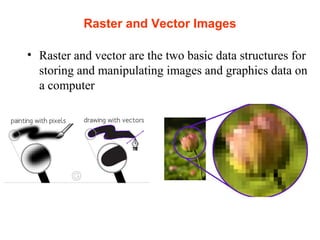
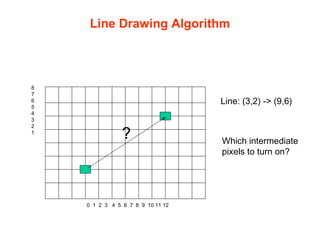
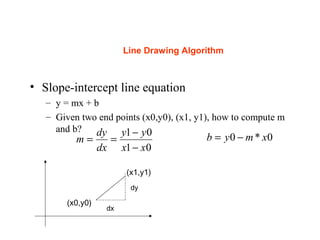
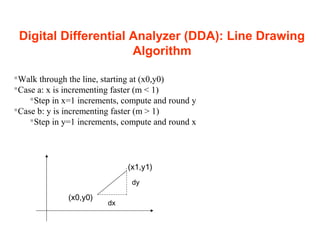
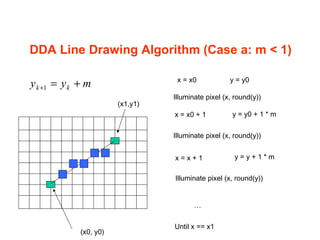
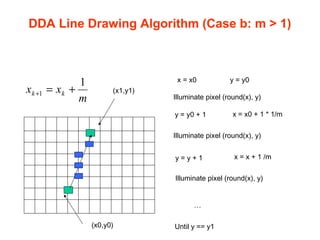
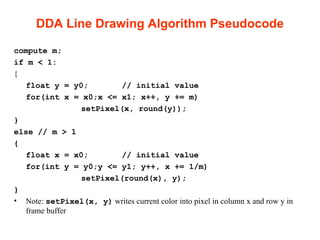
The document discusses computer graphics and line drawing algorithms. It begins with introductions to raster and vector images, as well as rasterization. It then describes the digital differential analyzer (DDA) line drawing algorithm, providing examples of how it works for lines with slopes less than and greater than 1. The DDA algorithm pseudocode is also presented. Finally, drawbacks of the DDA algorithm are noted and an optimized alternative, the Bresenham algorithm, is mentioned. The task for the next lab is to add OpenGL libraries in Visual Studio.