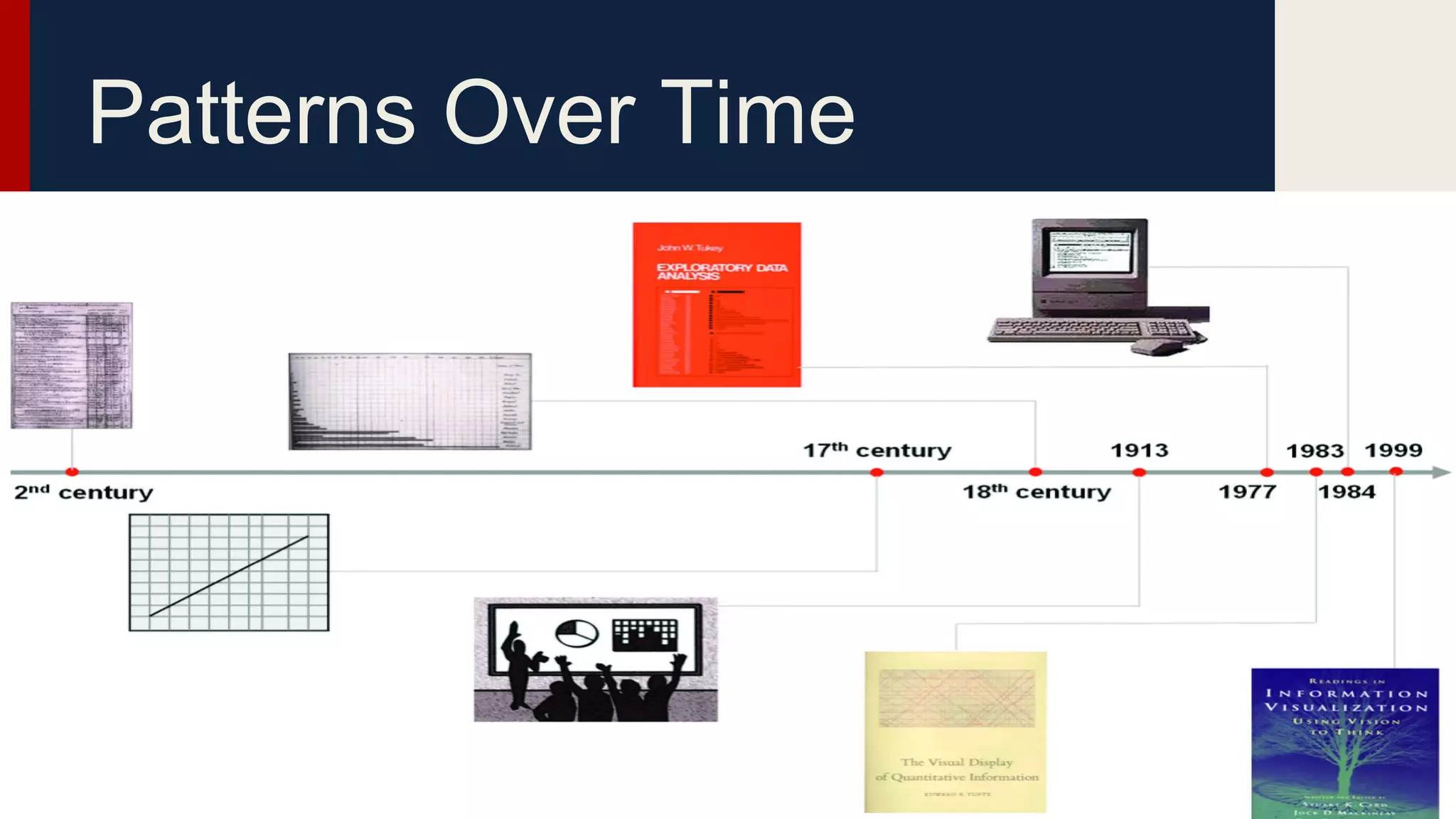
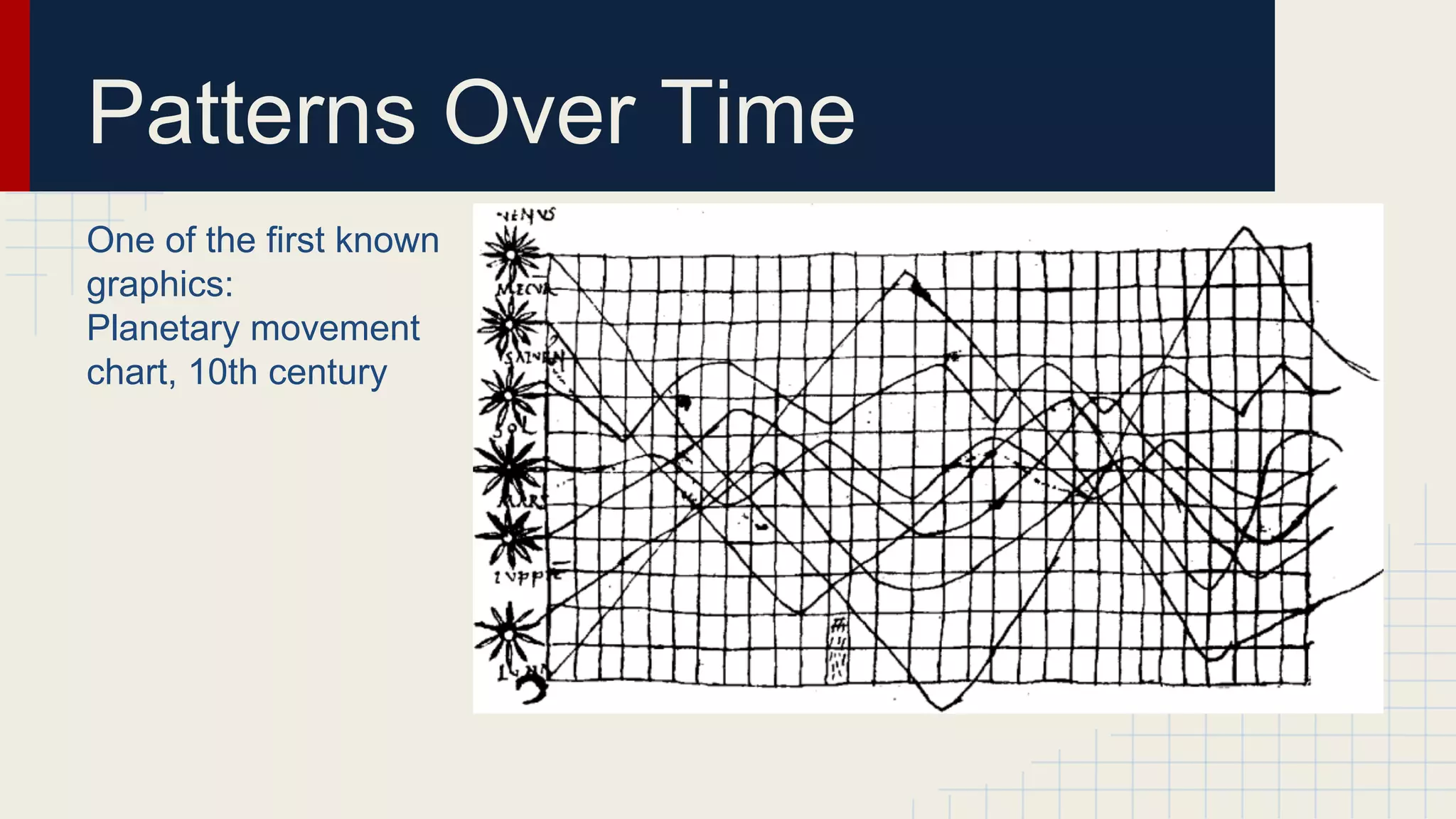
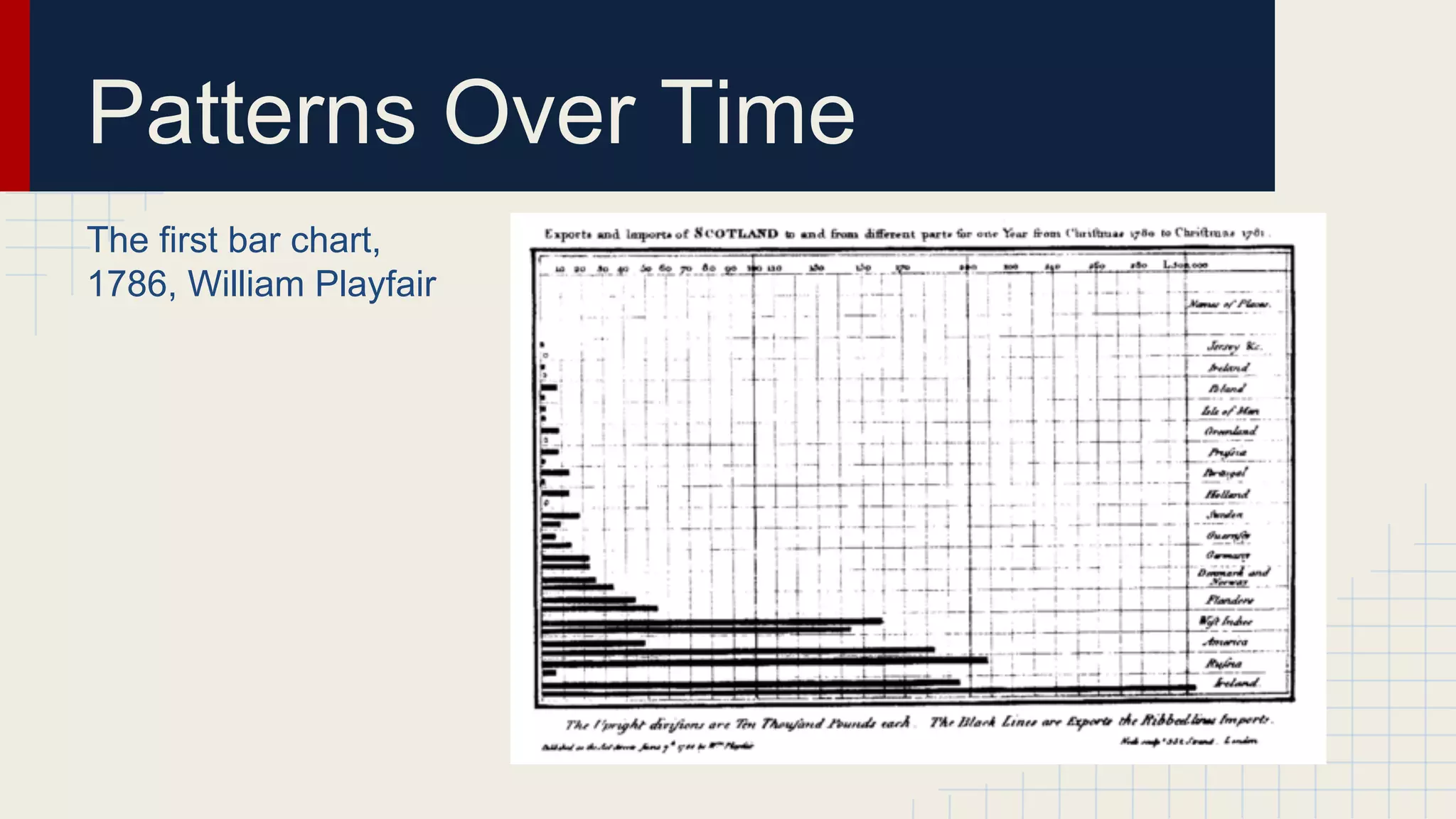
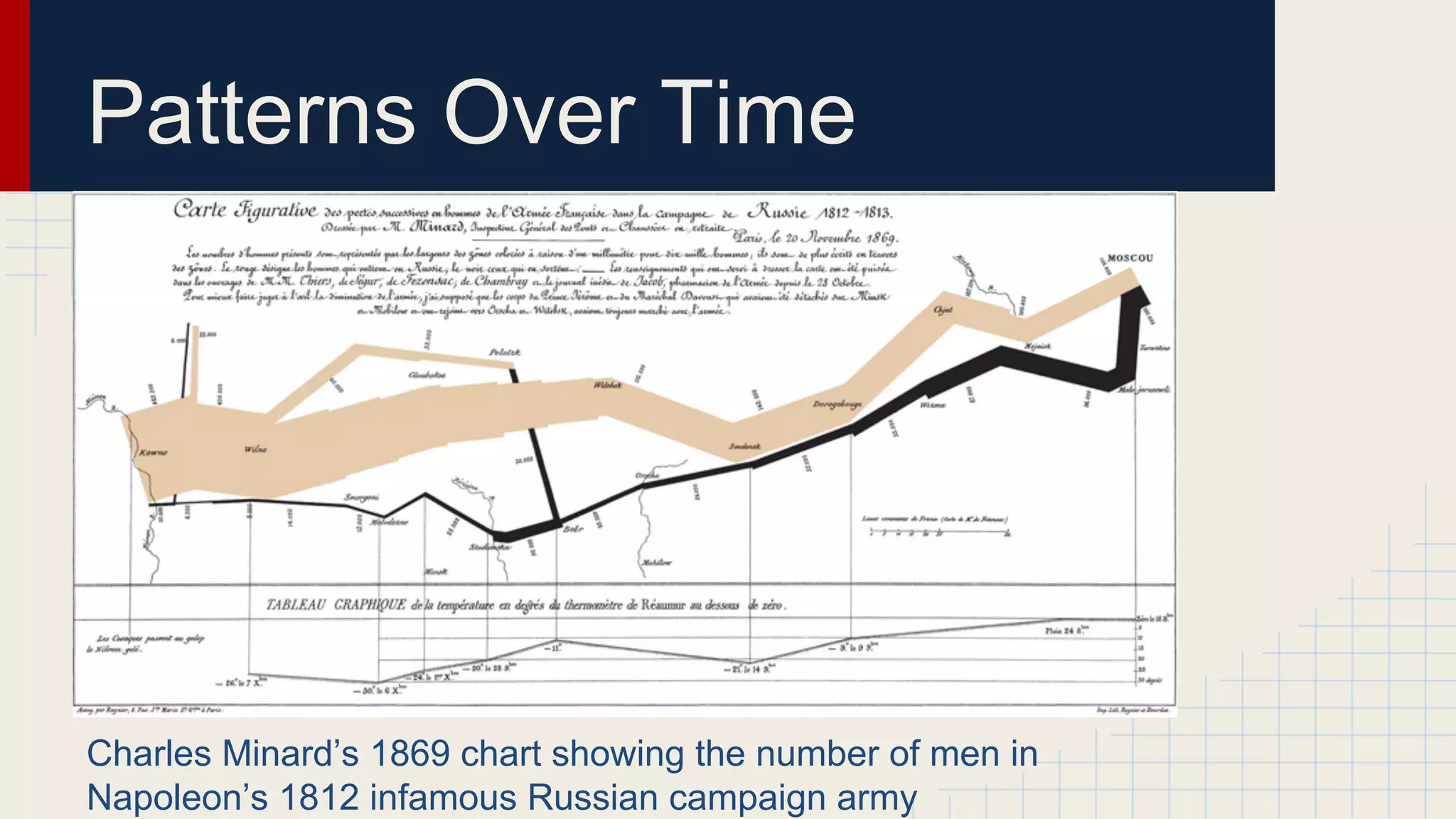
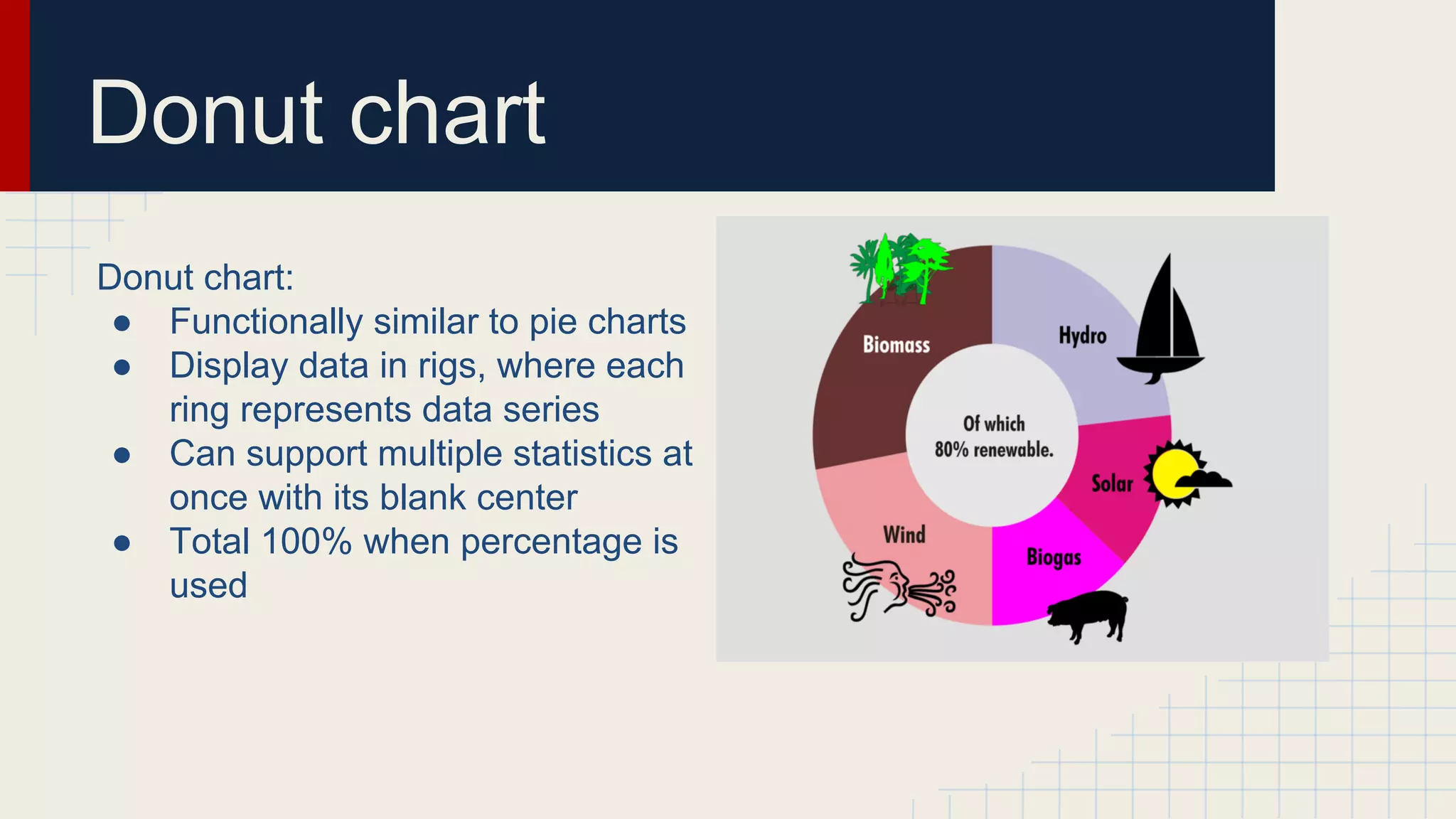
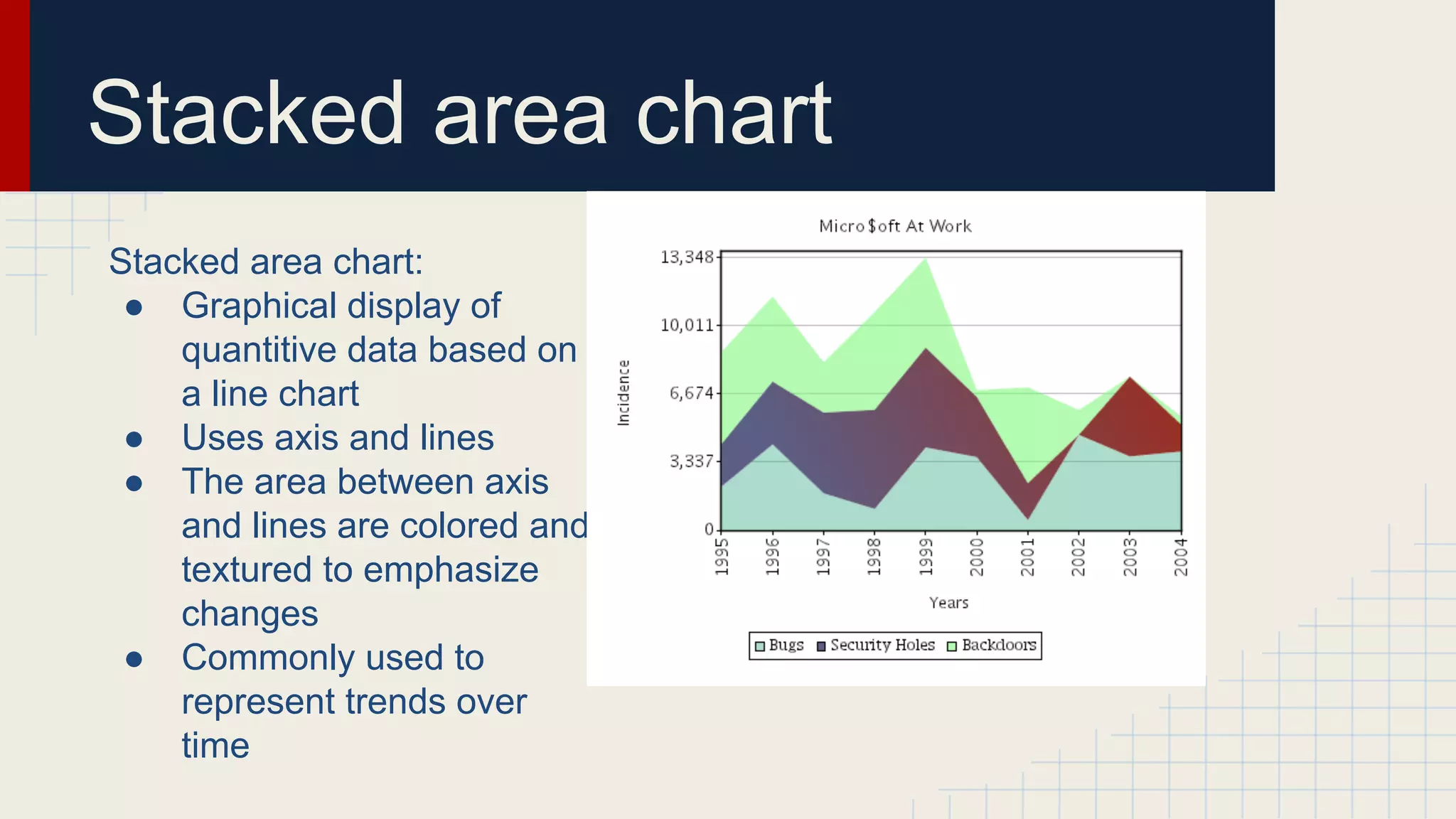
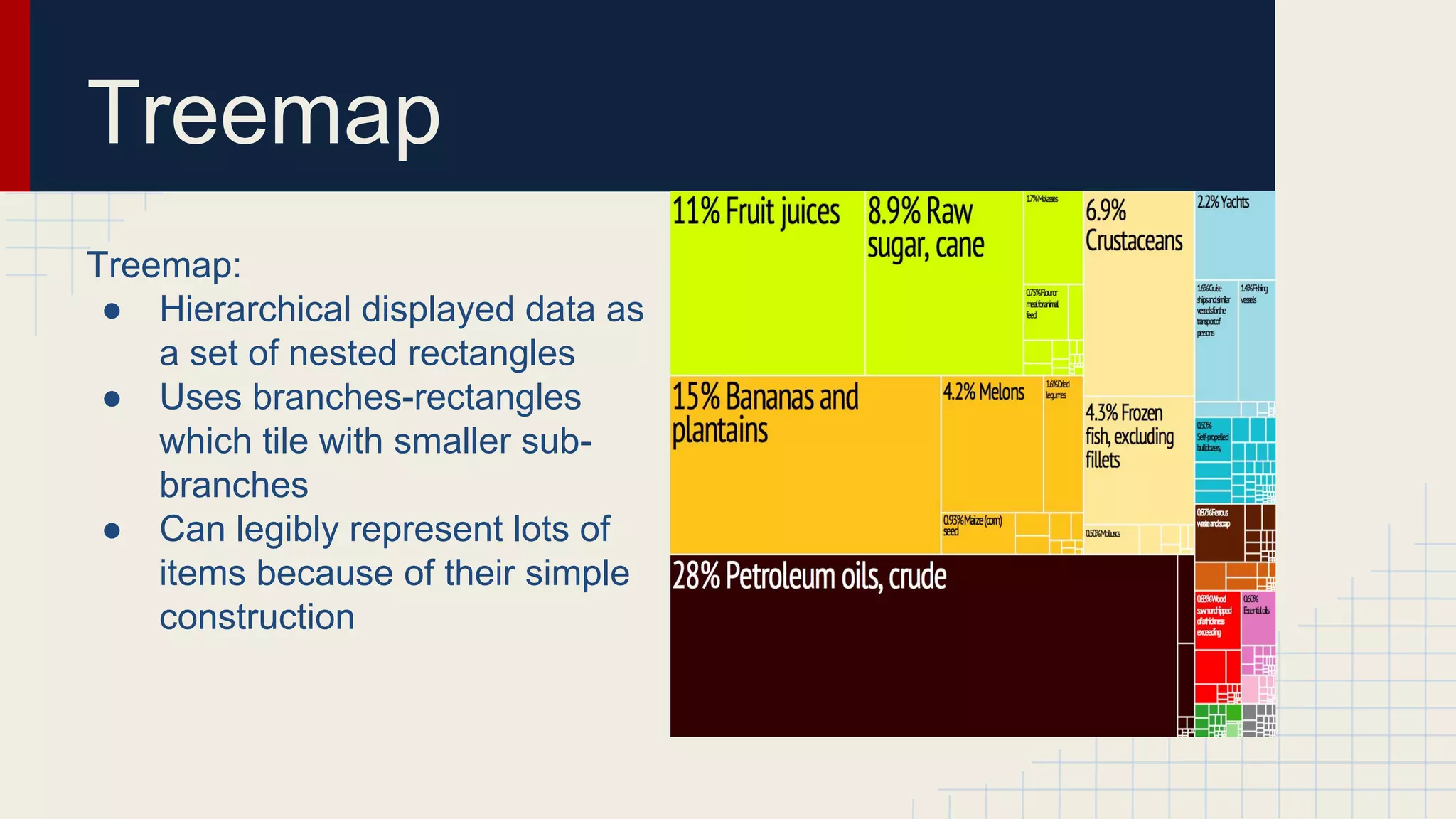
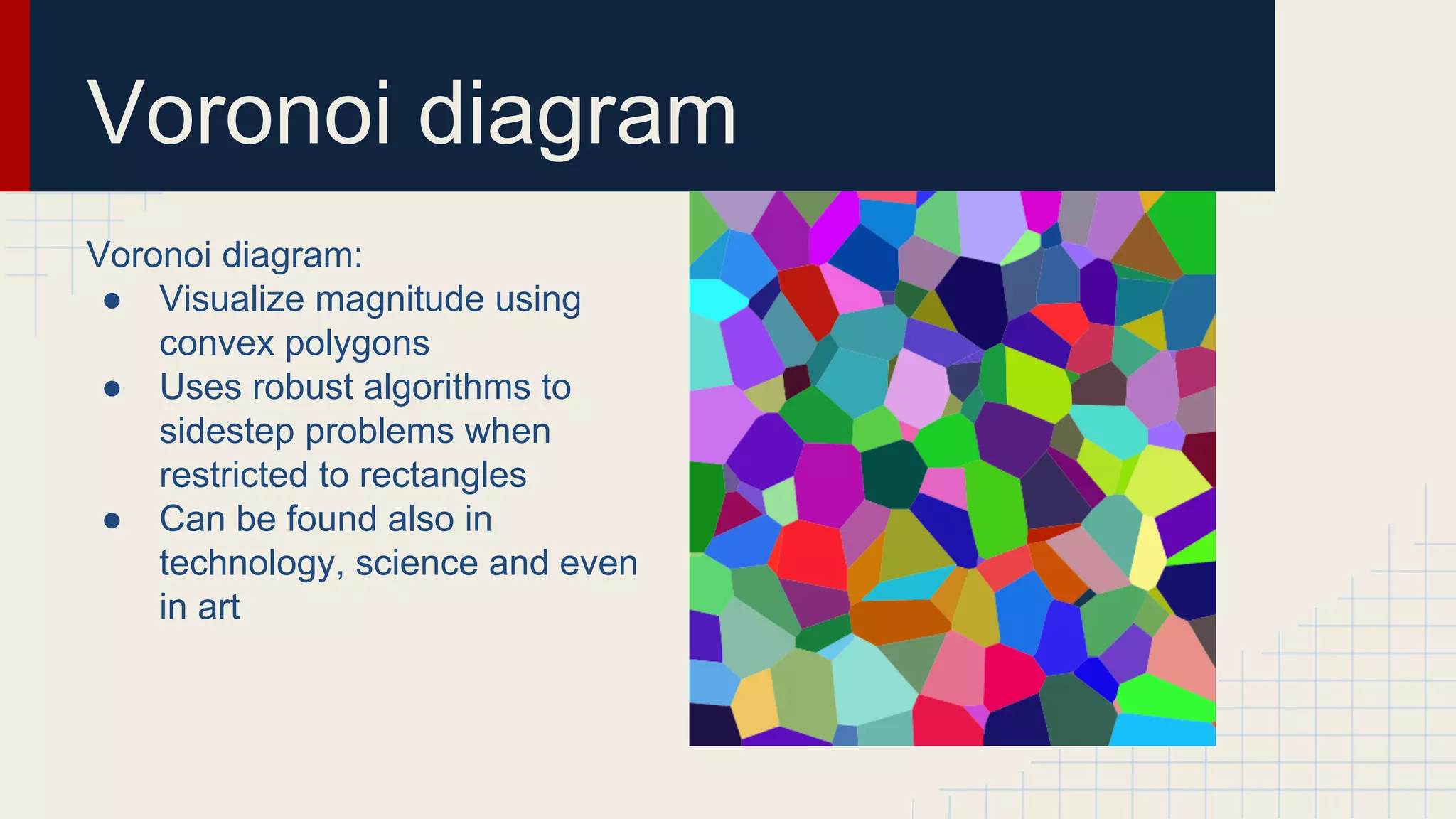
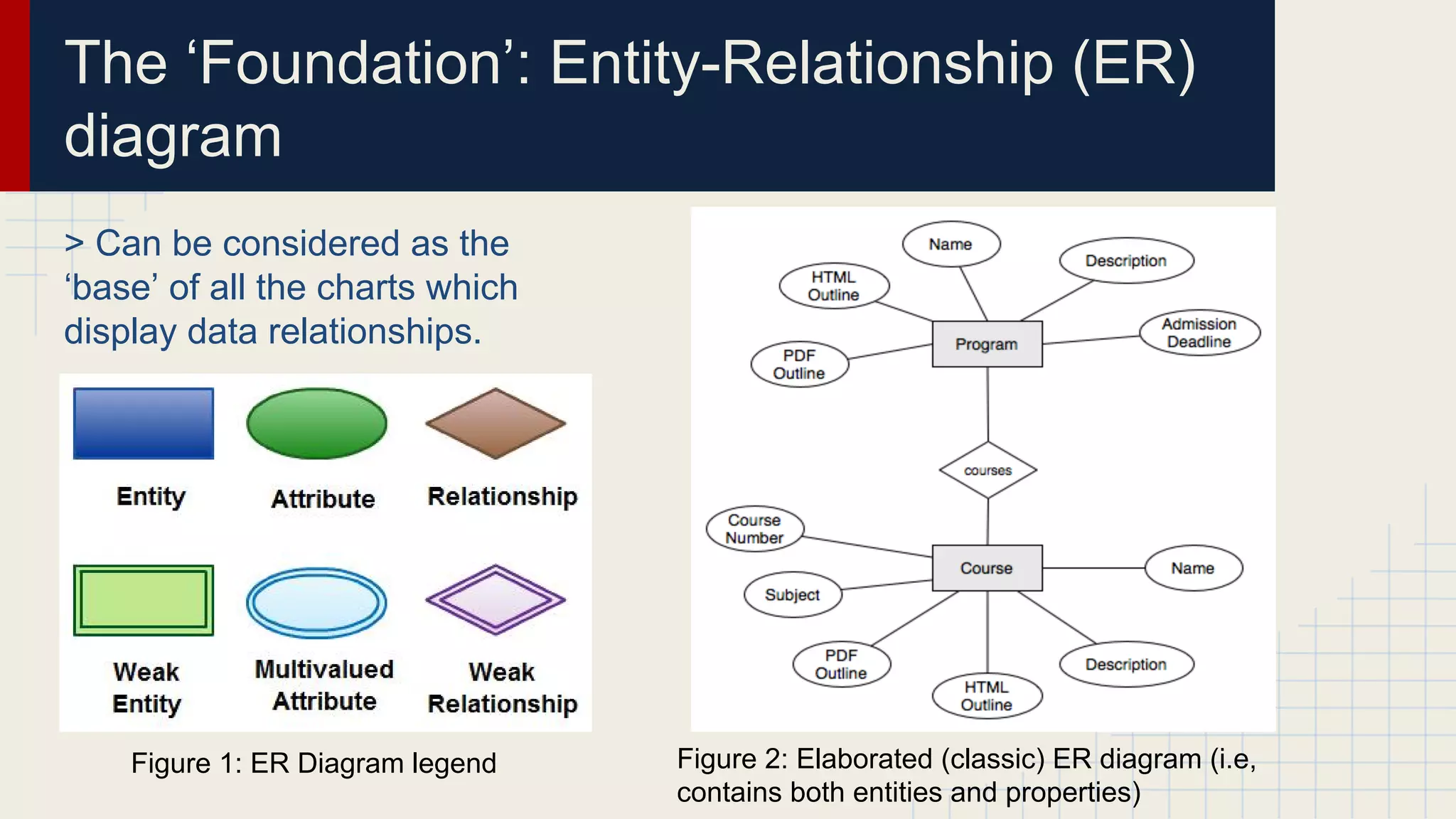
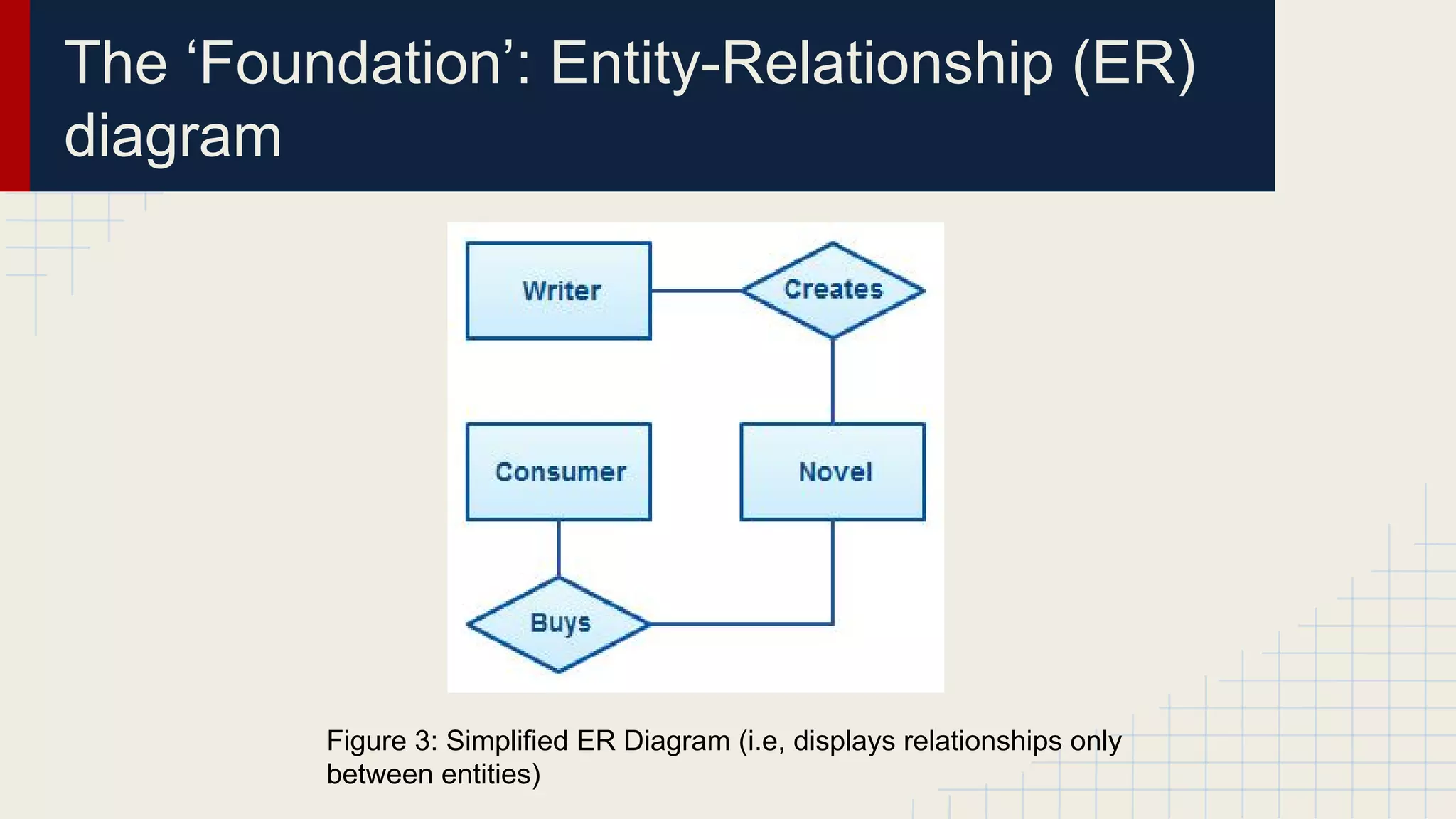
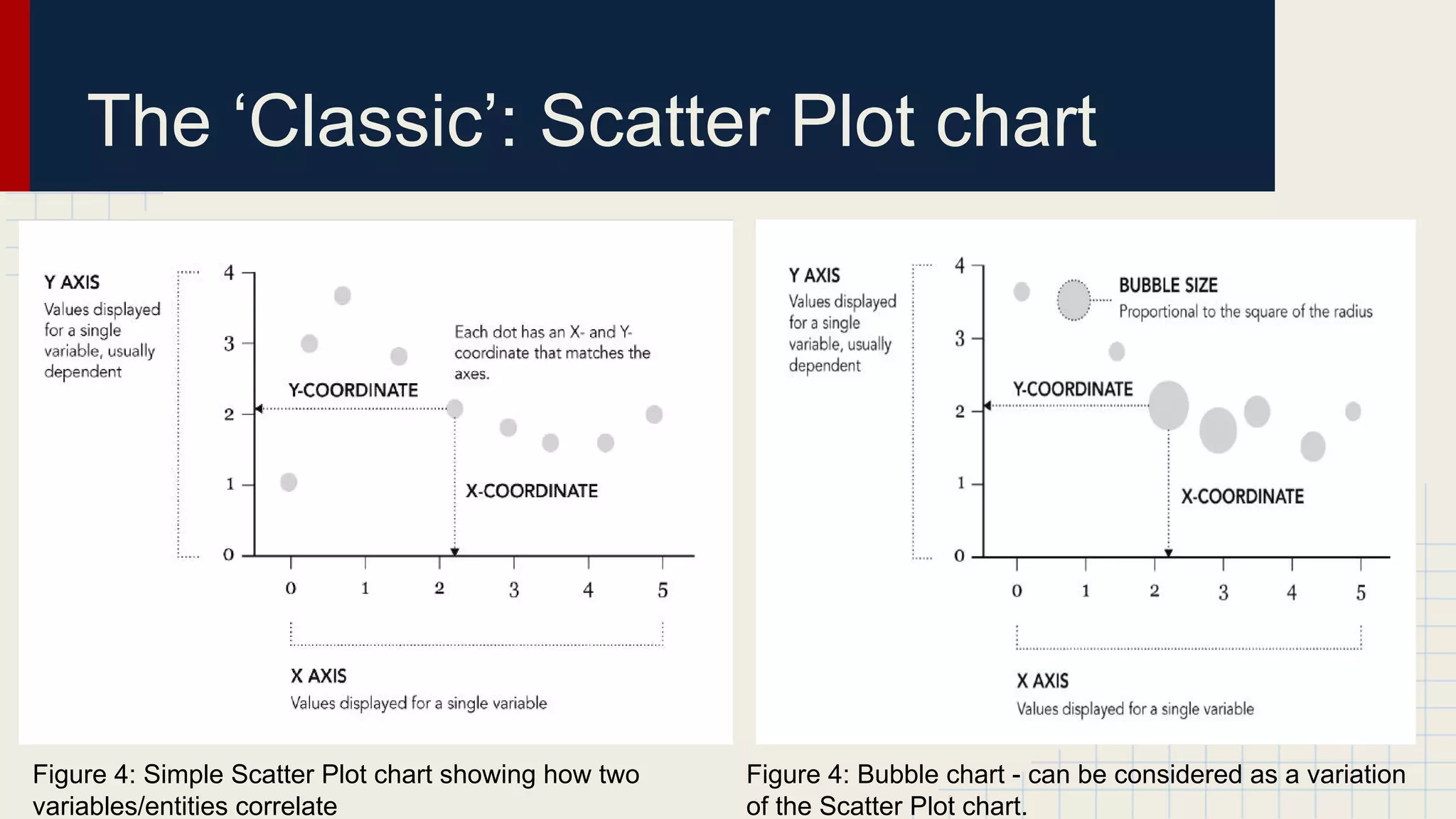
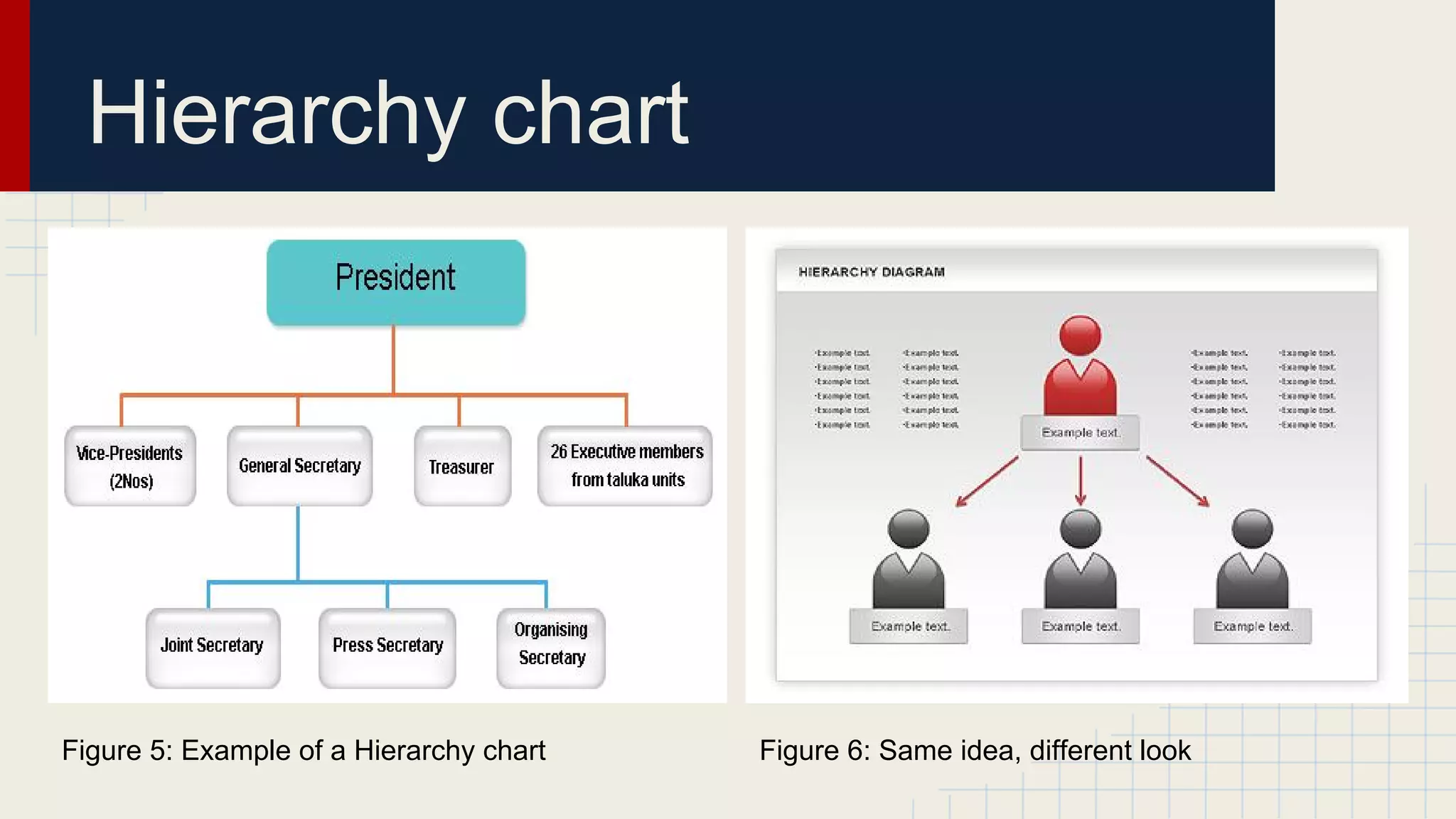
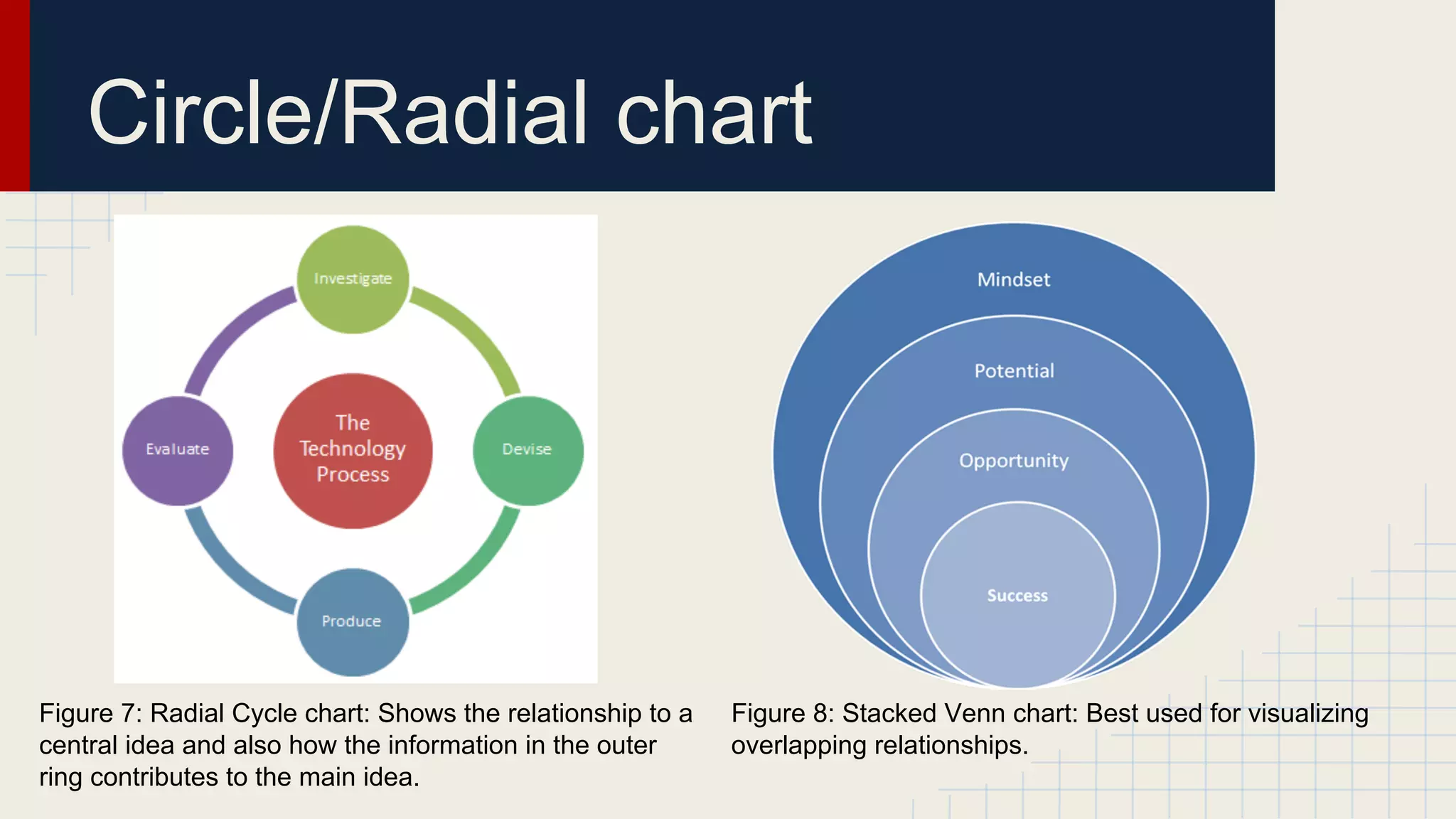
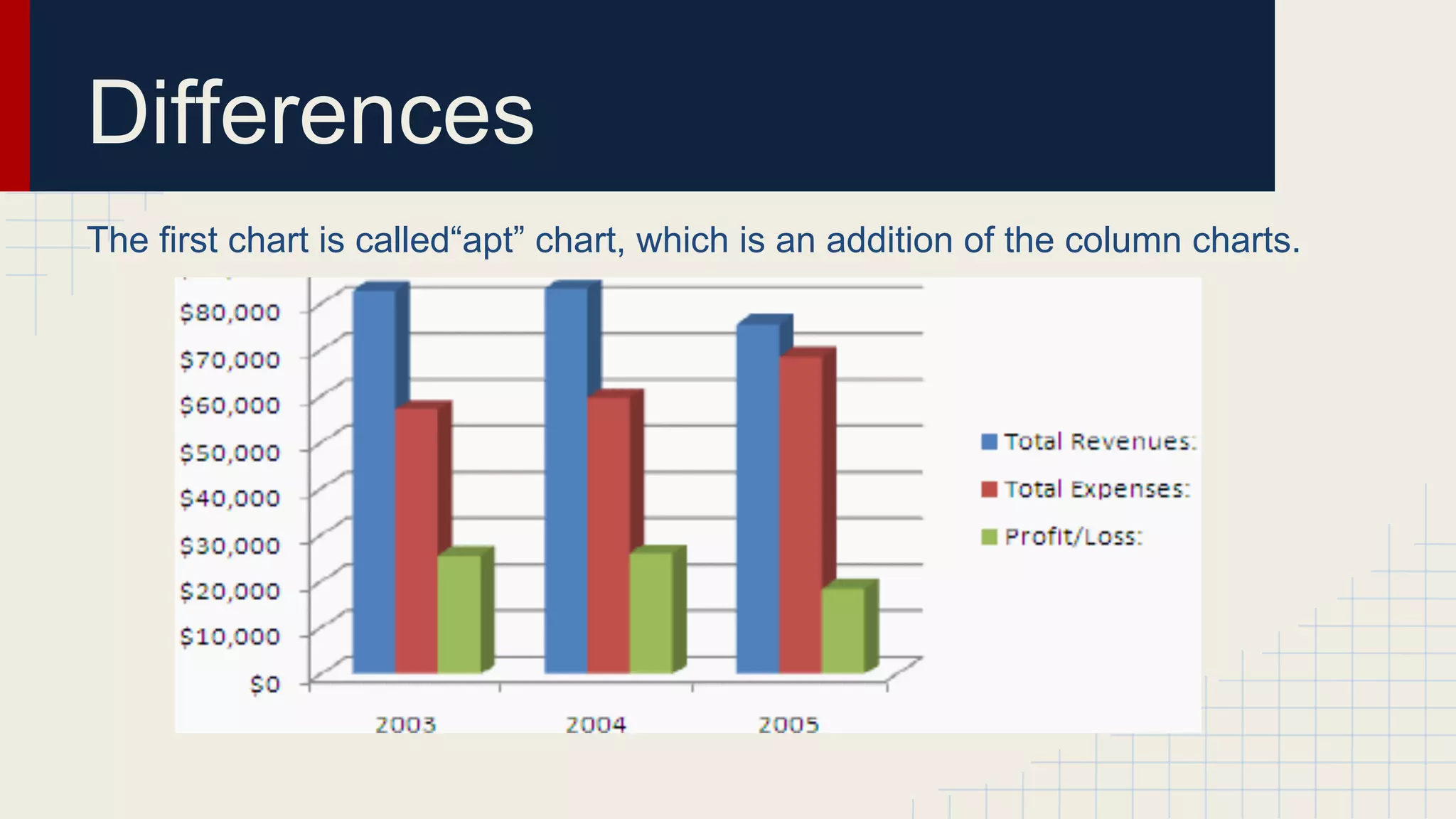
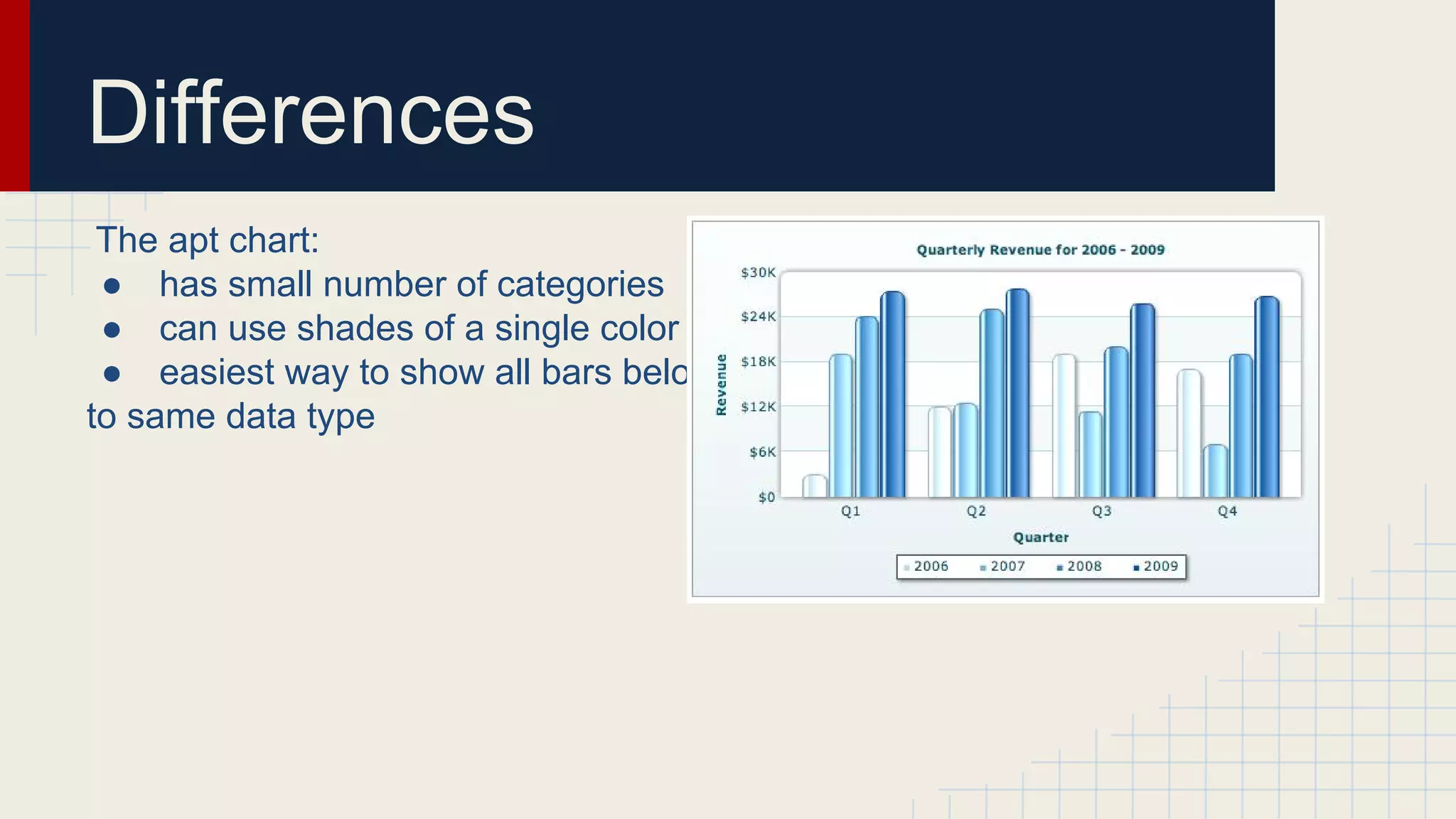
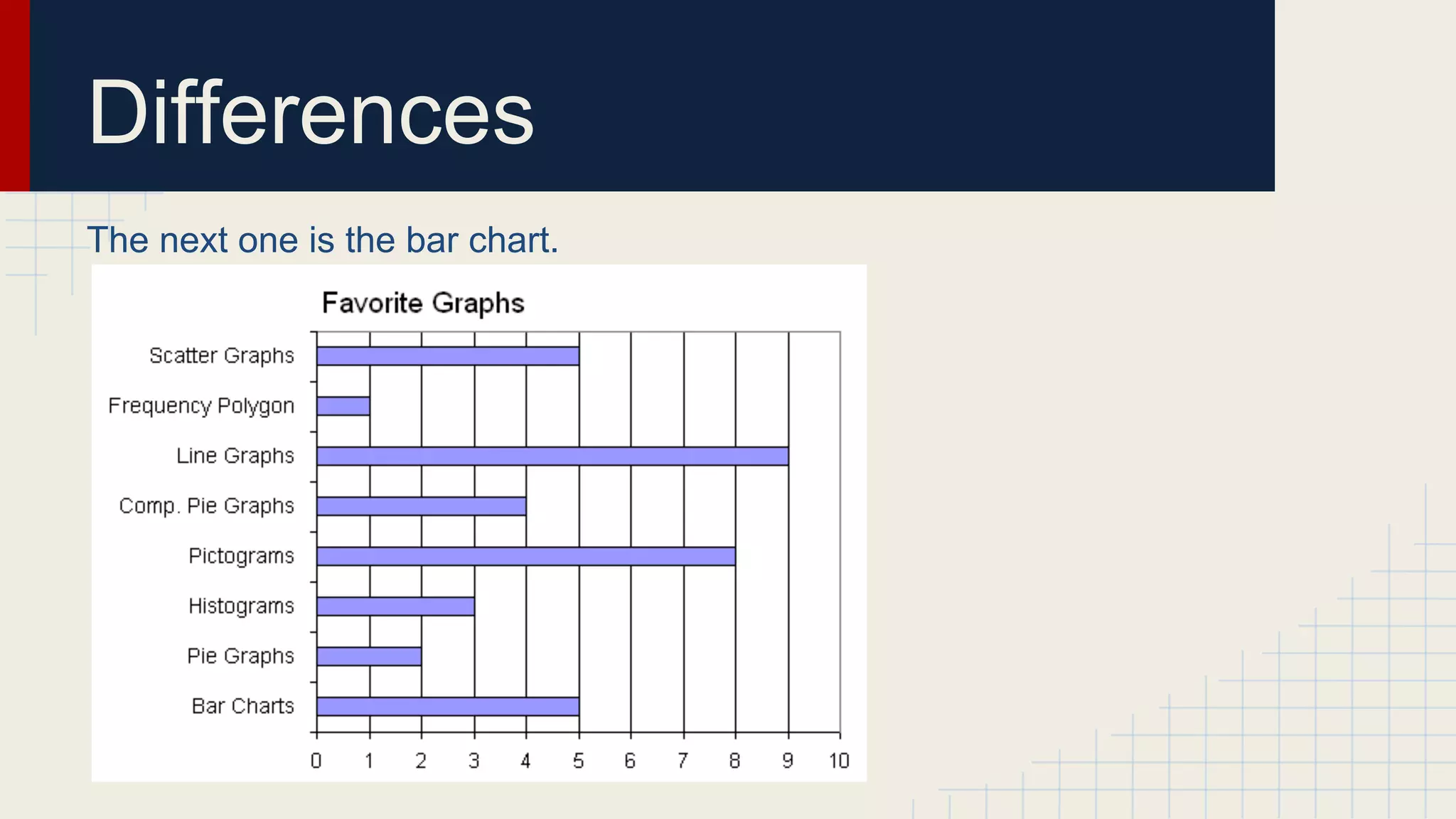
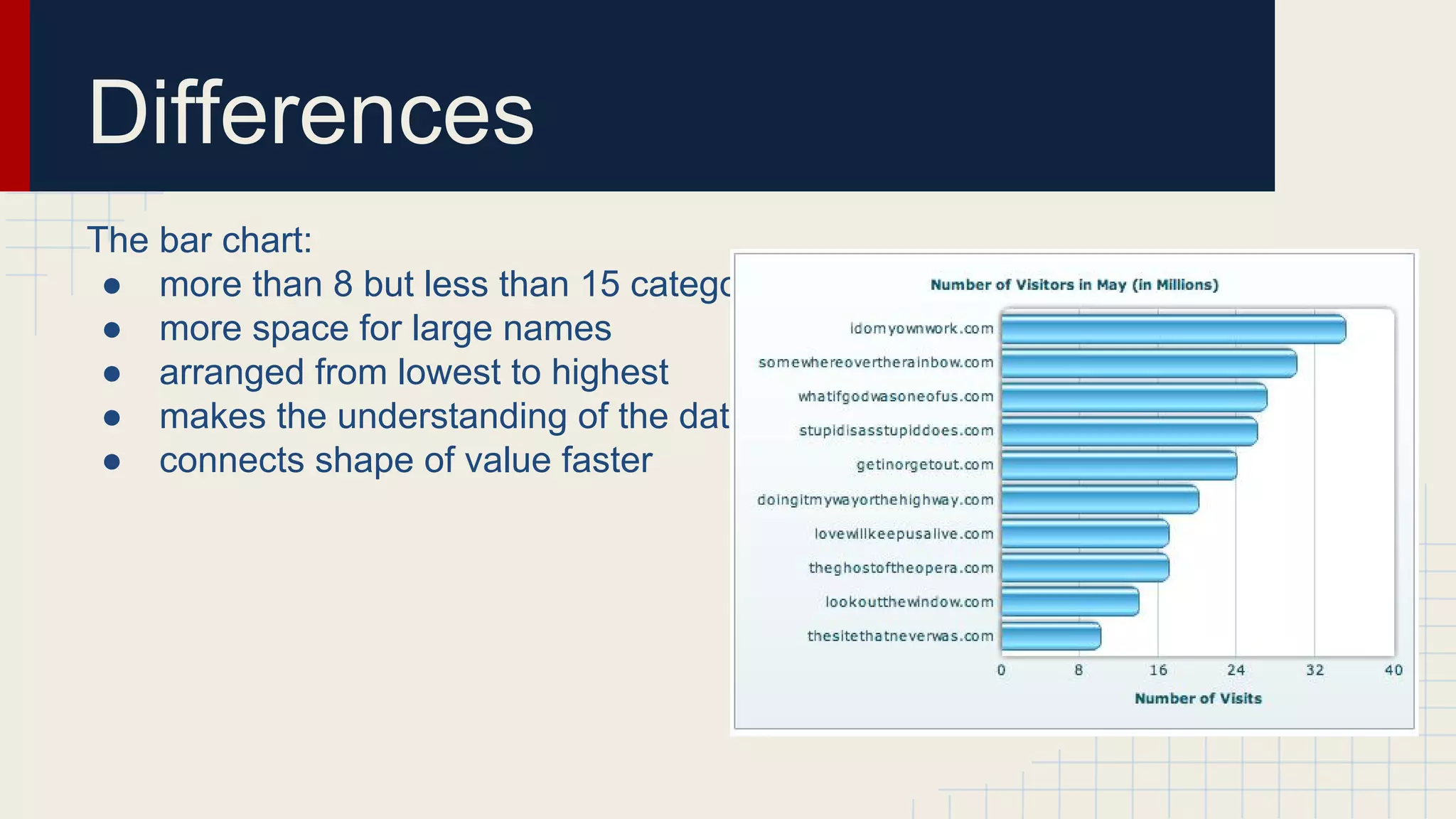
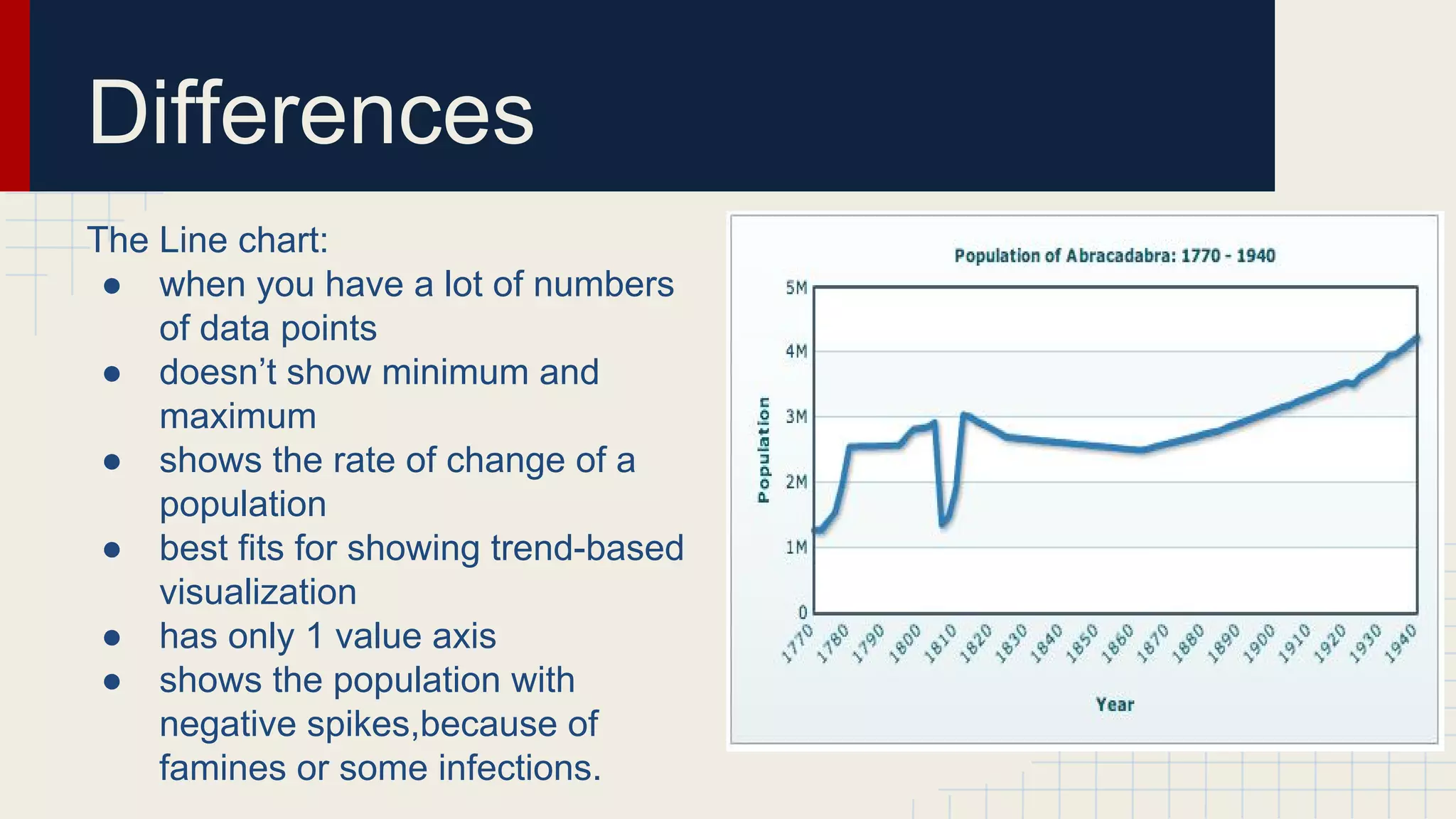
This document provides an overview of data visualization techniques. It discusses patterns over time including some of the earliest known data visualizations. It also covers proportions using charts like pie charts, donut charts and stacked area charts. Relationships are explored through entity relationship diagrams, scatter plots, hierarchy charts and circle/radial charts. Differences between chart types like bar charts and line charts are also examined. Sources for the information are provided.