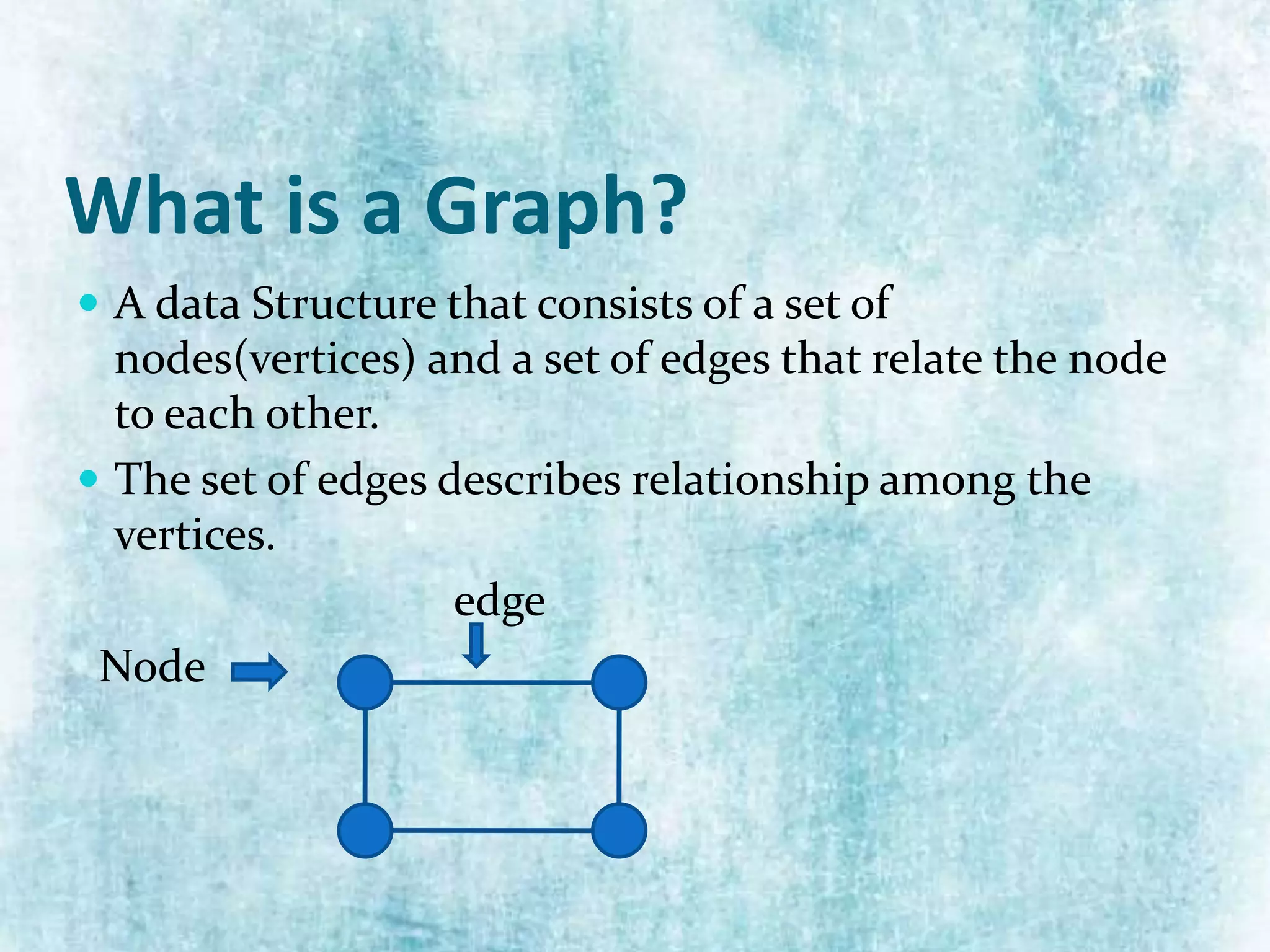
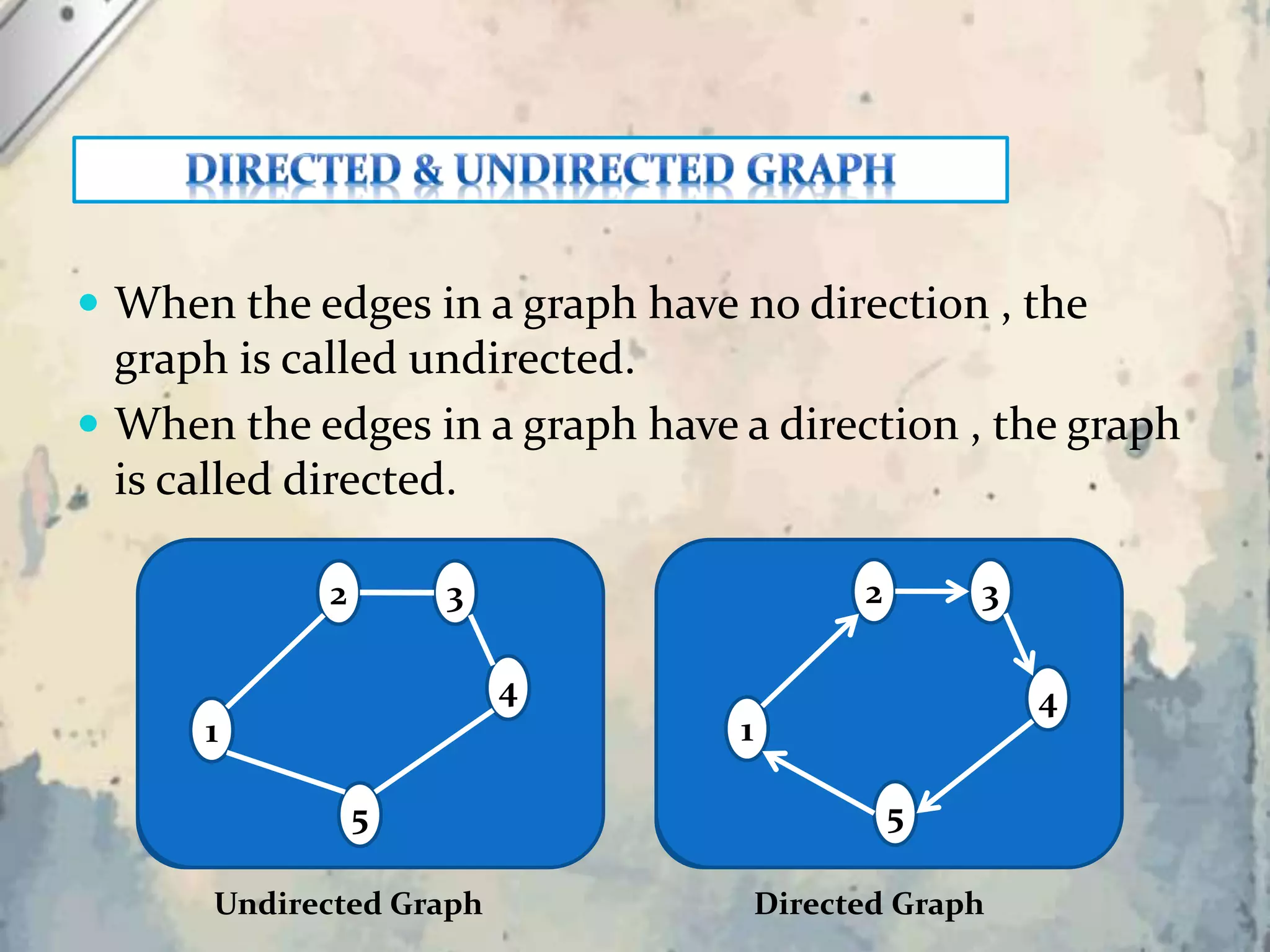
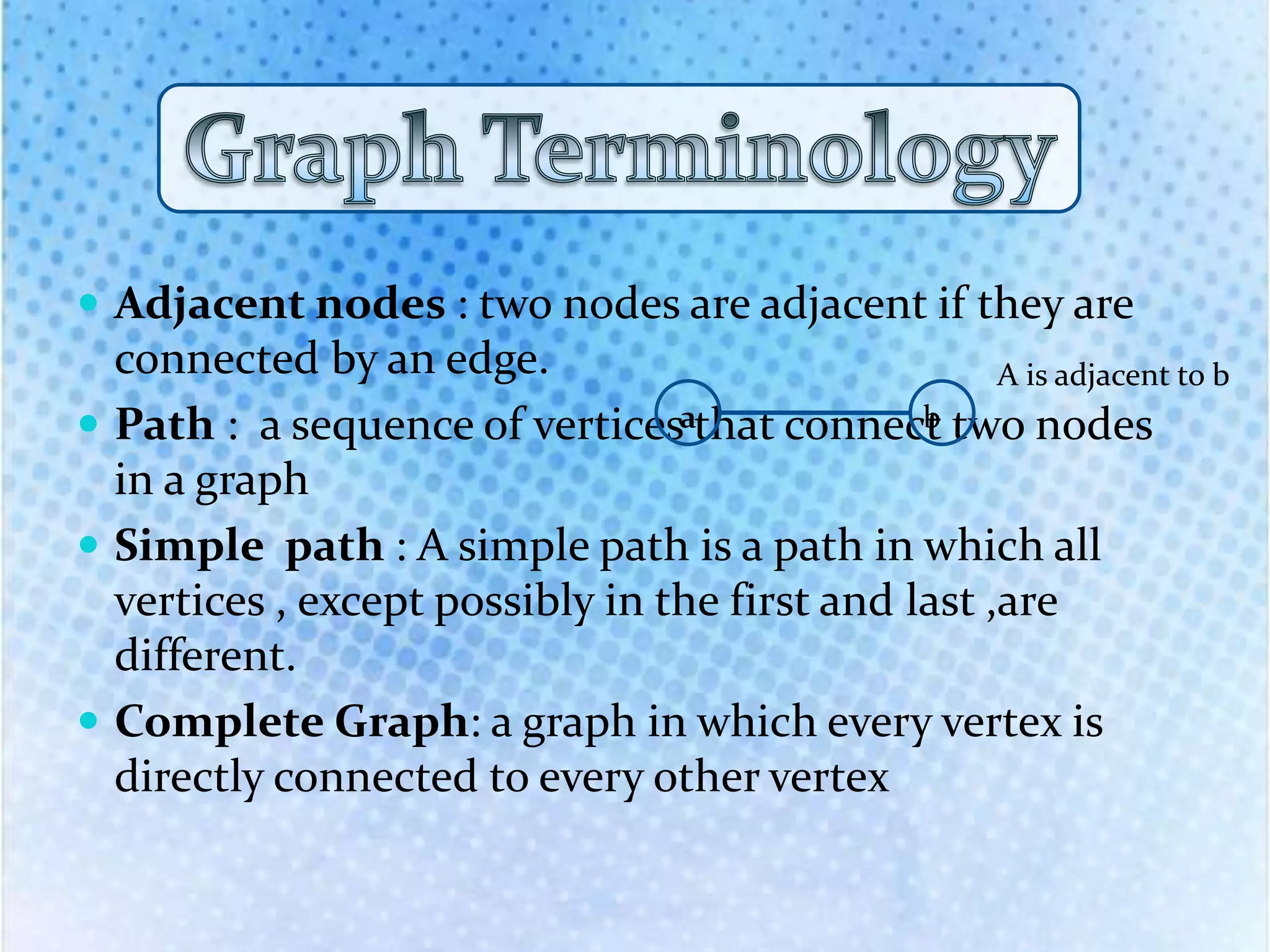
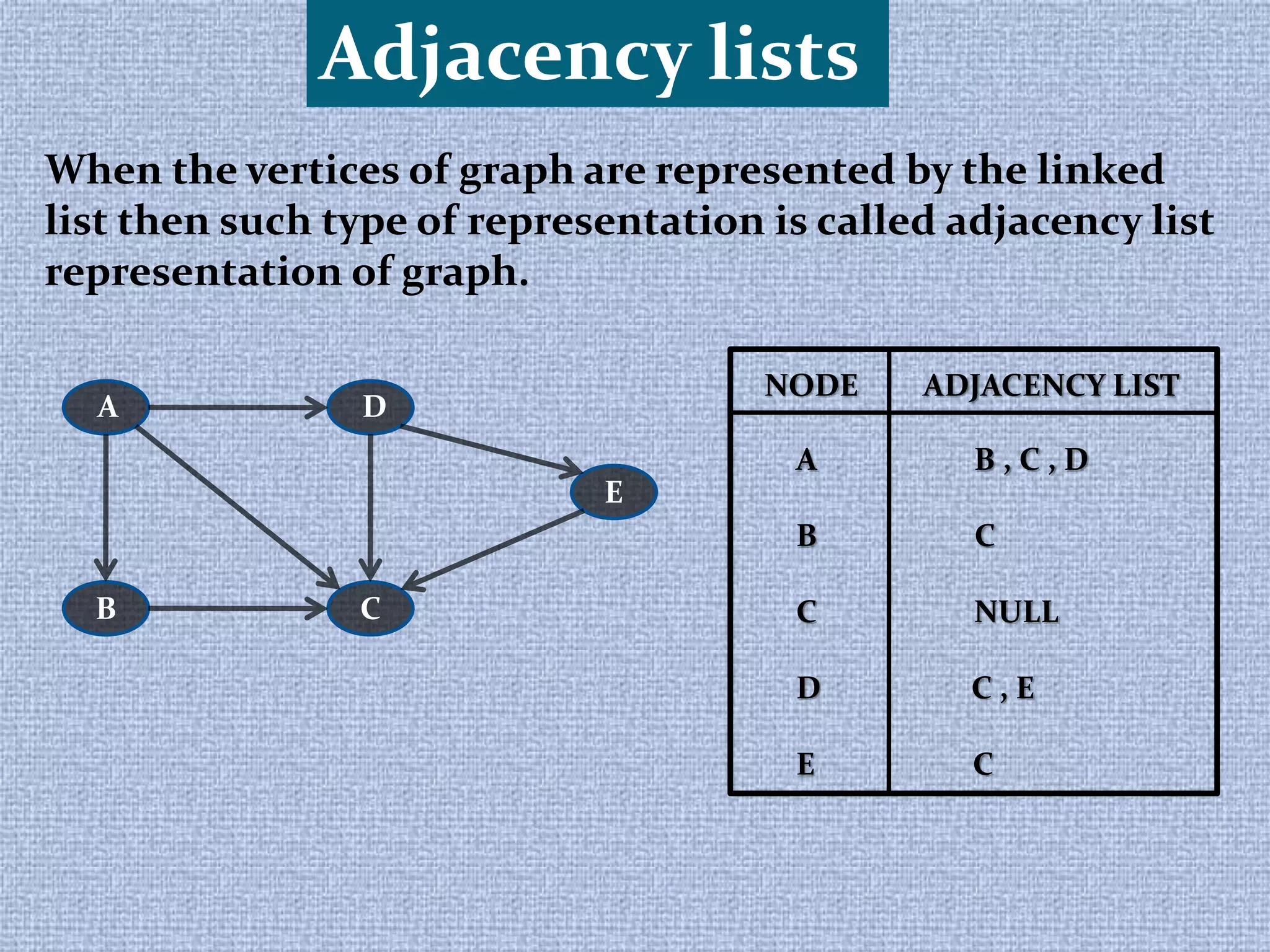
The document explains the concept of graphs as a data structure consisting of vertices and edges, detailing both undirected and directed graphs. It provides formal definitions, examples, and various representations of graphs including adjacency matrices and adjacency lists, along with methods for traversing graphs like breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS). The algorithms for these traversal methods are outlined step by step, emphasizing the states of nodes during processing.

![Adjacency matrix
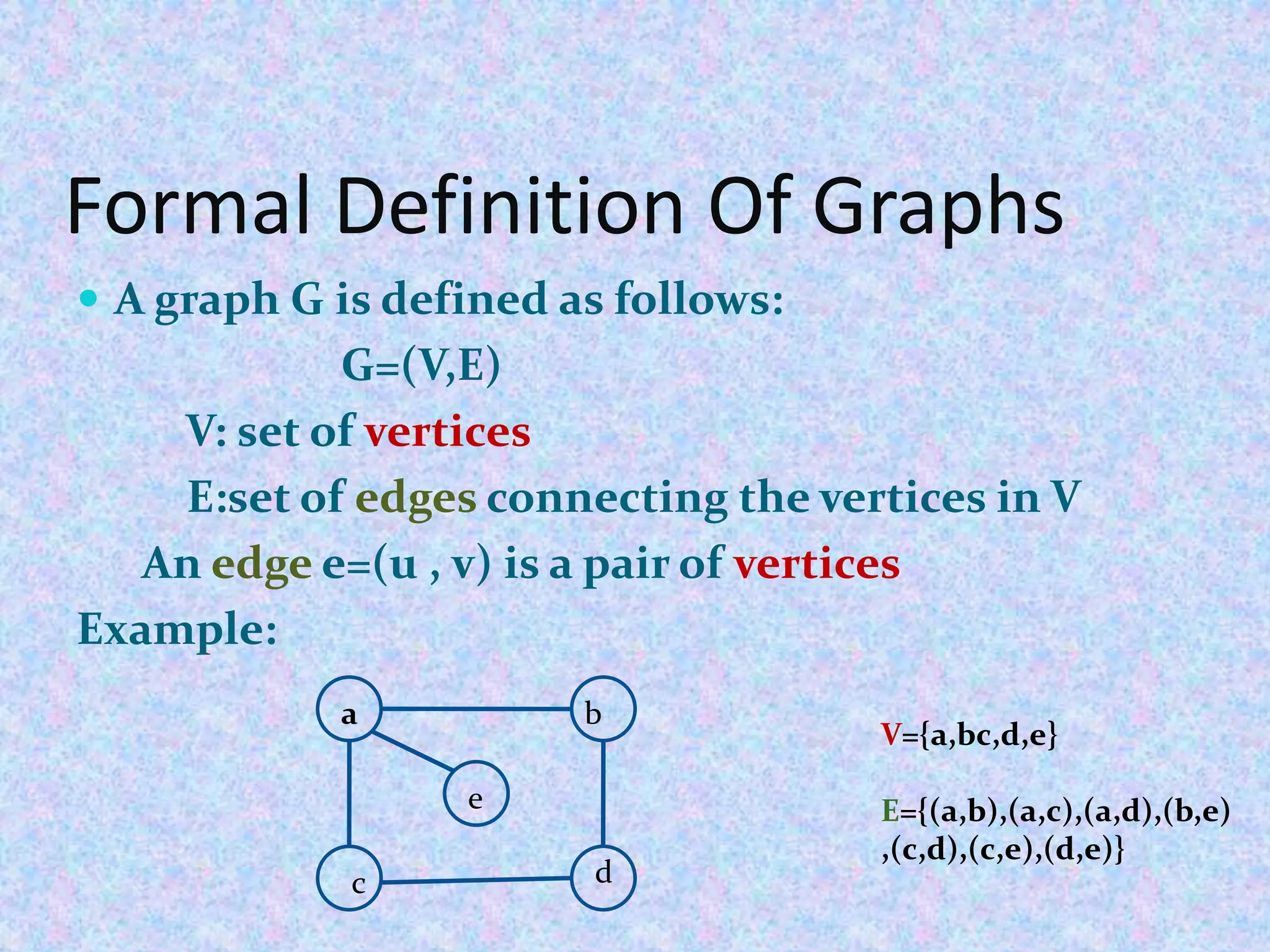
Let G=(V , E) be a graph with n vertices.
The adjacency matrix of G is a two dimensional array n by
n , say A[5][5].
A B
C D
E
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D)4
(E)5
(A)1 (B)2 (C)3 (D)4 (E)5
0 1 1 1 0
01 0 1 0
1 0 0 1 1
1 1 1 0 1
0 0 1 1 0
When the adjacent vertices of a graph is represented in the form of matrix
then such type of representation is called Adjacency Matrix
Representation of graph. E.g. A[i][j]
Number of rows = Number of Column
A ij =
O , if Vi is not adjacent to Vj
1 , if Vi , Vj is adjacent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-171124060858/75/Data-structure-7-2048.jpg)


![ED
C
F
A
B
Algorithm
1.Initialize all nodes to the ready state
(STATUS=1)
2.Put the starting node A in Queue and
change its status to the waiting state
(STATUS=2)
3. [LOOP]
Repeat steps 4 and 5 until queue is empty
4. Remove the front node N of Queue.
Process N and change the status of N to
the processed state (STATUS=3)
5. Add to the rear of queue all the
neighbors of N that are in ready state
(STATUS=1), and change their status to
waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Loop]
6. Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-171124060858/75/Data-structure-11-2048.jpg)
![A
ED
CB
F
1.Initialize all nodes to the ready state
(STATUS=1)
1
1
1
1
1
1
2.Put the starting node A in Queue and
change its status to the waiting state
(STATUS=2)
A
2 1.Initialize all nodes to the ready state
(STATUS=1)
2.Put the starting node A in Queue and
change its status to the waiting state
(STATUS=2)
3. [LOOP]
Repeat steps 4 and 5 until queue is
empty
4. Remove the front node N of Queue.
Process N and change the status of N
to the processed state (STATUS=3)
5. Add to the rear of queue all the
neighbors of N that are in ready state
(STATUS=1), and change their status to
waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Loop]
6. Exit
3
B C E
2 2
2
D F
3
2
2
3
3
3
3
B
A
C E
D F
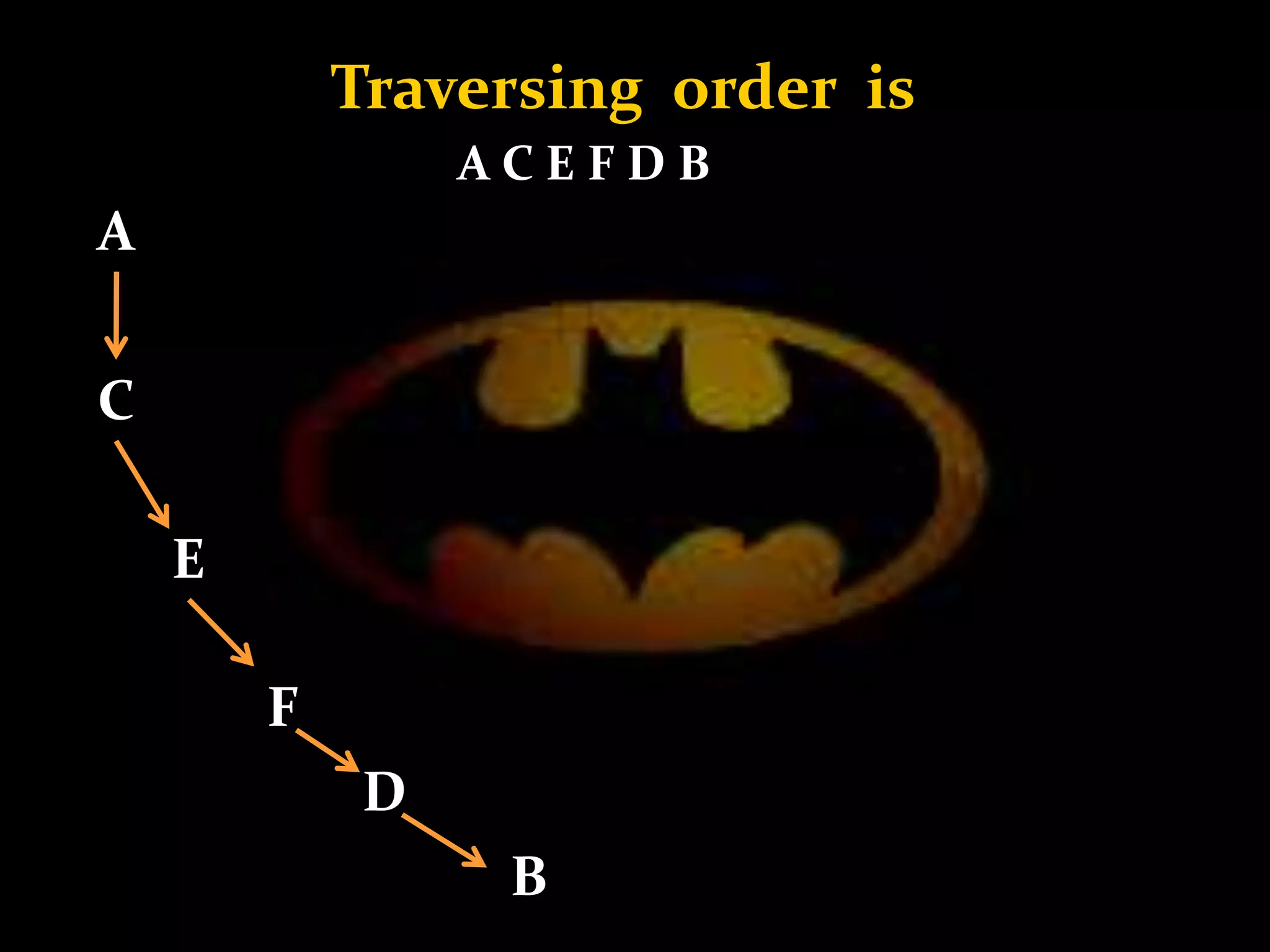
Traversing order – A B C E D F](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-171124060858/75/Data-structure-12-2048.jpg)

![A F
D
C E
B
1.Initialize all nodes to the ready state
(STATUS=1)
2.Push the starting node A onto stack
and change its status to the waiting state
(STATUS=2)
3. [LOOP]
Repeat steps 4 and 5 until stack is
empty
4. Pop the top node N of Stack.
Process N and change the status of N
to the processed state (STATUS=3)
5. Push onto Stack all the neighbors of
N that are still in ready state
(STATUS=1), and change their status to
waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Loop]
6. Exit
Algorithm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-171124060858/75/Data-structure-14-2048.jpg)
![A F
D
C E
B
1.Initialize all nodes to the ready state
(STATUS=1)
1
1
11
1
1
2.Push the starting node A onto stack
and change its status to the waiting state
(STATUS=2)
A
2
A
1.Initialize all nodes to the ready state
(STATUS=1)
2.Push the starting node A onto stack
and change its status to the waiting state
(STATUS=2)
3. [LOOP]
Repeat steps 4 and 5 until stack is
empty
4. Pop the top node N of Stack.
Process N and change the status of N
to the processed state (STATUS=3)
5. Push onto Stack all the neighbors of
N that are still in ready state
(STATUS=1), and change their status to
waiting state (STATUS=2).
[End of Loop]
6. Exit
A
B
C
3
2
2
C
3
D
E
2
2
E
3
F
2
F
3
3 3
D B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-171124060858/75/Data-structure-15-2048.jpg)