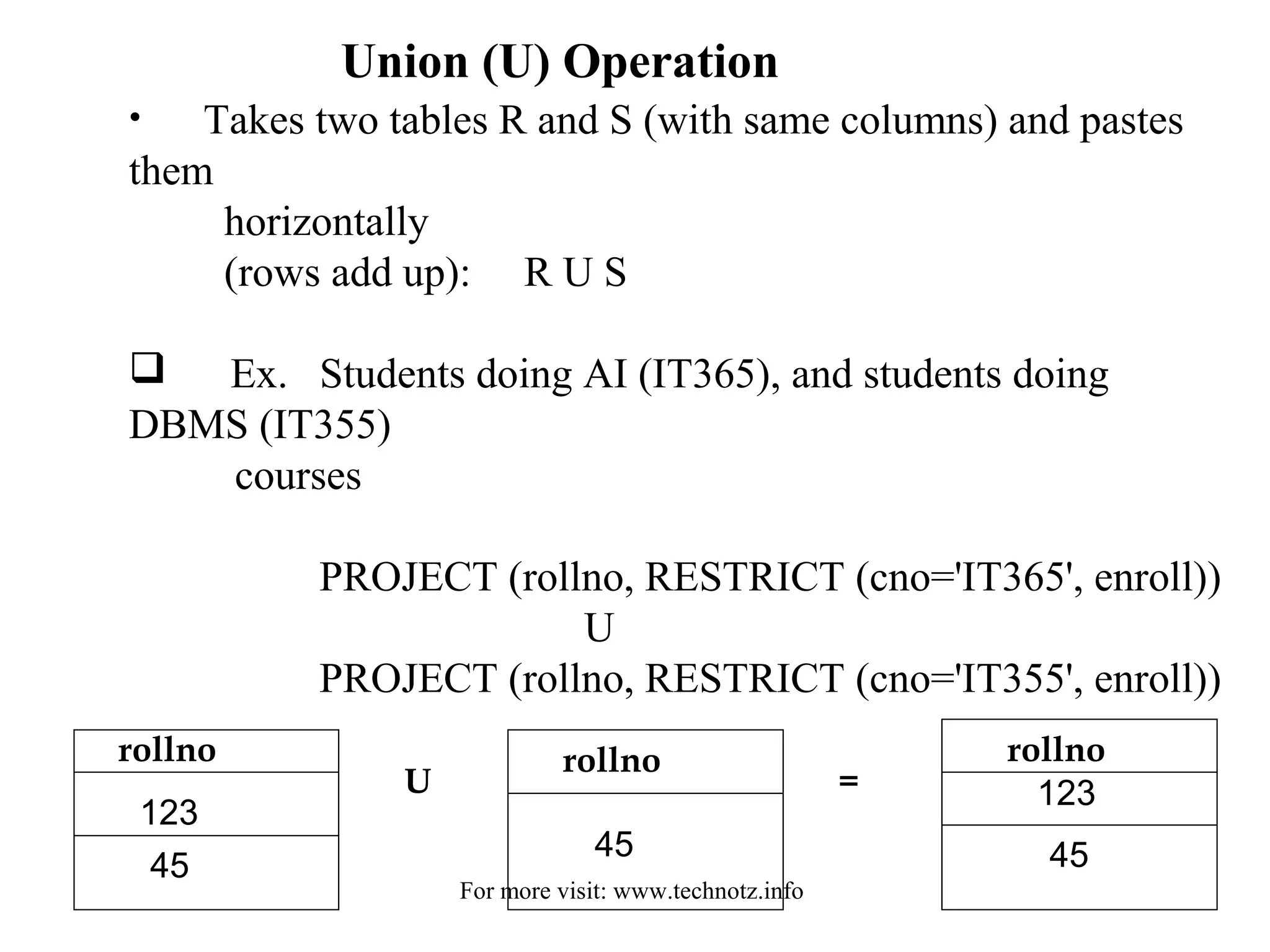
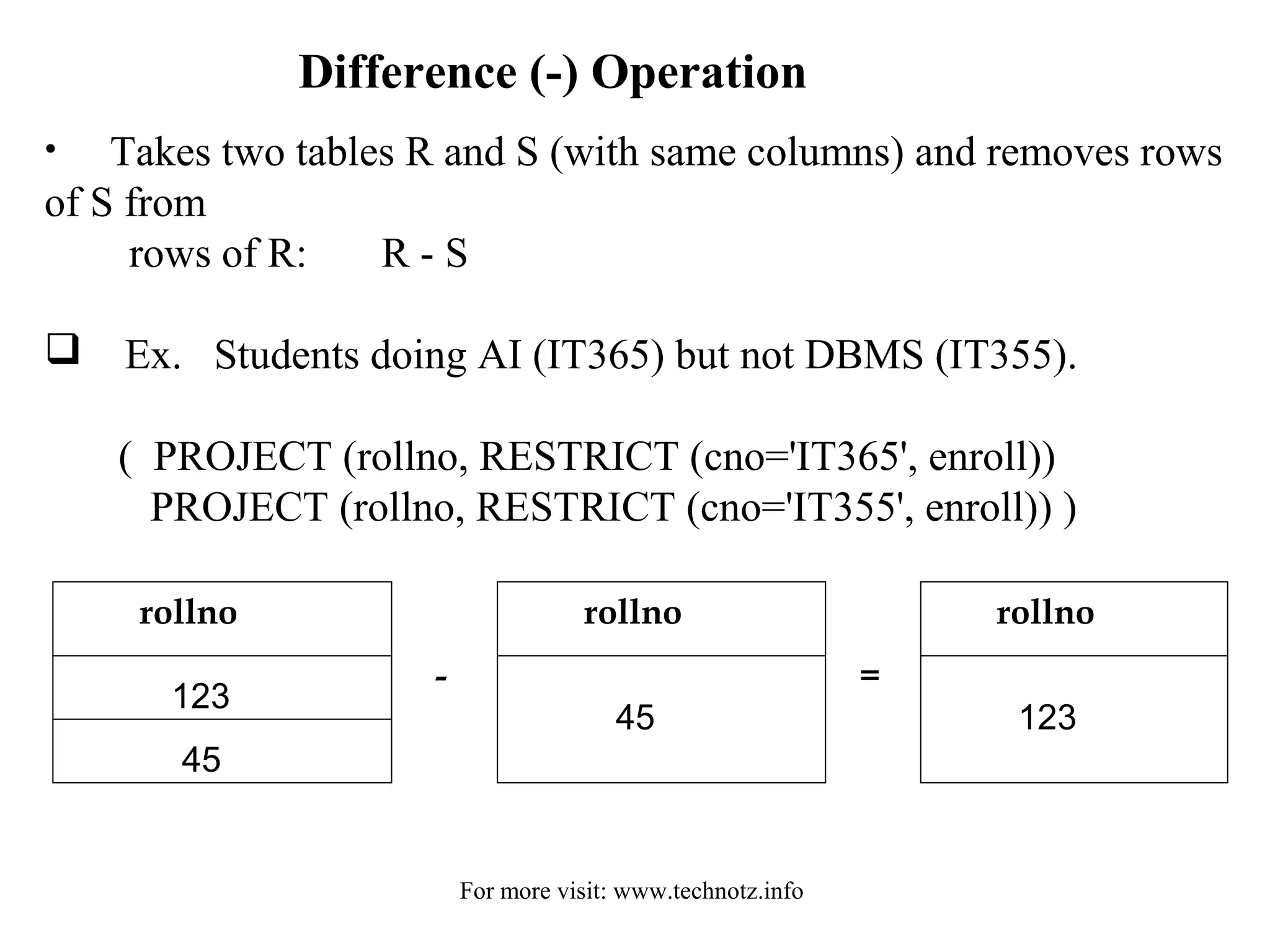
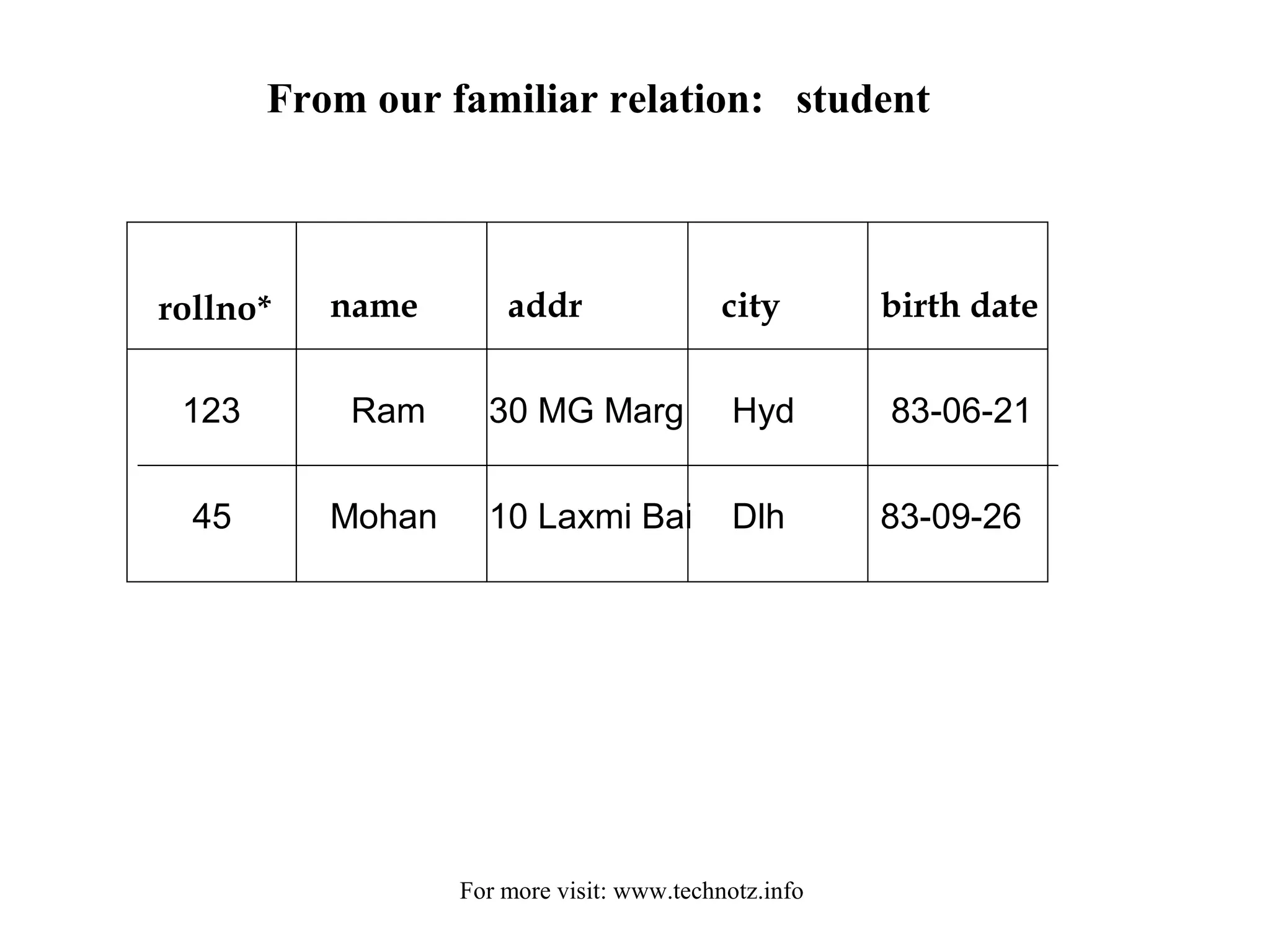
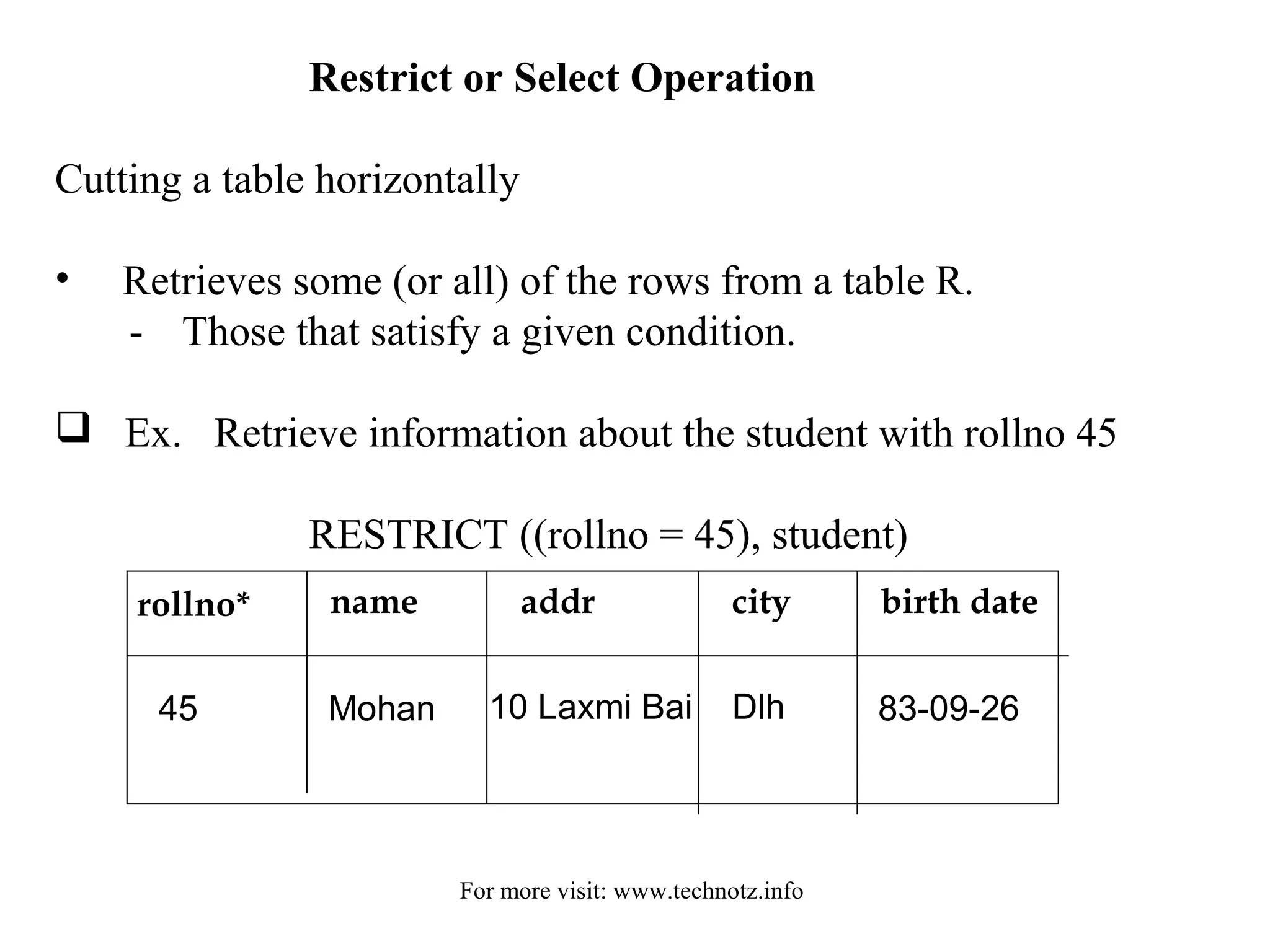
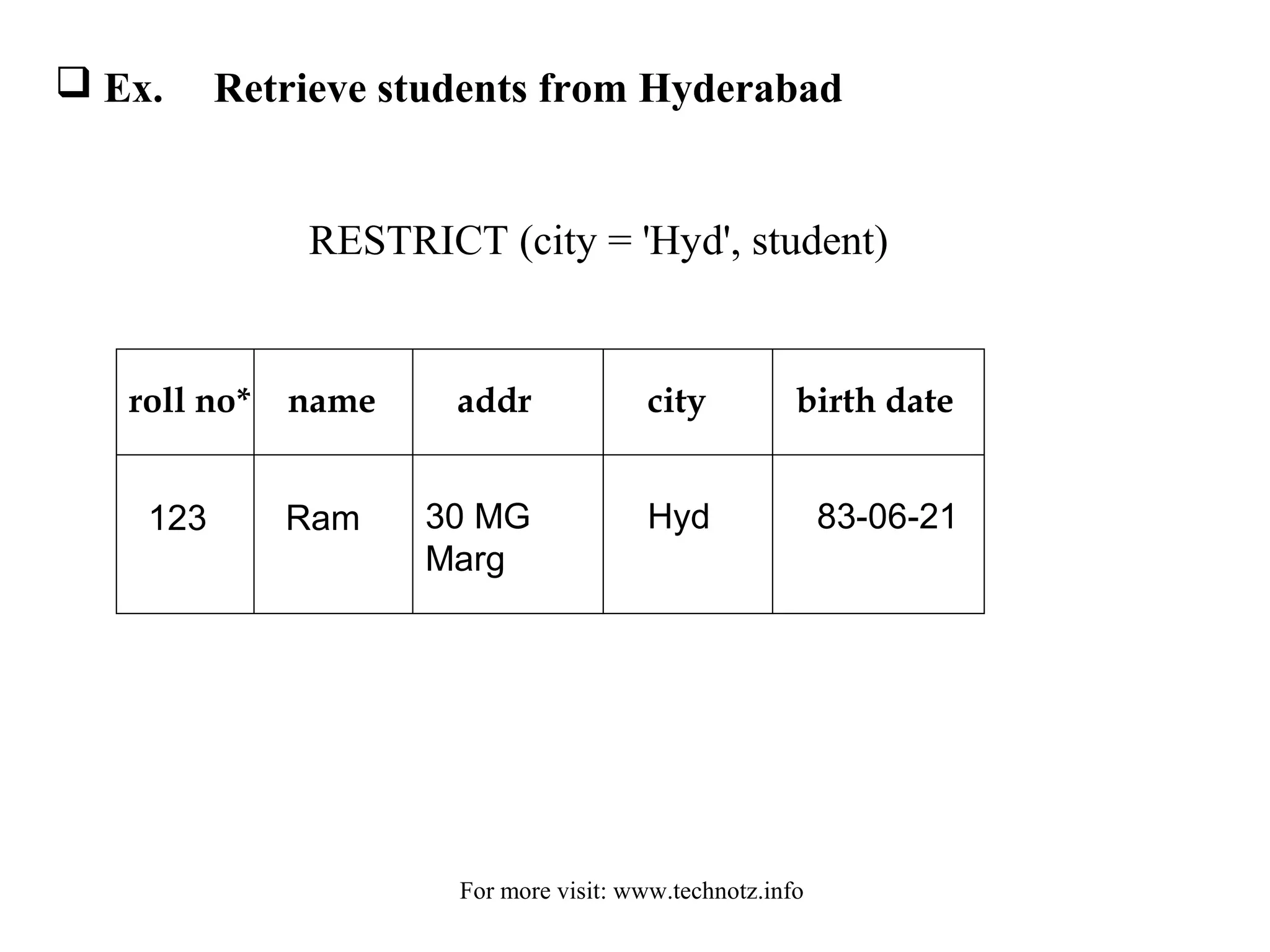
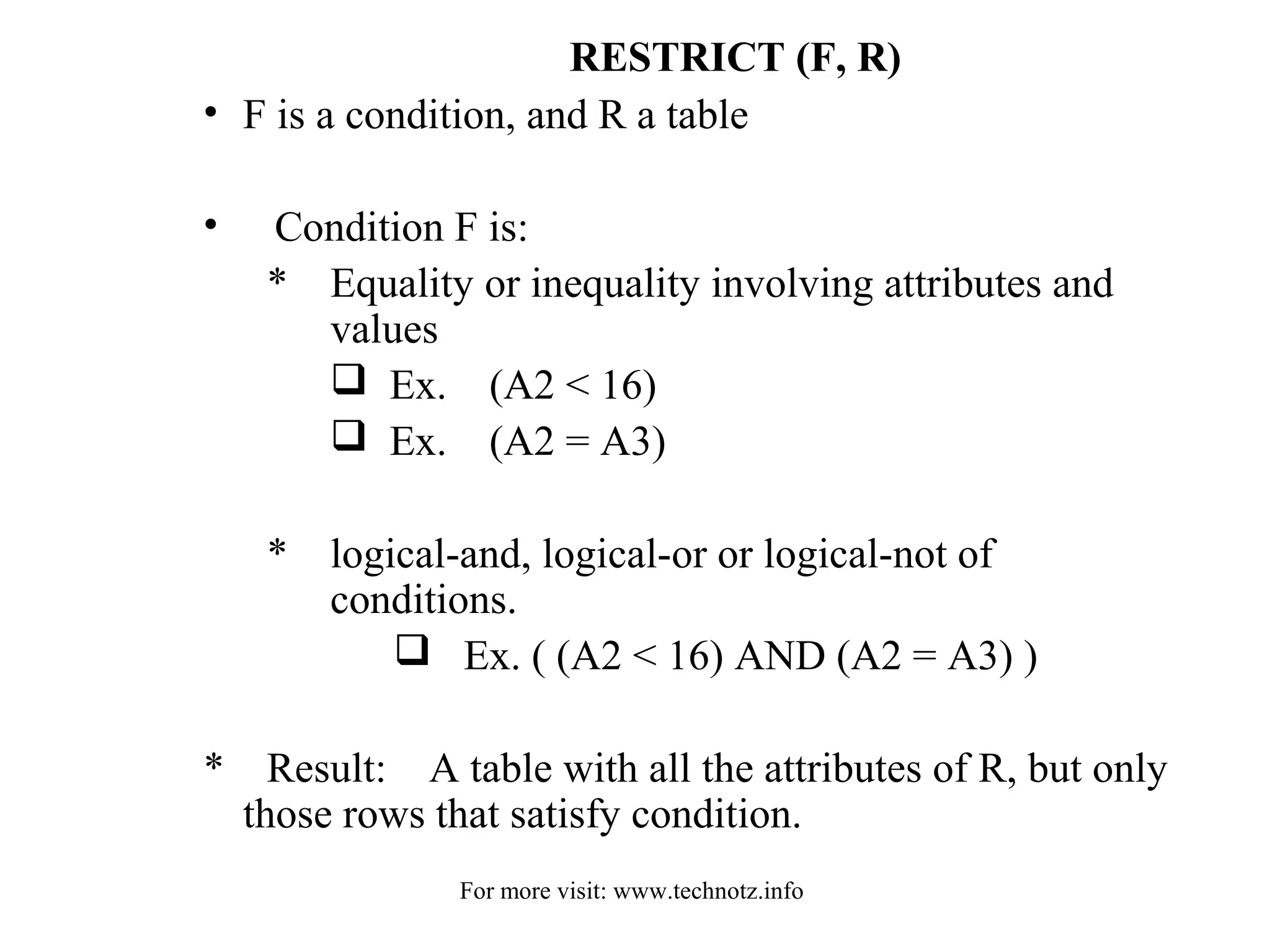
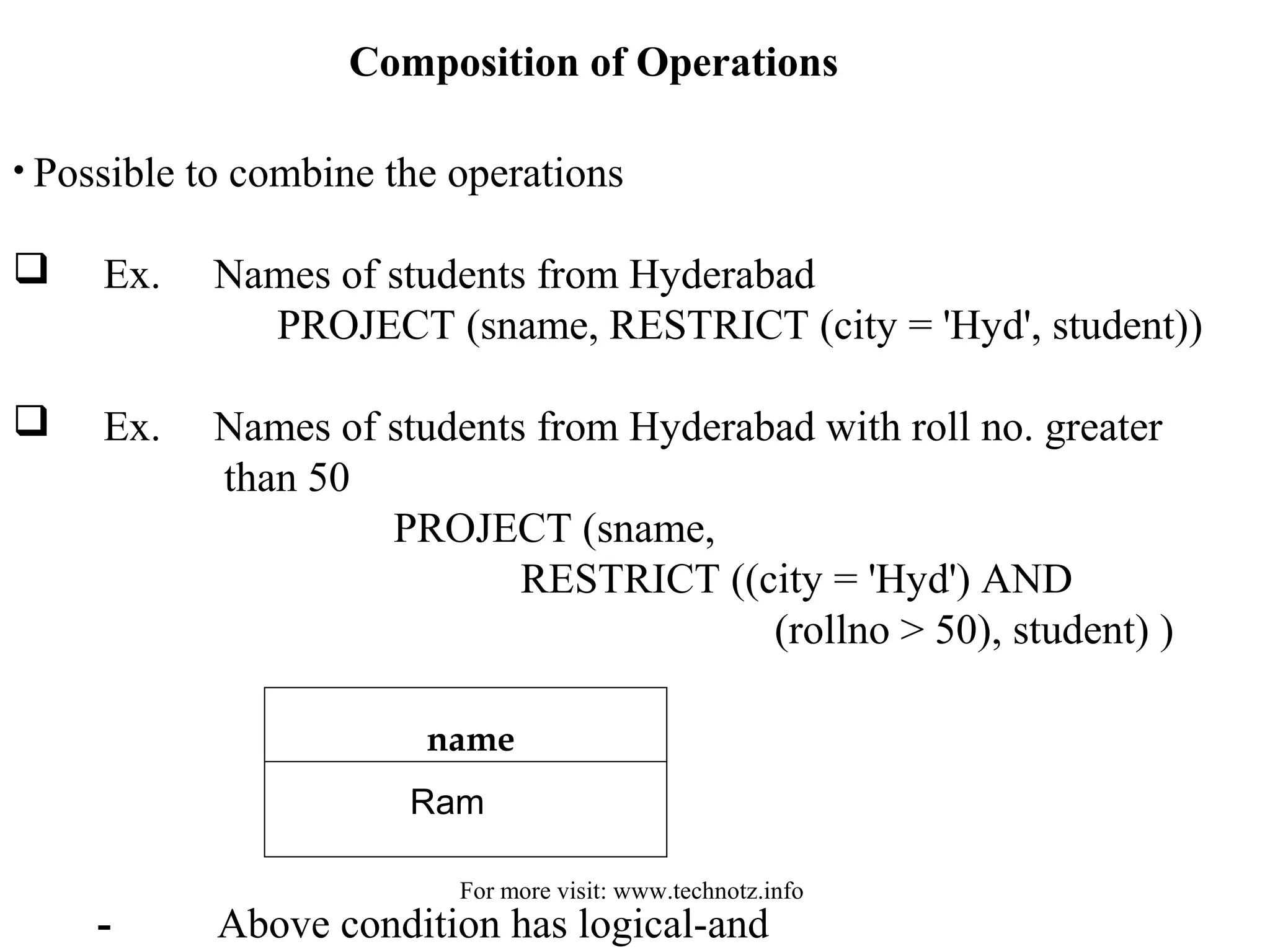
The document discusses relational algebra and its operators. It introduces the five basic relational algebra operators - project, restrict, cartesian product, union and difference. It provides examples of how each operator works and how they can be combined. The operators allow querying relational databases at a logical level and provide data independence from the physical storage structure.



![Project Operation
Cuts a table vertically.
• Retrieves some (or all) columns from a table R
Example: Retrieve rollno and address of each student
PROJECT (rollno, name, student)
or
student [rollno, name]
rollno name
123
45
Ram
Mohan
For more visit: www.technotz.info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2a-141203002649-conversion-gate01/75/DBMS-Relational-Algebra-4-2048.jpg)
![Project Operation: Definition
• Definition
PROJECT (A1, ..., Ak, R)
or
R [A1, ..., Ak]
- A1 to Ak are attribute names,
- R is a relation/table.
* Result: A table with all the rows of R but only k
attributes (A1 to Ak)
For more visit: www.technotz.info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2a-141203002649-conversion-gate01/75/DBMS-Relational-Algebra-6-2048.jpg)

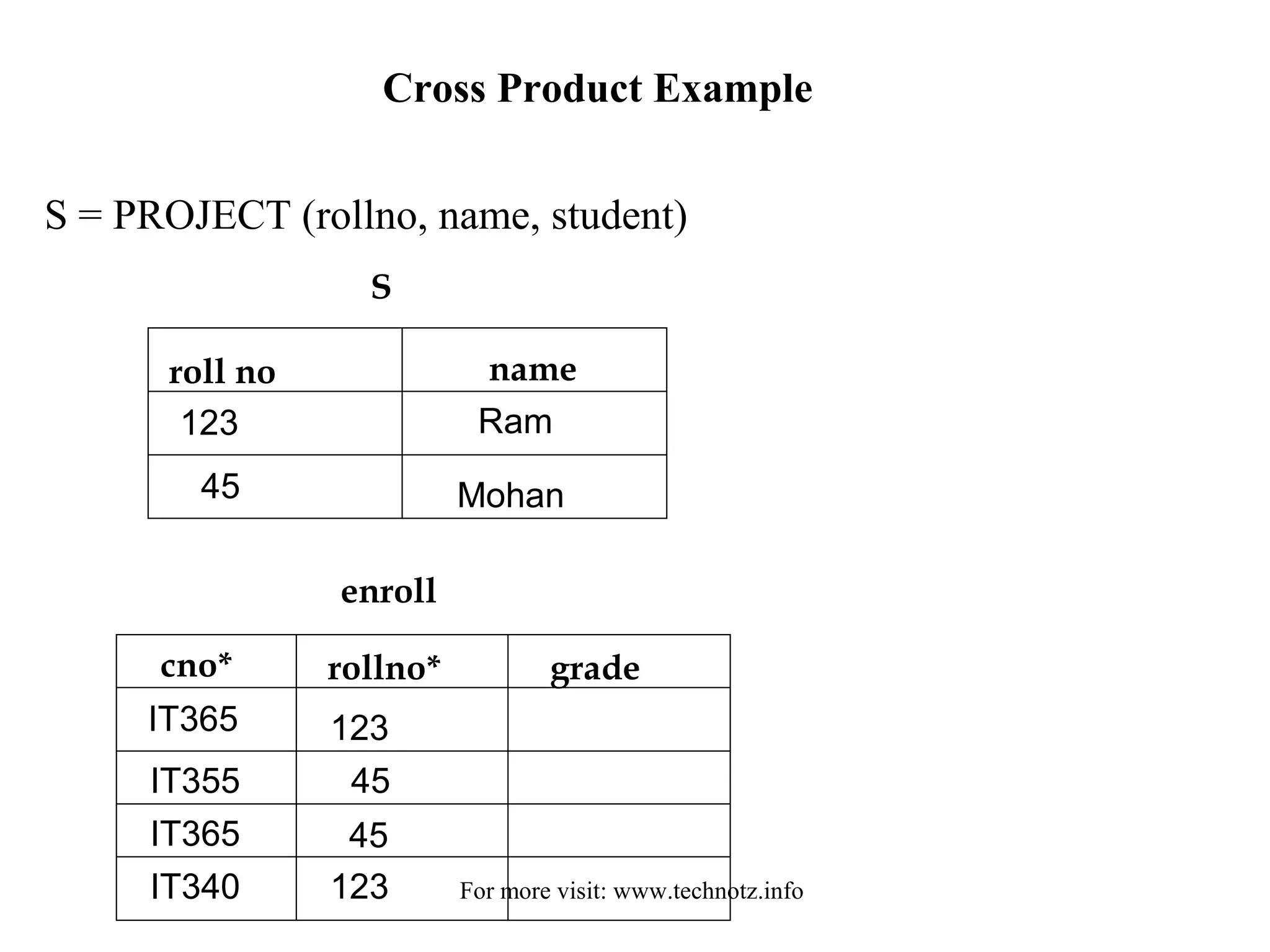
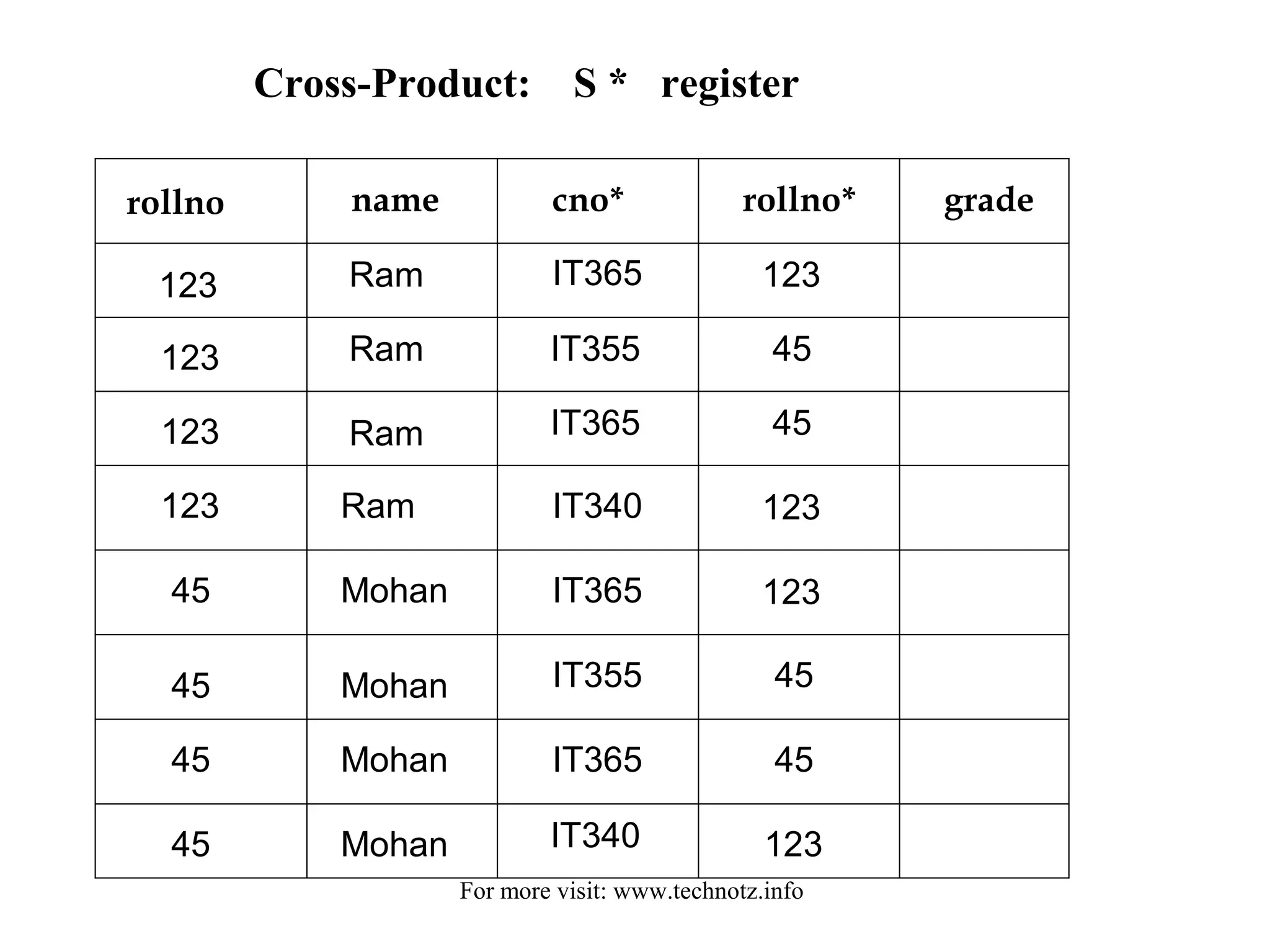
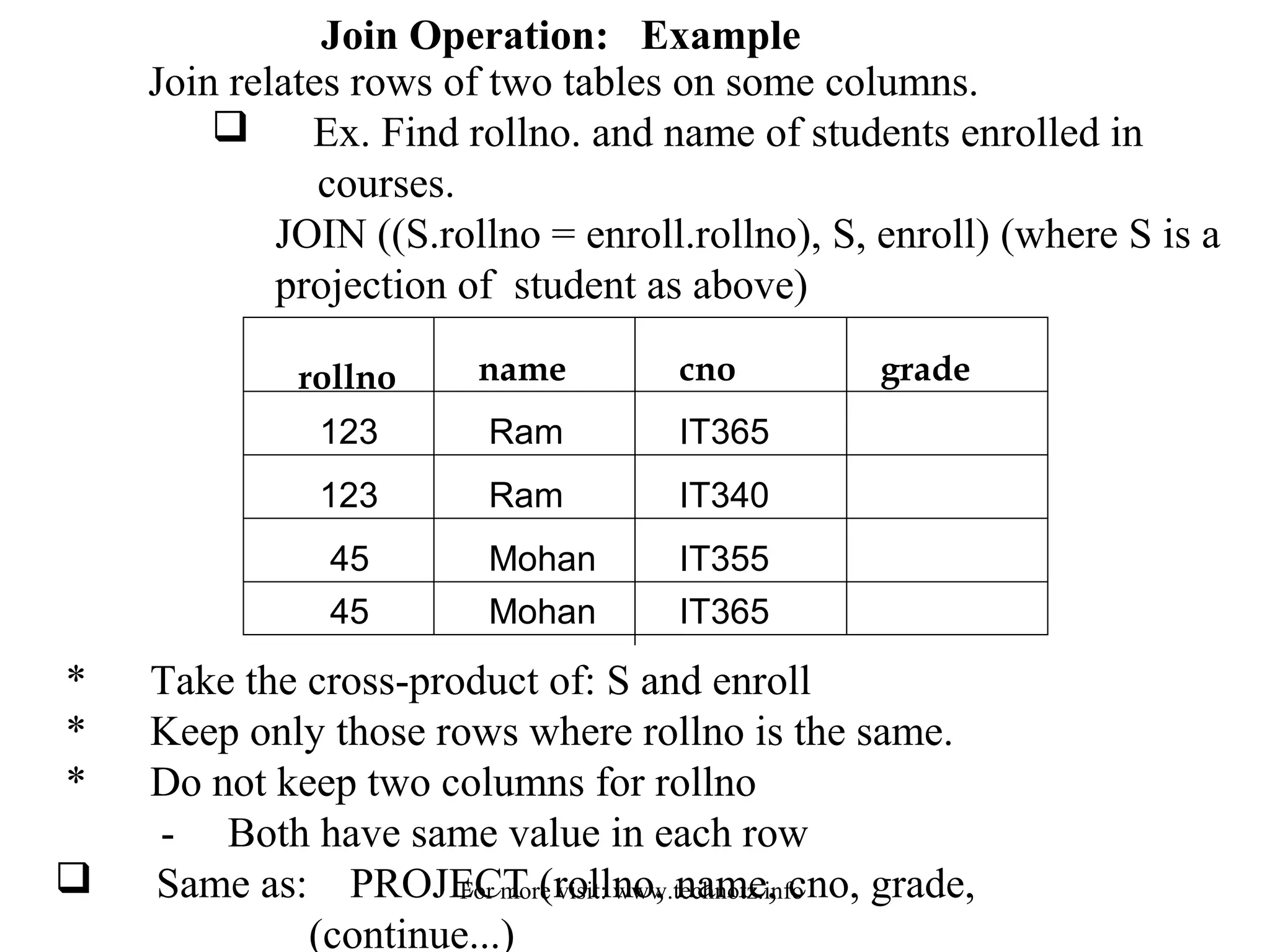
![...continued
RESTRICT [ (S.rollno = enroll.rollno), S * enroll ] )
rollno name cno grade
123
123
45
45
Ram
Ram
Mohan
Mohan
IT365
IT340
IT355
IT365
For more visit: www.technotz.info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2a-141203002649-conversion-gate01/75/DBMS-Relational-Algebra-15-2048.jpg)