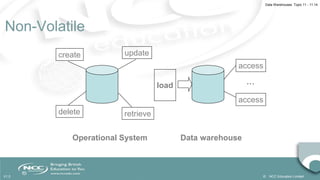
The document outlines the importance of data warehouses in business intelligence, highlighting their role in supporting decision-making through on-line analytical processing (OLAP) as opposed to on-line transaction processing (OLTP). It details the need for data integration from various sources, the transformation of data into useful information, and the methodologies used in building and structuring data warehouses. Furthermore, it discusses different data warehouse schemas and the functionalities of OLAP tools, alongside the steps for effective data warehouse construction.