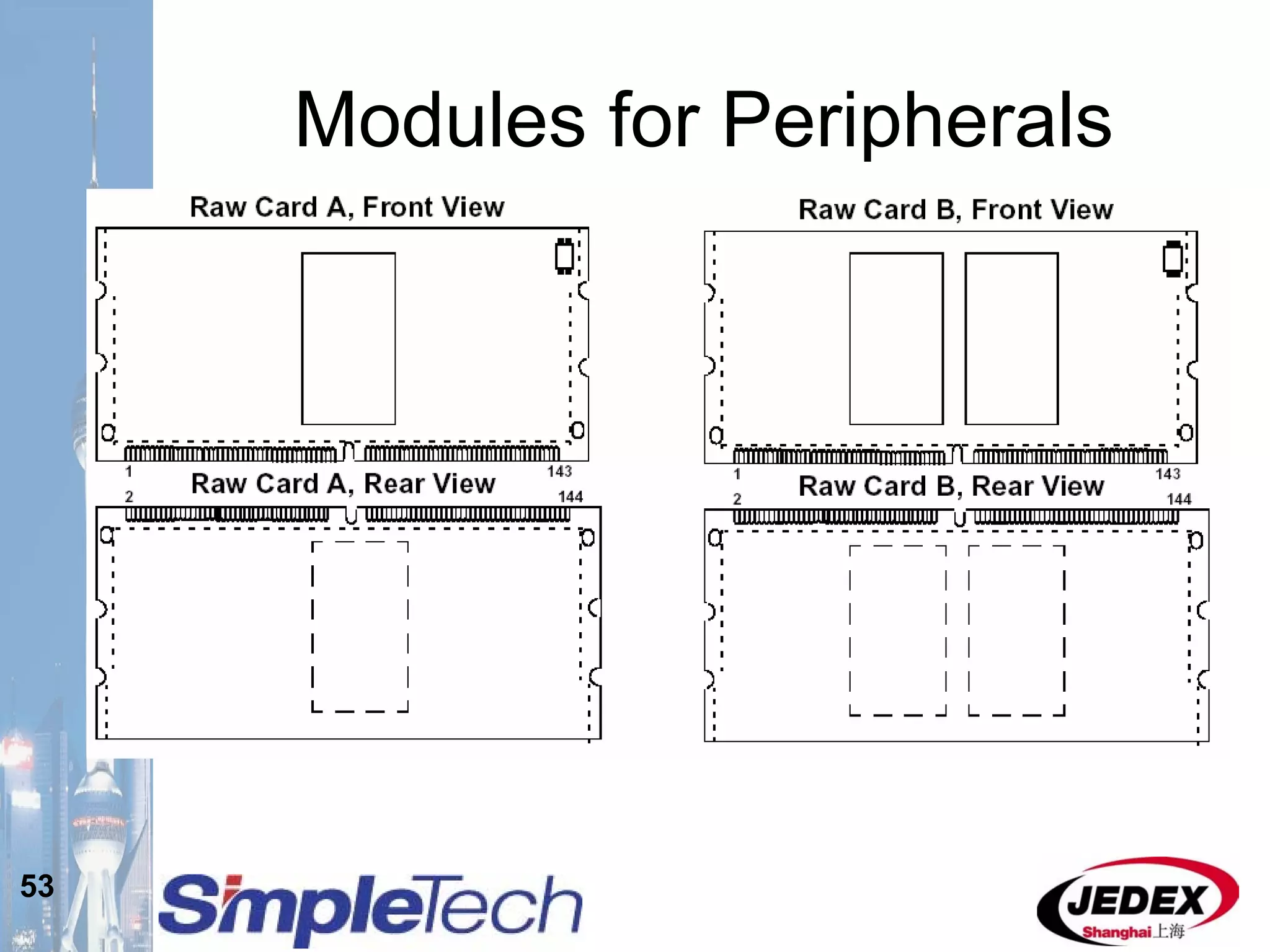
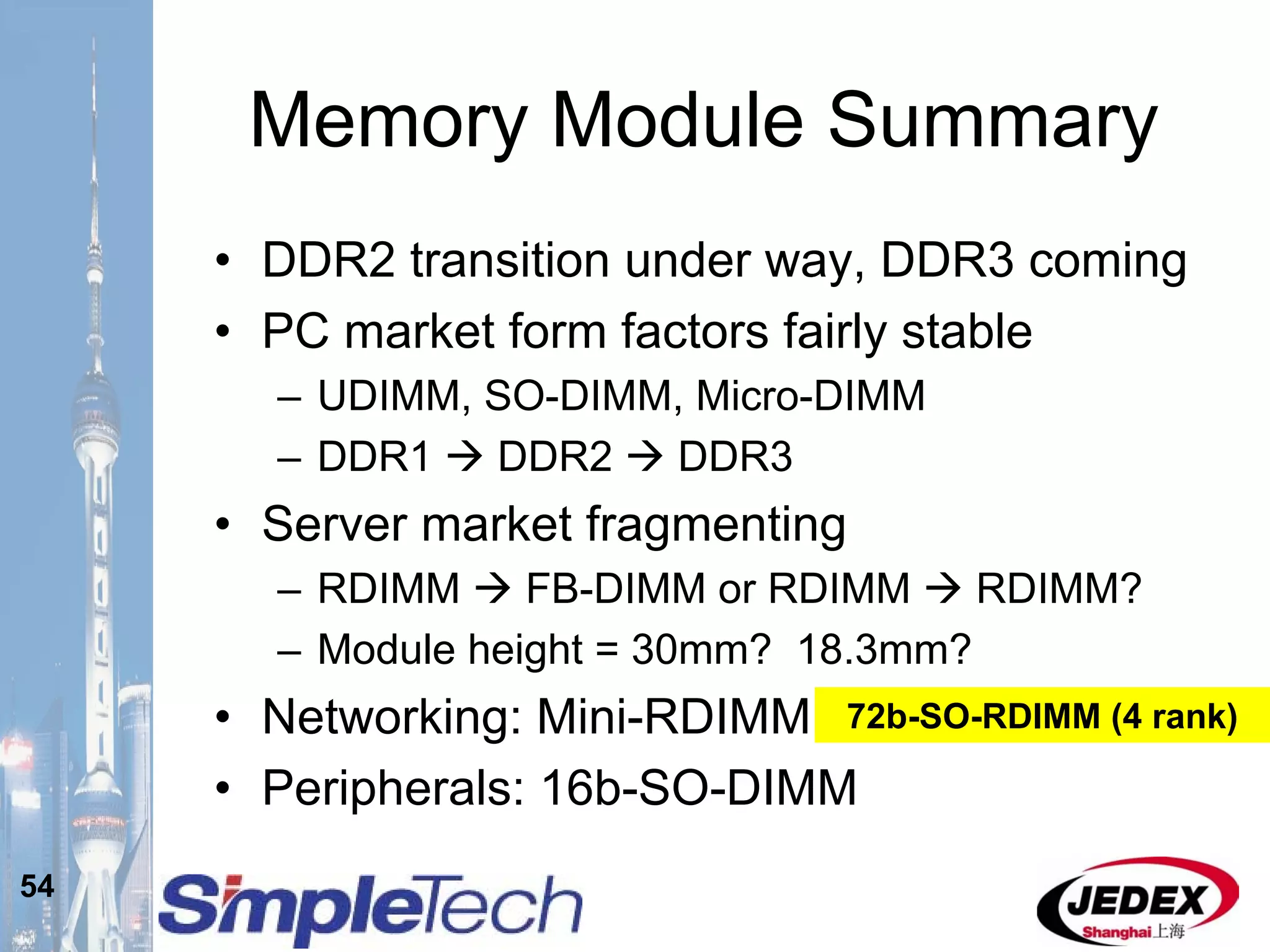
This document provides an overview of the DRAM module market and discusses various module configurations for different applications. It describes the transition from DDR1 to DDR2 and upcoming shift to DDR3. Key markets discussed include personal computers, servers, networking equipment, and peripherals. For servers, it notes ongoing debate around using fully buffered DIMMs (FB-DIMMs) versus registered DIMMs (RDIMMs). New module formats like mini-RDIMMs and 72b SO-RDIMMs are presented as solutions for networking routers and other embedded applications.