This document discusses various topics related to data communications including:
1. A simplified model of data communications consisting of a source, transmitter, transmission system, receiver and destination.
2. Guided media such as twisted pair, coaxial cable, and optical fiber which have different characteristics like bandwidth and attenuation.
3. Wireless transmission using antennas and frequencies ranging from microwave to satellite to broadcast radio to infrared.
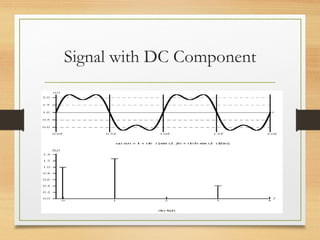
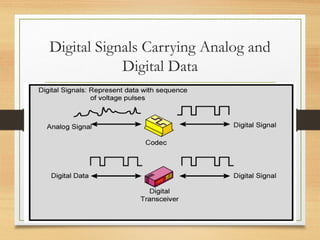
4. Key concepts in data communications including analog vs. digital signals, bandwidth, attenuation, noise and error rates which impact system design factors and capacity.