Embed presentation
Downloaded 30 times
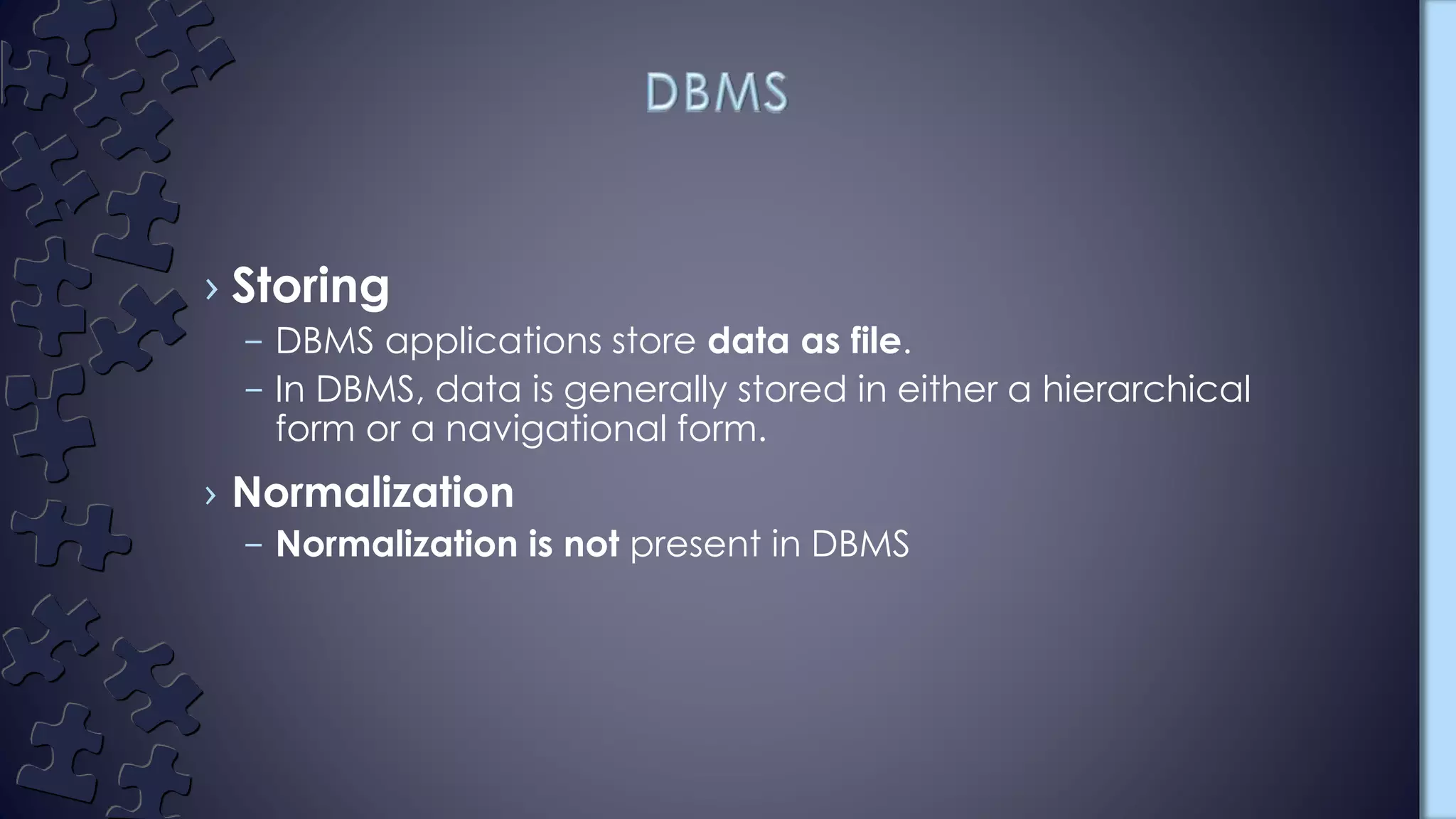


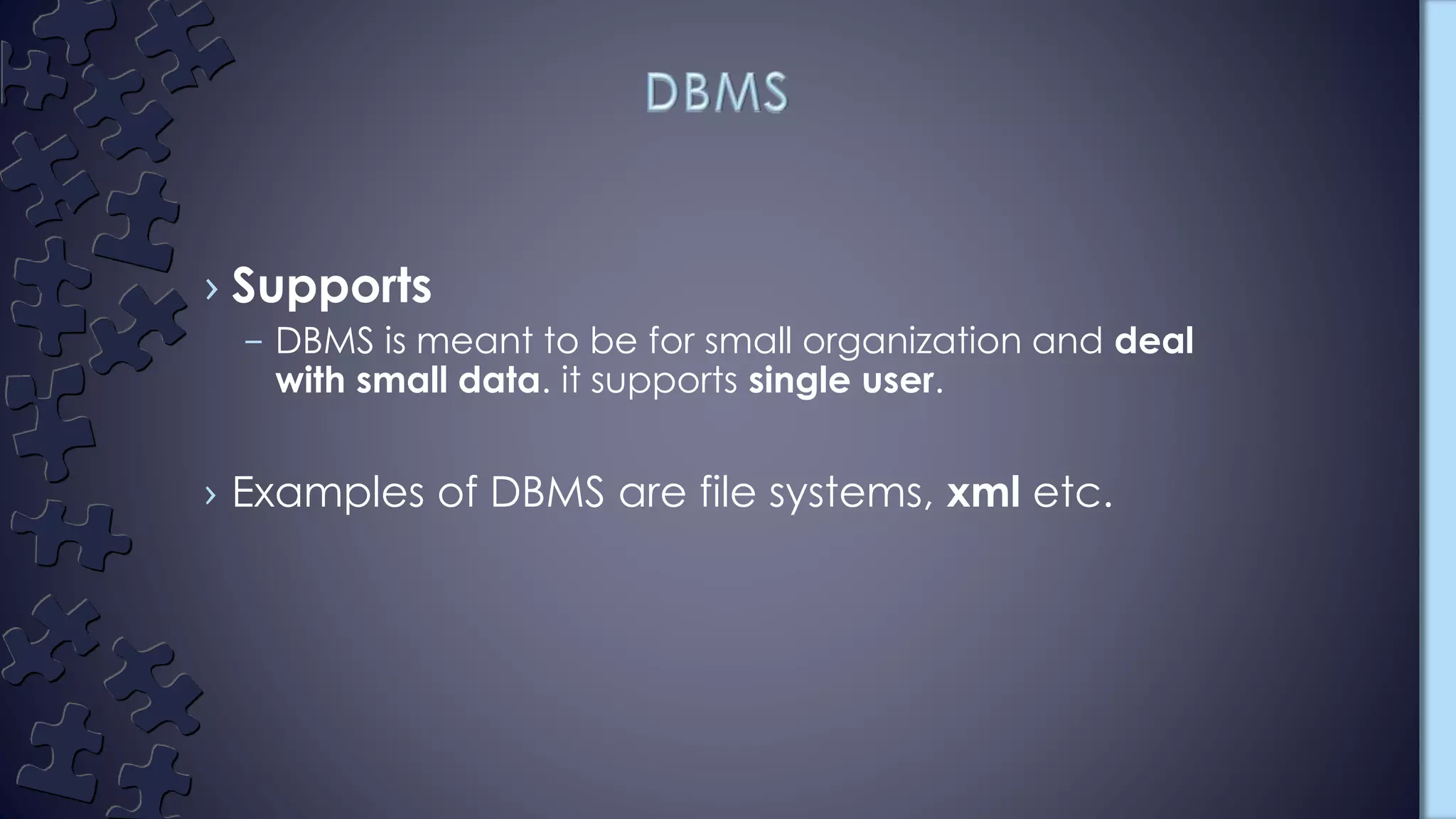
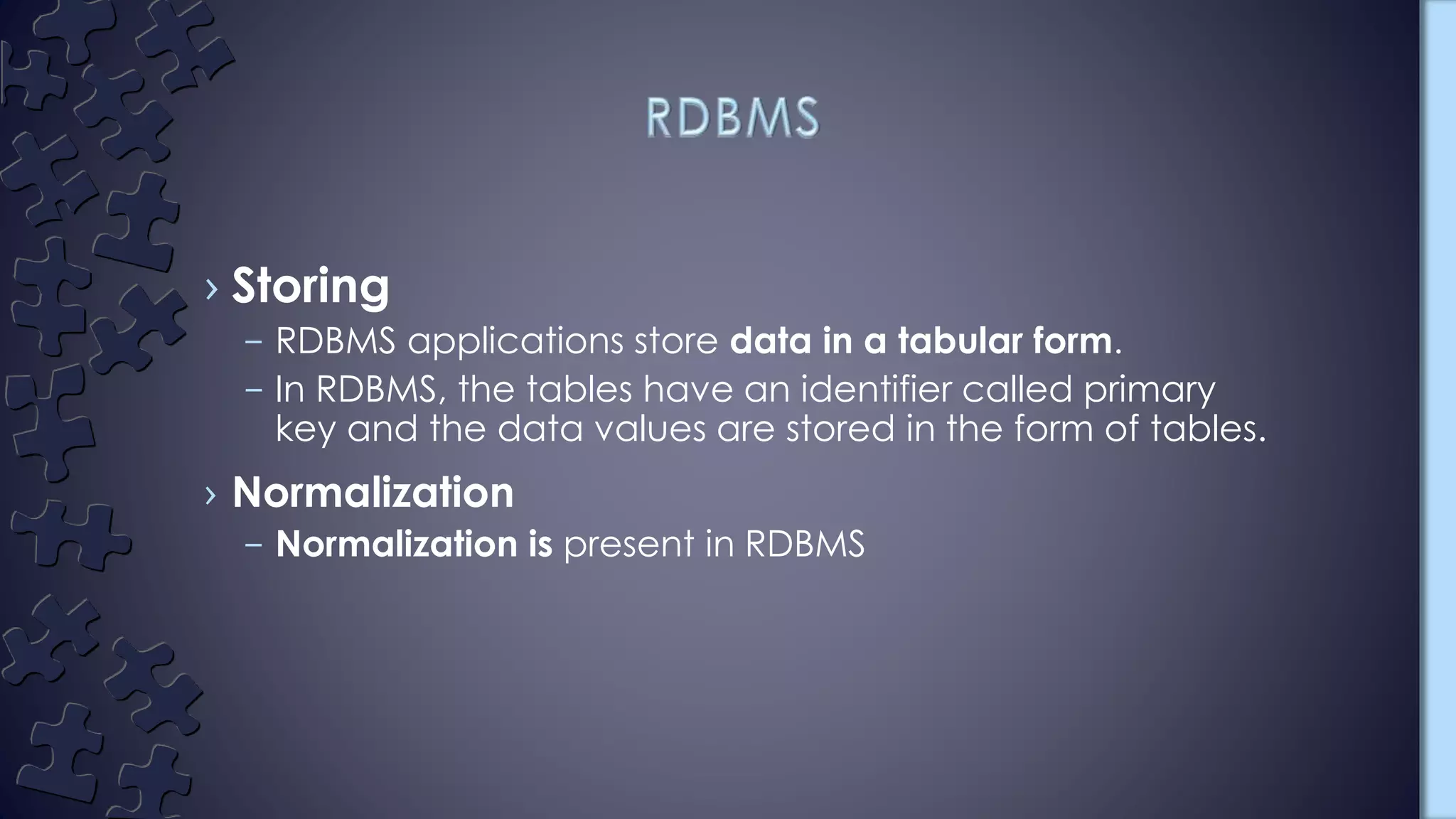



The document compares DBMS and RDBMS systems. DBMS stores data in hierarchical or navigational forms without normalization, uses file systems without relationships between tables, does not support security or distributed databases, and is meant for small organizations. RDBMS stores tabular data with primary keys, supports normalization, defines integrity constraints for ACID properties, stores relationships between tables, supports distributed databases, and is designed for large amounts of data from multiple users. Examples of RDBMS include MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and Oracle.








