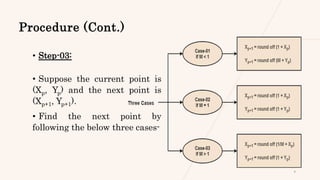
The document discusses the Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) line drawing algorithm. It begins with an introduction to DDA and how it is used to draw lines on a computer screen. It then covers the understanding, procedure, practice problems, advantages, limitations, and conclusion of the DDA algorithm. The core steps of the DDA algorithm include calculating delta X and Y values and the slope between starting and ending points, determining the number of steps, and generating new points along the line through rounding until the ending point is reached. While simple to implement, DDA has limitations such as a lack of smoothness from rounding, but remains a useful basic line drawing technique.