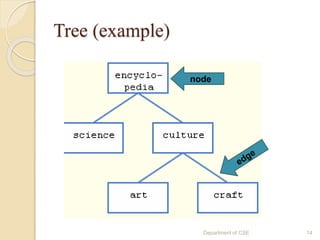
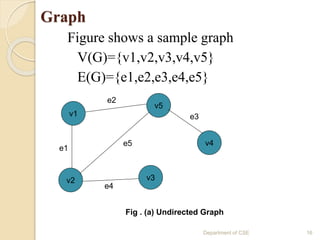
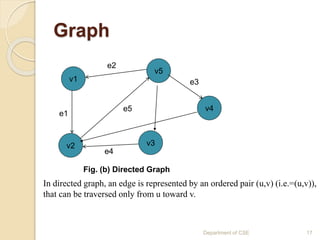
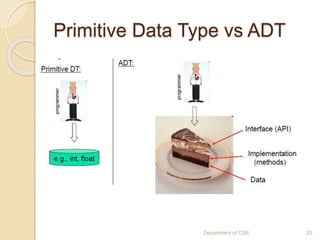
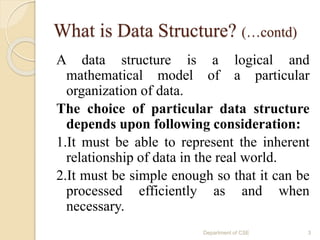
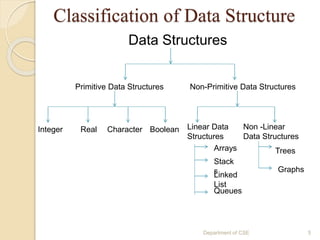
The document provides an introduction to data structures, defining them as ways to efficiently store and organize data in computers. It classifies data structures into primitive and non-primitive types, and further divides them into linear and non-linear structures, covering examples such as arrays, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Additionally, the document discusses various operations associated with data structures, including creation, insertion, deletion, traversal, searching, sorting, and merging.


![Array & Linked List
Department of CSE 8
[0] [1] [2]
A B CArray
linked
A B CLinked list
Linked lists are unbounded
(maximum number of items limited only by memory)
node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1introduction-191021211508/85/Introduction-to-data-structure-ppt-8-320.jpg)