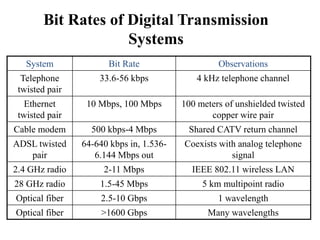
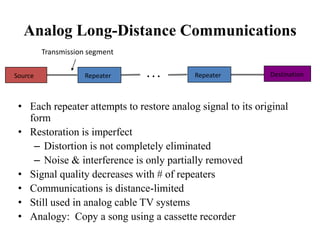
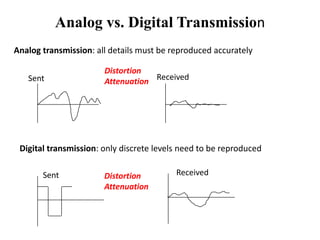
Data transmission rates depend on three main factors: available bandwidth, the signal used, and noise levels. Bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies a channel can pass and is measured in Hertz, while transmission rate is measured in bits per second. Digital data uses discrete states represented by bits, while analog data is continuous. Common digital transmission systems include telephone lines, Ethernet, cable modems, DSL, wireless networks, and optical fiber, with rates ranging from kilobits per second to several gigabits per second. Analog transmission faithfully reproduces all signal details but quality degrades with each repeater, while digital only needs to reproduce discrete levels.