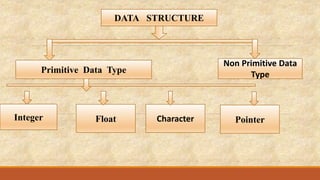
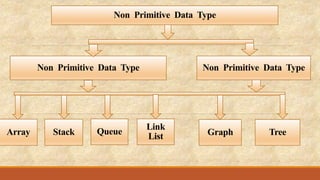
This document introduces different data structures. It defines data structures as logical models for organizing data that are important for algorithm development and program implementation. It classifies data structures into primitive and non-primitive types. Primitive types include basic data like integers, while non-primitive types are more complex structures like arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues that organize groups of data. Key non-primitive data structures are then defined, including their purposes and common operations.





![Array
ARRAY is a set of finite collection of homogeneous or same types of data items.
Which means that we can store only one type of data in the array.
We can declare array as : int ARR[14]
Int specifies the type of data we want to store in array.
ARR is the name of ARRAY.
The number inside the square bracket denotes the number of items or elements
stored in ARRAY. It is called as the length or size of ARRAY.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure2-191017090115/85/Introduction-to-data-structure-9-320.jpg)

![Stack
A stack is a linear structure in which items are added or removed only at one end.
It is also known as “LAST IN FIRST OUT” [LIFO] lists.
Stack is also known as “PILES” and “ PUSH DOWN ” lists.
OPERATION ASSOCIATED WITH STACK
1. PUSH: It is used to insert an element into stack.
2. POP: It is used to remove or delete an element from a stack.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure2-191017090115/85/Introduction-to-data-structure-11-320.jpg)

![Queue
A queue is also called as FIRST IN FIRST OUT [FIFO] system.
It is a linear list in which deletion can take place only at one end of the list i.e.
“FRONT” of the list
In queue Insertion can take place only at other end of the list. i.e. “REAR”
Figure : Array Representation Of Queue
AAA BBB CCC …………DDD
1 32 4 5 N
Front=1
Rear = 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontodatastructure2-191017090115/85/Introduction-to-data-structure-13-320.jpg)
