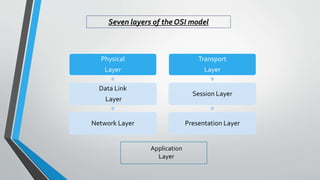
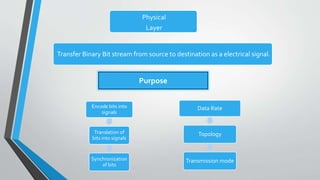
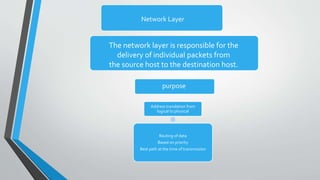
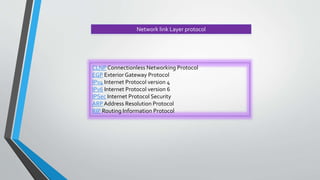
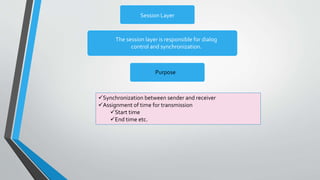
The document outlines the OSI model, introduced by the International Standards Organization (ISO) in the late 1970s, detailing its seven layers: physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application. Each layer has specific functions and associated protocols, facilitating error-free data transmission, routing, dialog control, and user service interactions. The document provides a comprehensive overview of the purpose of each layer and examples of protocols utilized within them.