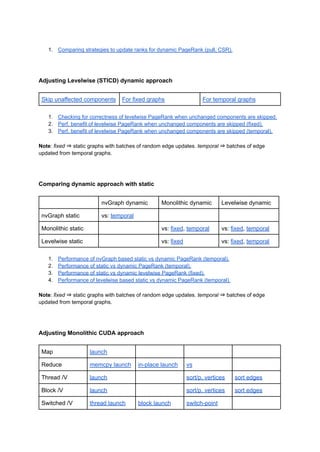
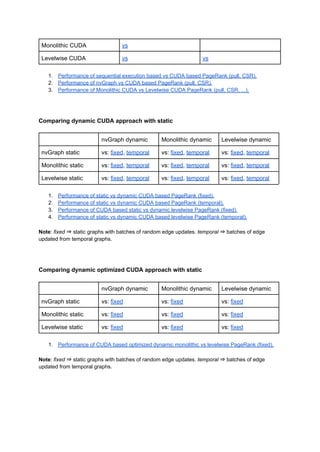
The document details various performance evaluations and comparisons of PageRank algorithms using different data types (float, bfloat16) and methods (pull, csr) in different contexts such as static and dynamic graphs. It includes analyses of performance improvements through adjusting parameters like damping factors, utilizing OpenMP, and CUDA configurations. Additionally, it discusses the benefits of optimizing sequential and monolithic approaches for vector operations in both static and dynamic settings.