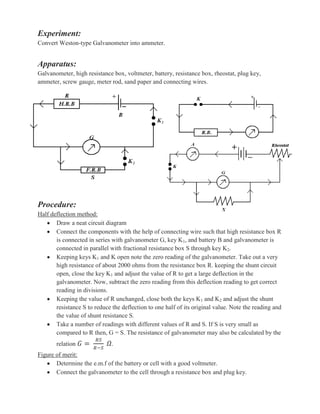
The document describes an experiment to convert a Weston-type galvanometer into an ammeter. Key steps include:
1. Connecting the galvanometer and other circuit components like a battery, resistance box, and keys.
2. Taking readings at half deflection to calculate the galvanometer's resistance.
3. Using additional readings and calculations to determine the figure of merit and suitable shunt resistance value.
4. Cutting and connecting a wire to serve as the shunt resistance and verifying readings match the ammeter.