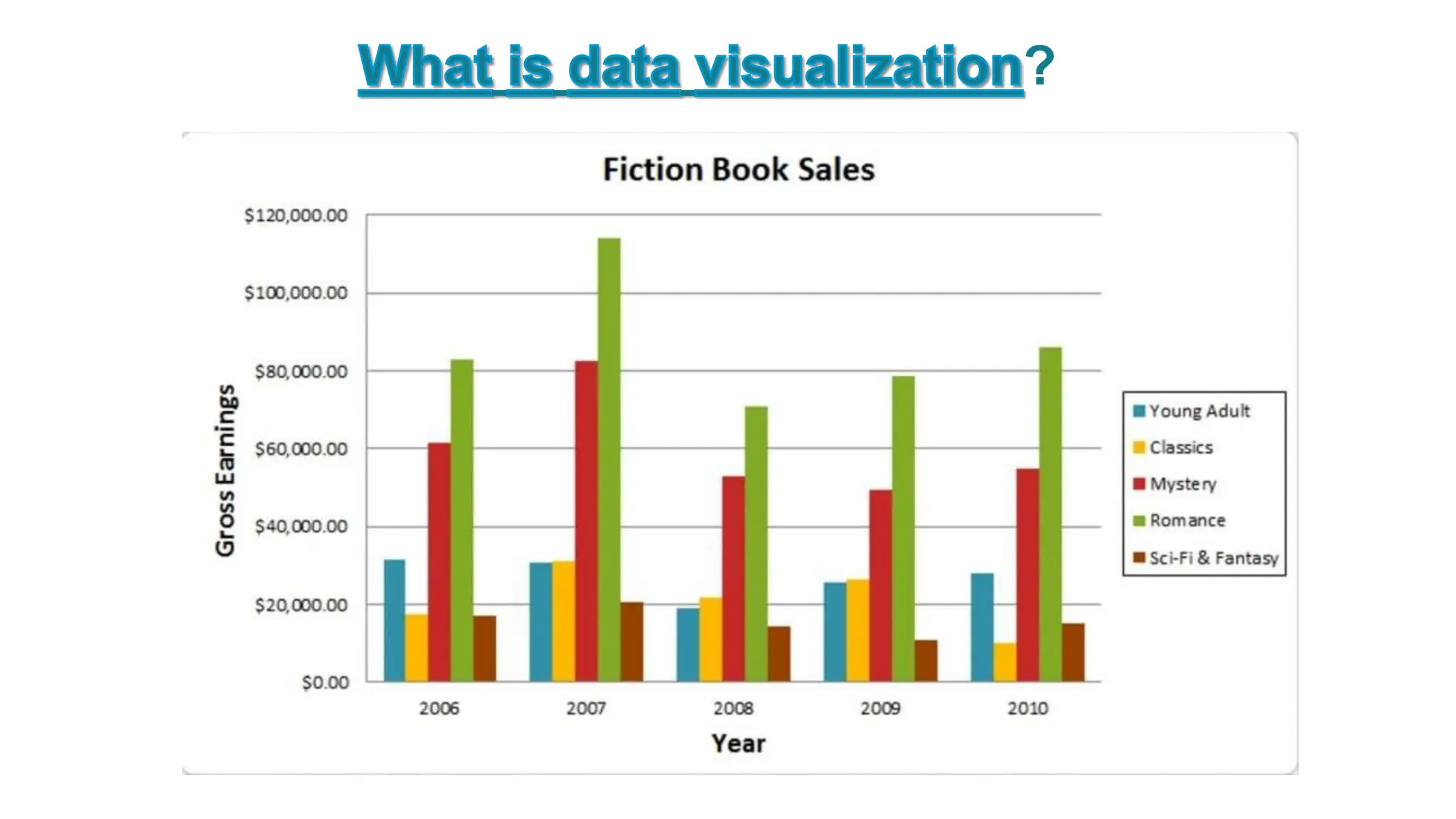
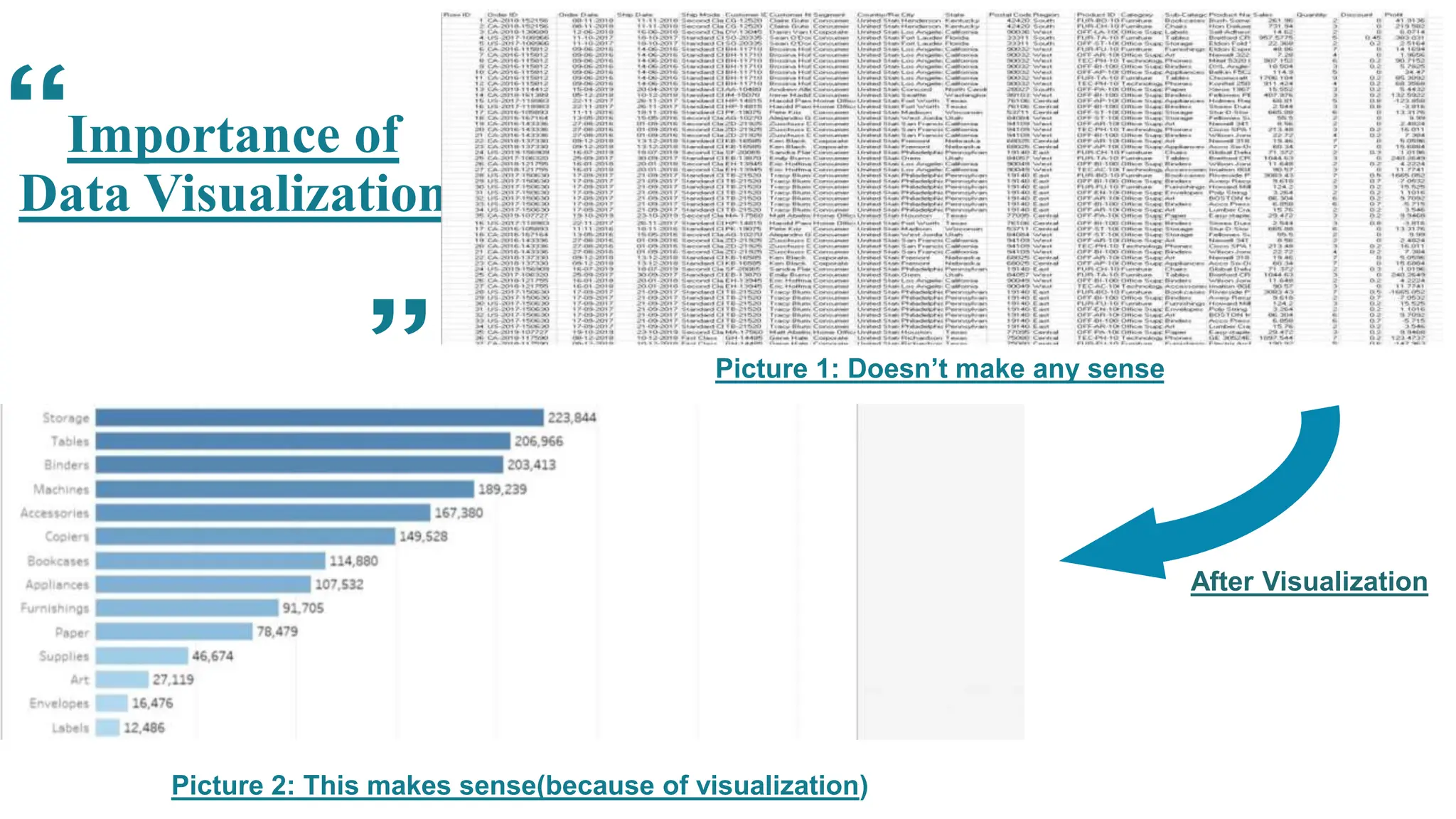
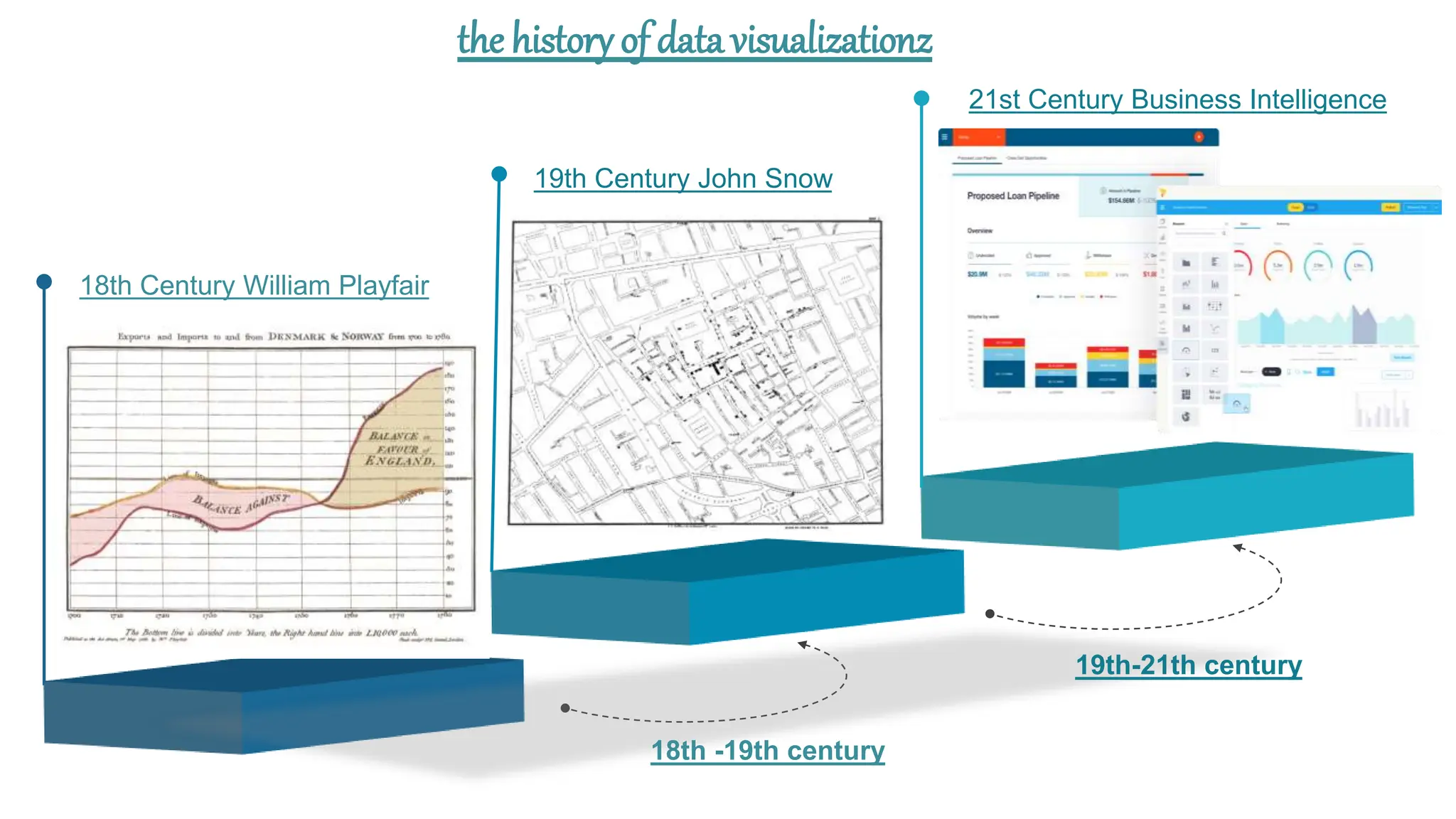
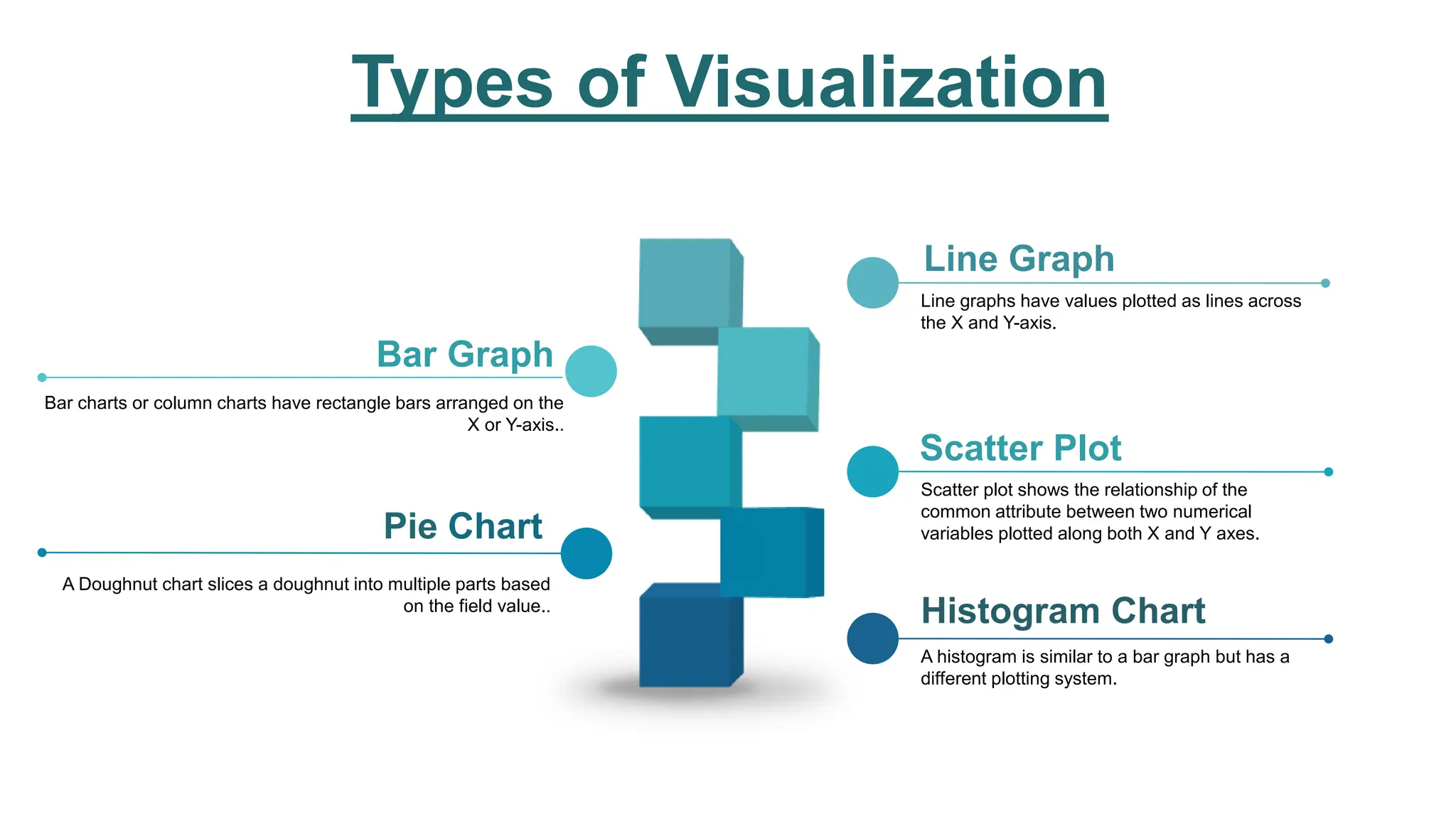
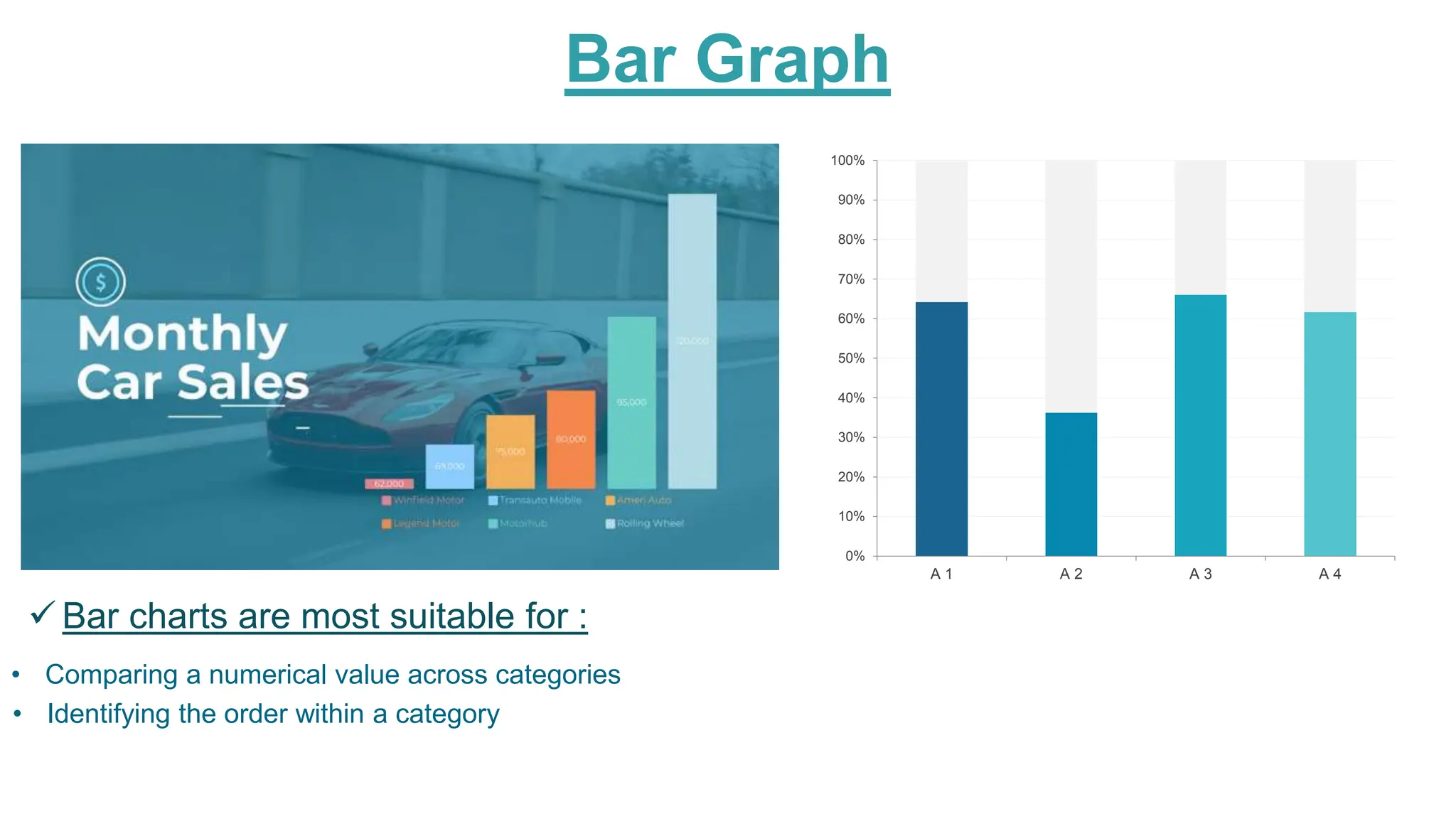
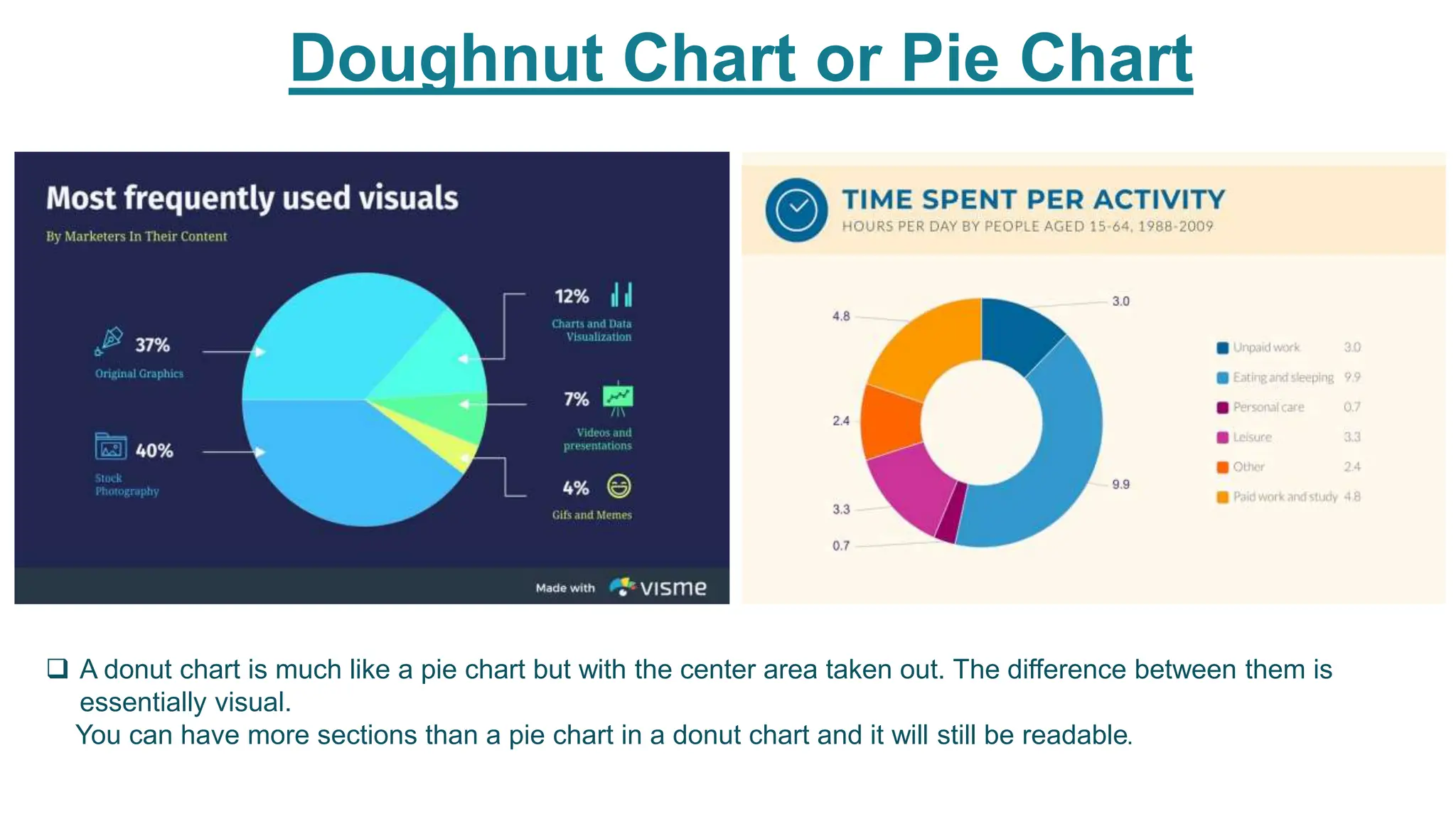
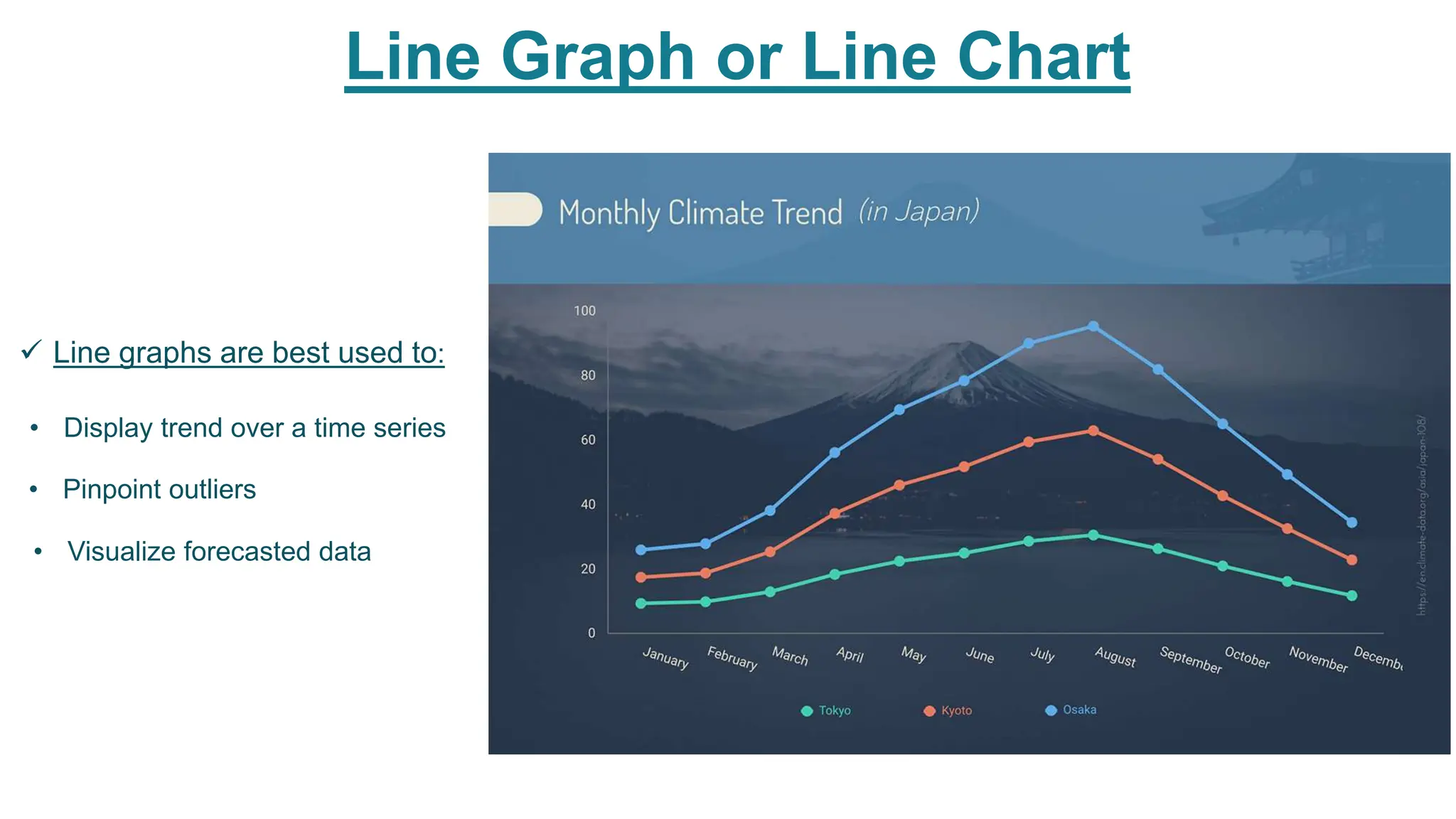
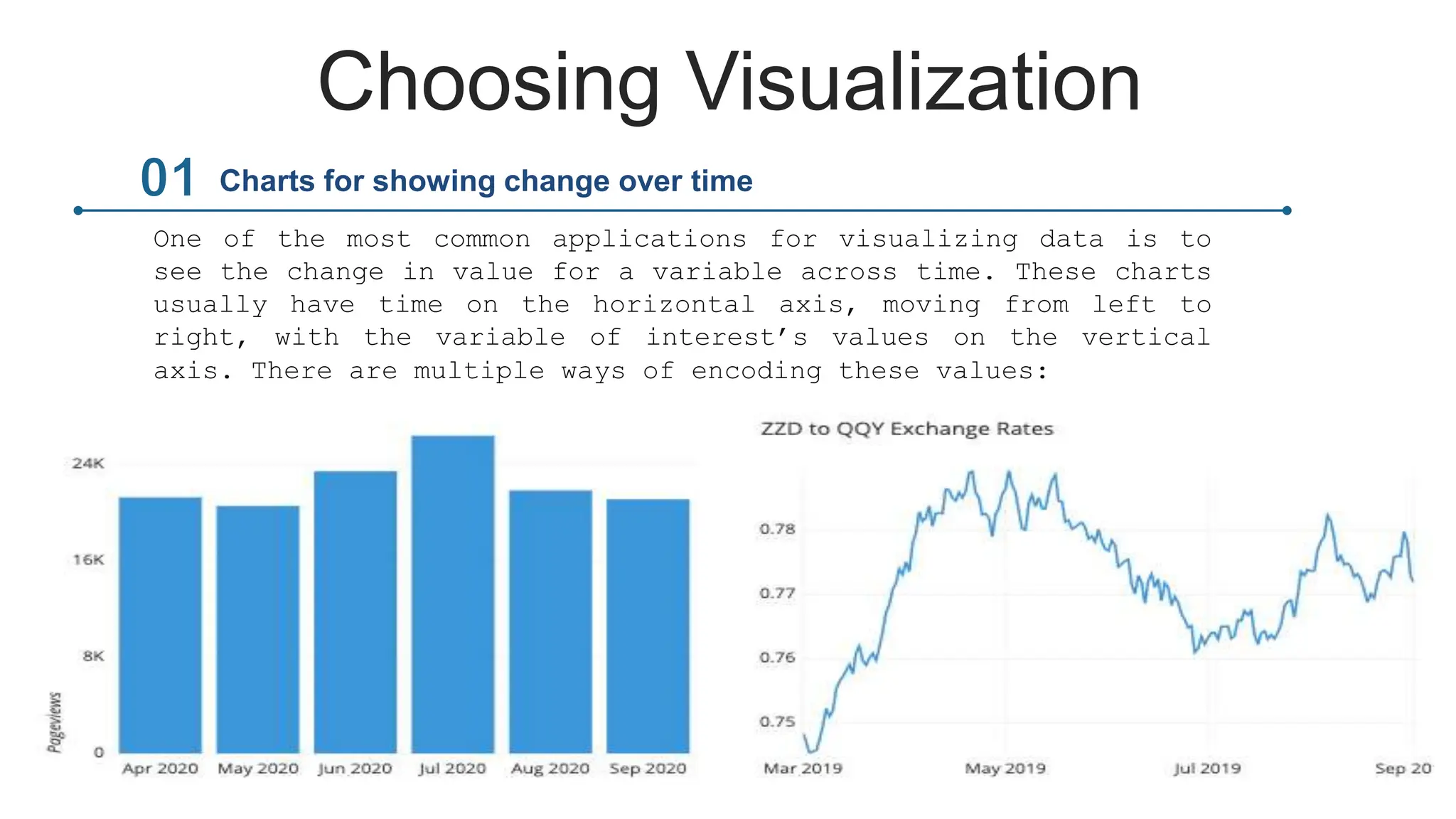
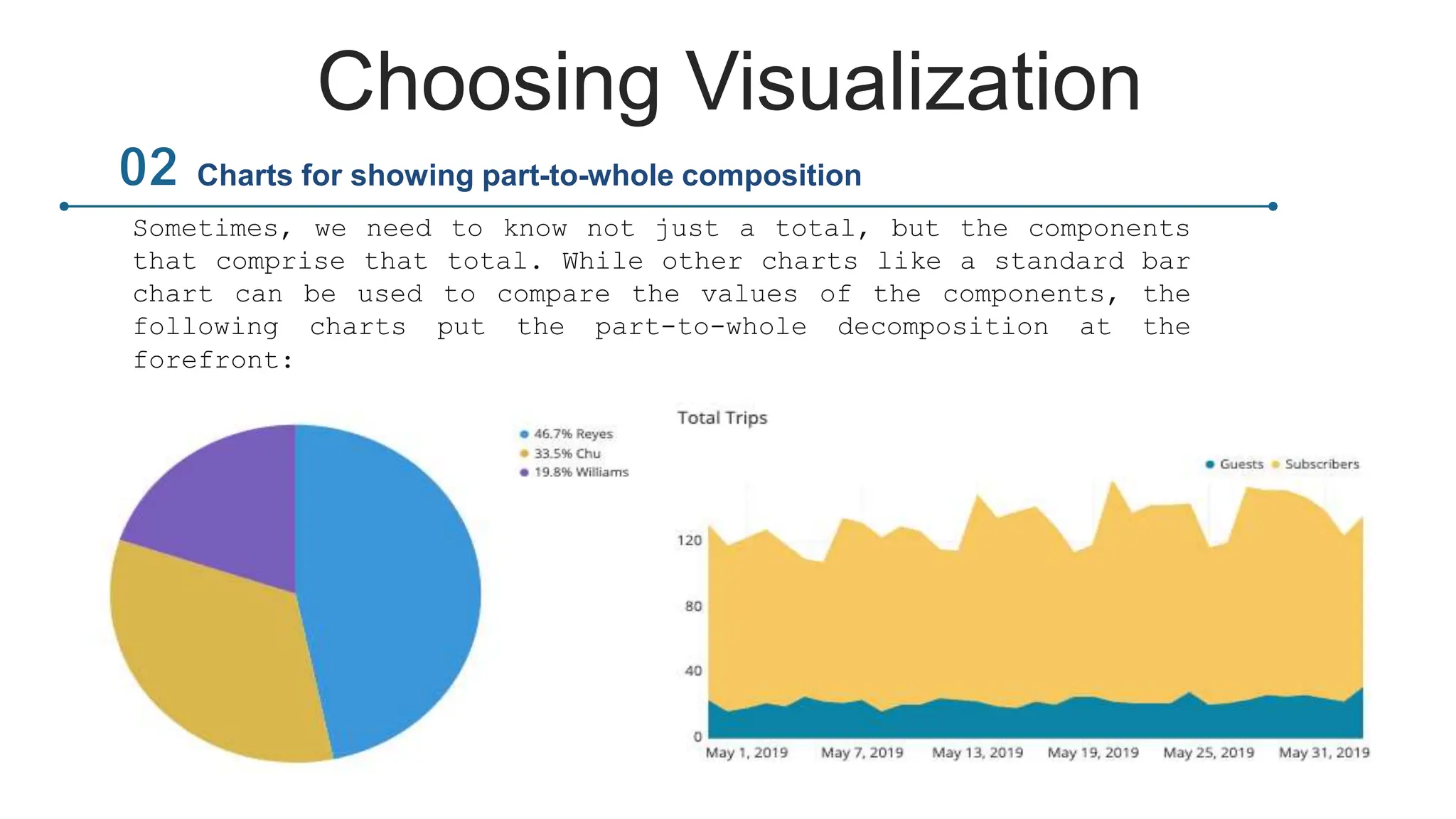
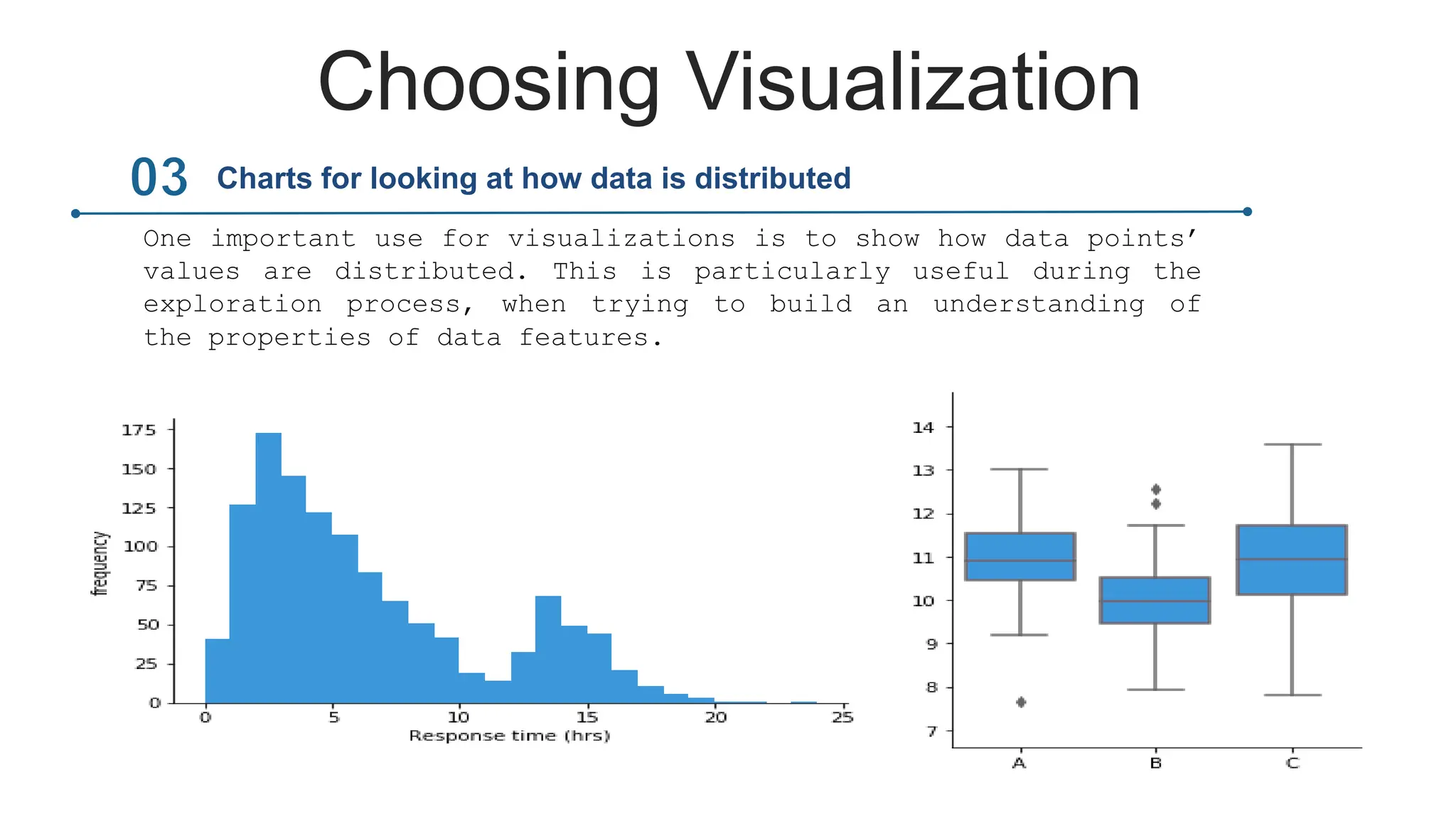
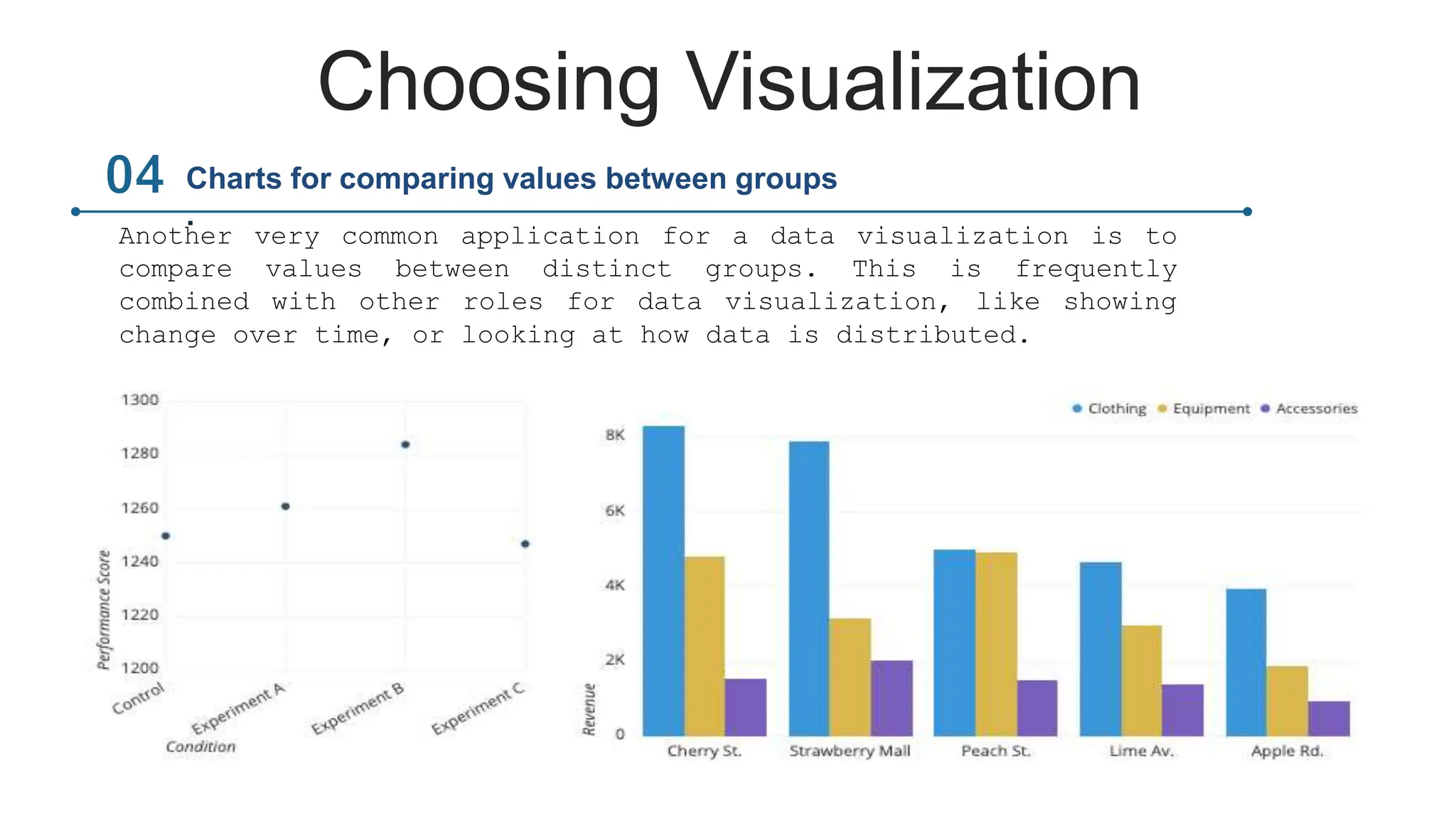
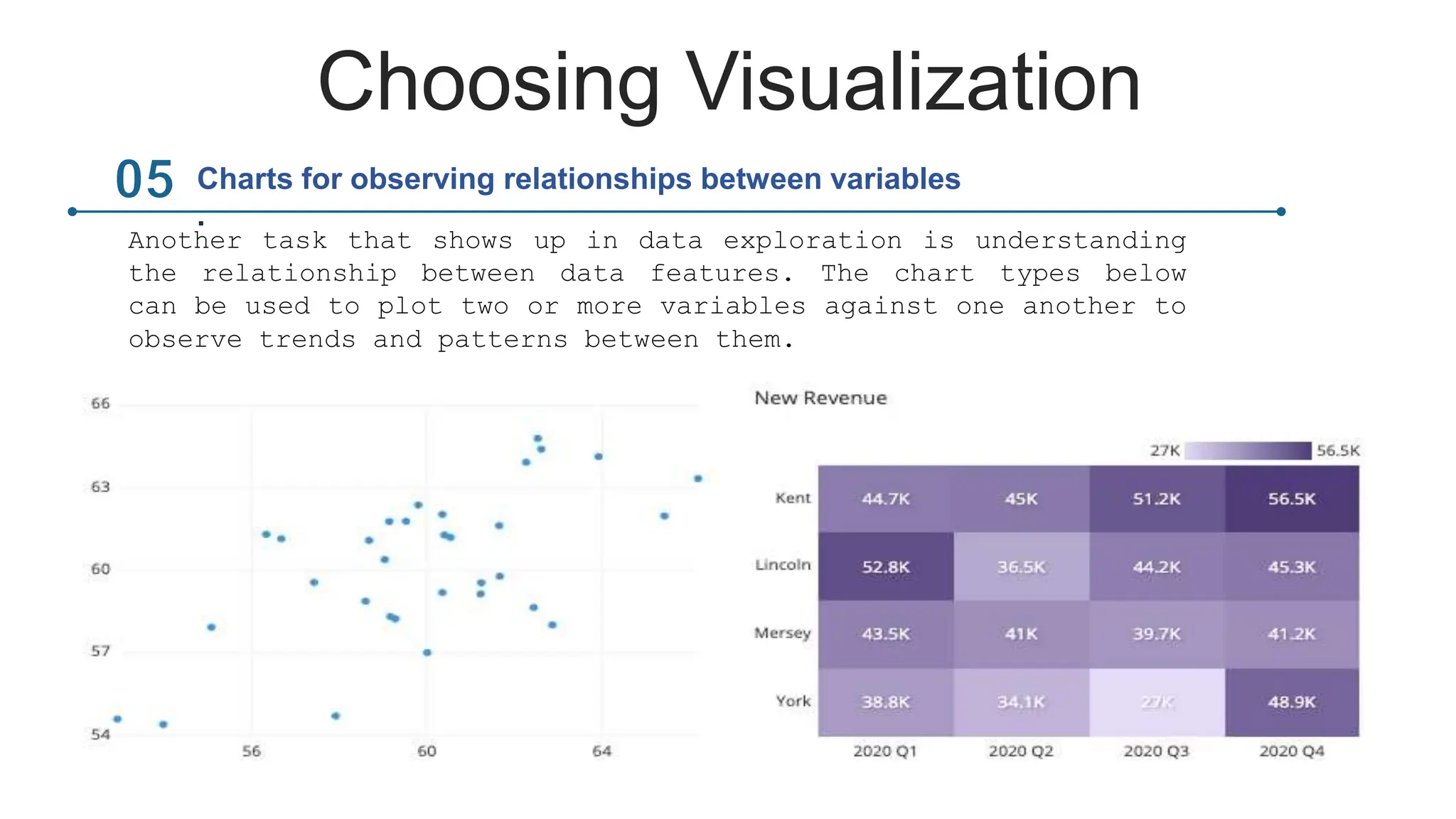
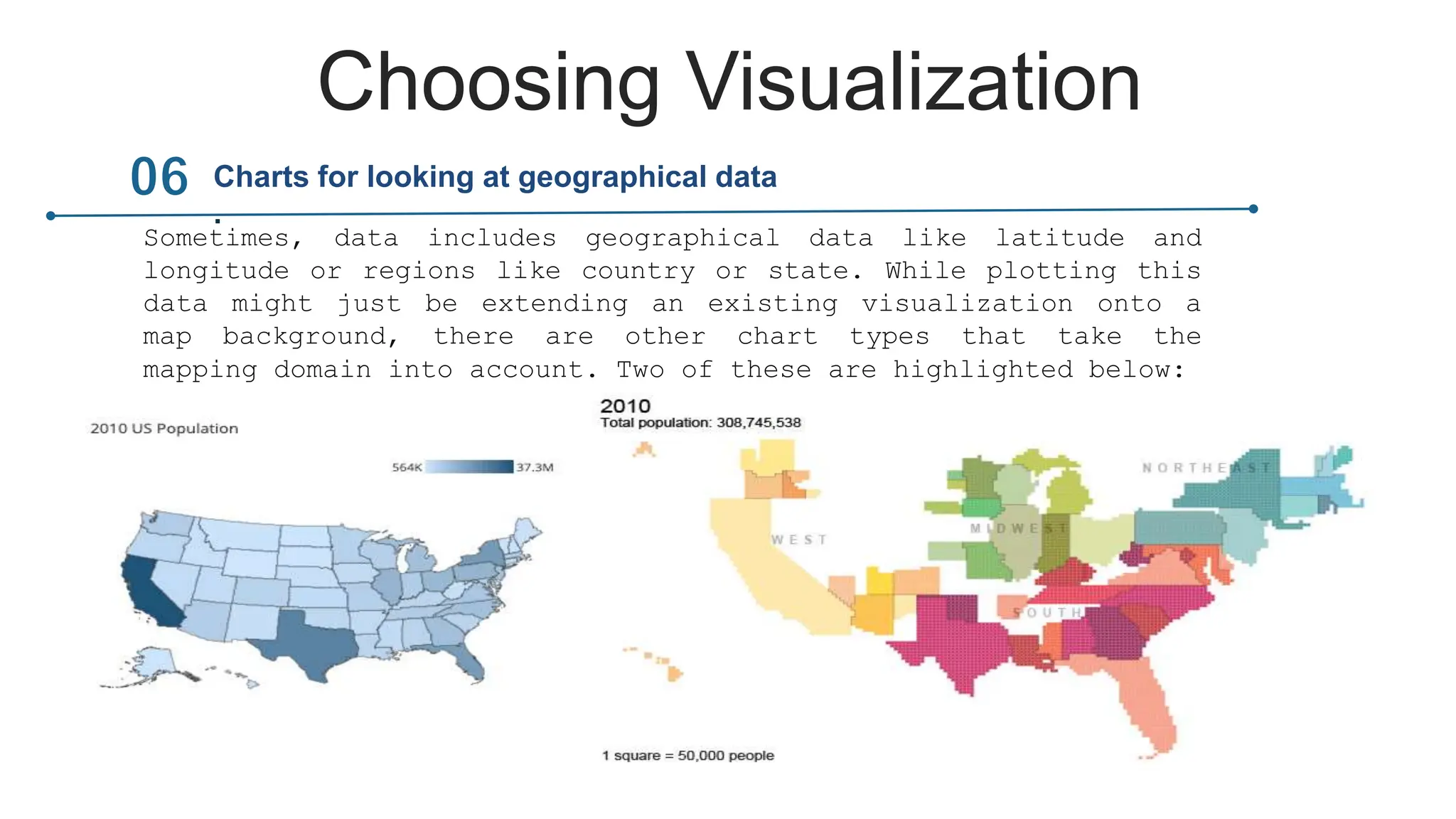
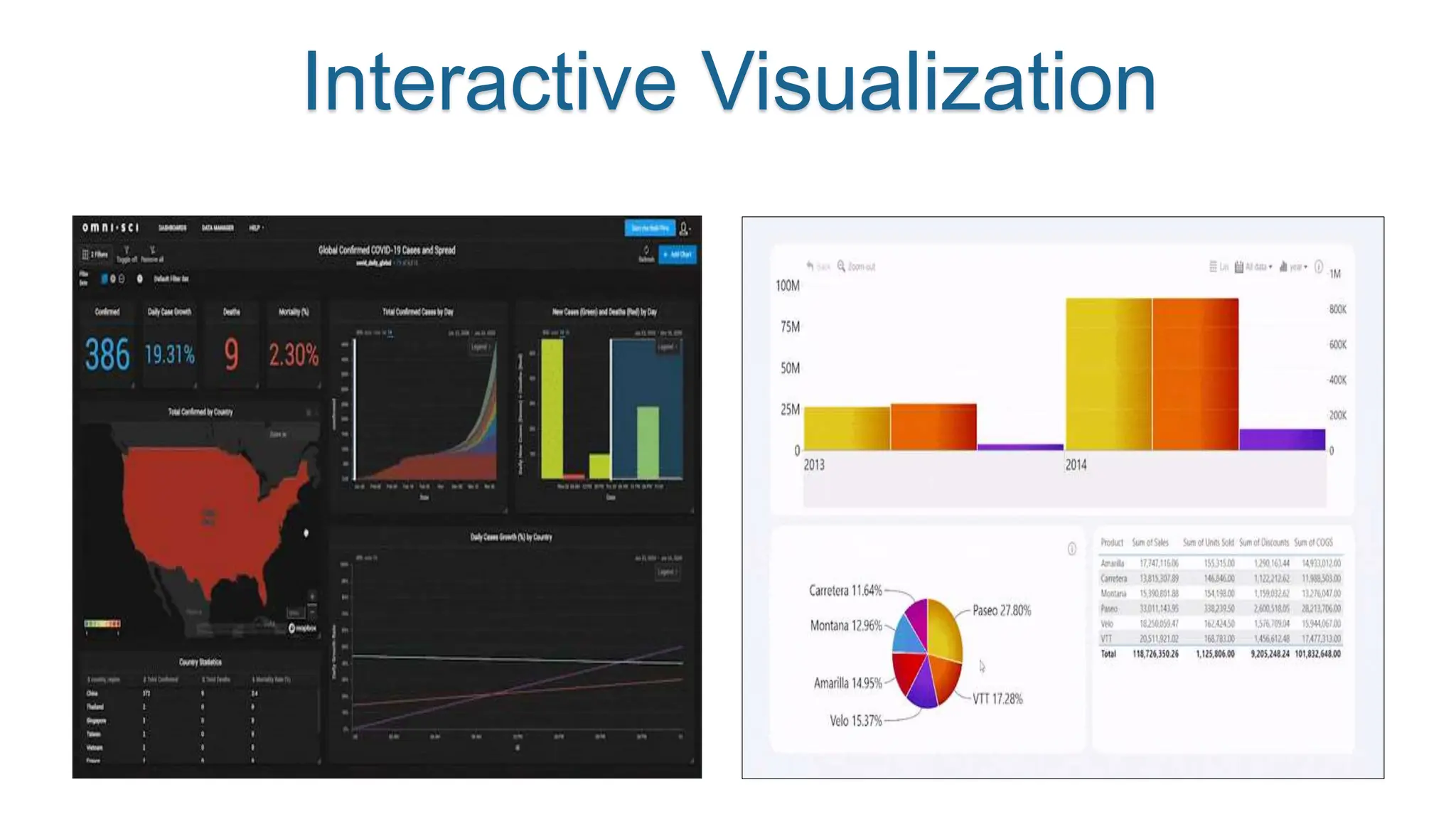
This document provides an overview of data visualization. It discusses the importance of visualization and provides a brief history. It then describes common types of visualizations like line graphs, bar charts, scatter plots and pie/doughnut charts. The document outlines tools for creating visualizations and discusses interactive visualization. It covers challenges and trends in the field, such as interactive visualization becoming more common. The document provides guidance on choosing visualizations based on common roles like showing change over time, part-to-whole compositions, distributions, comparisons and relationships. It concludes with thanks.