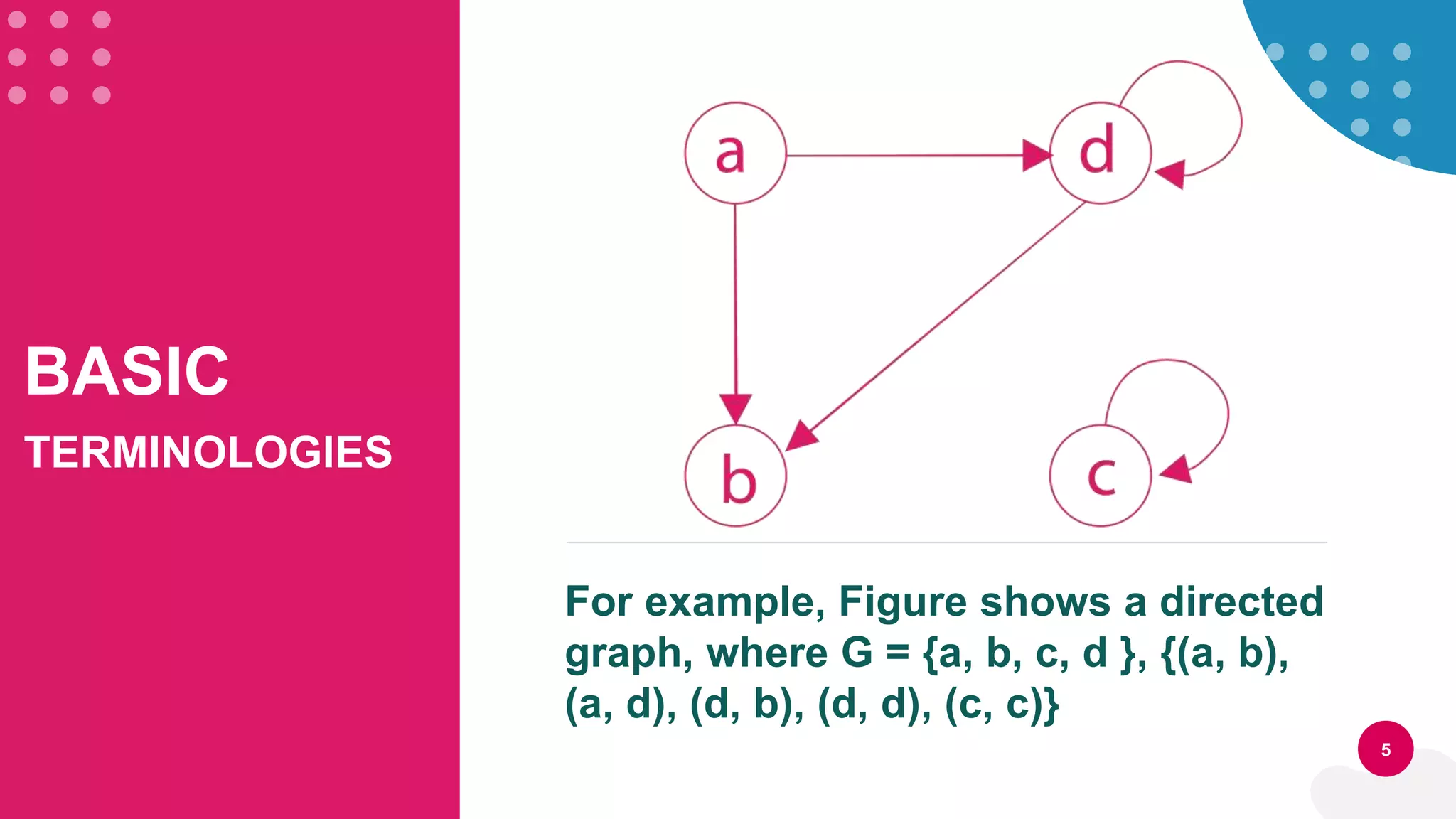
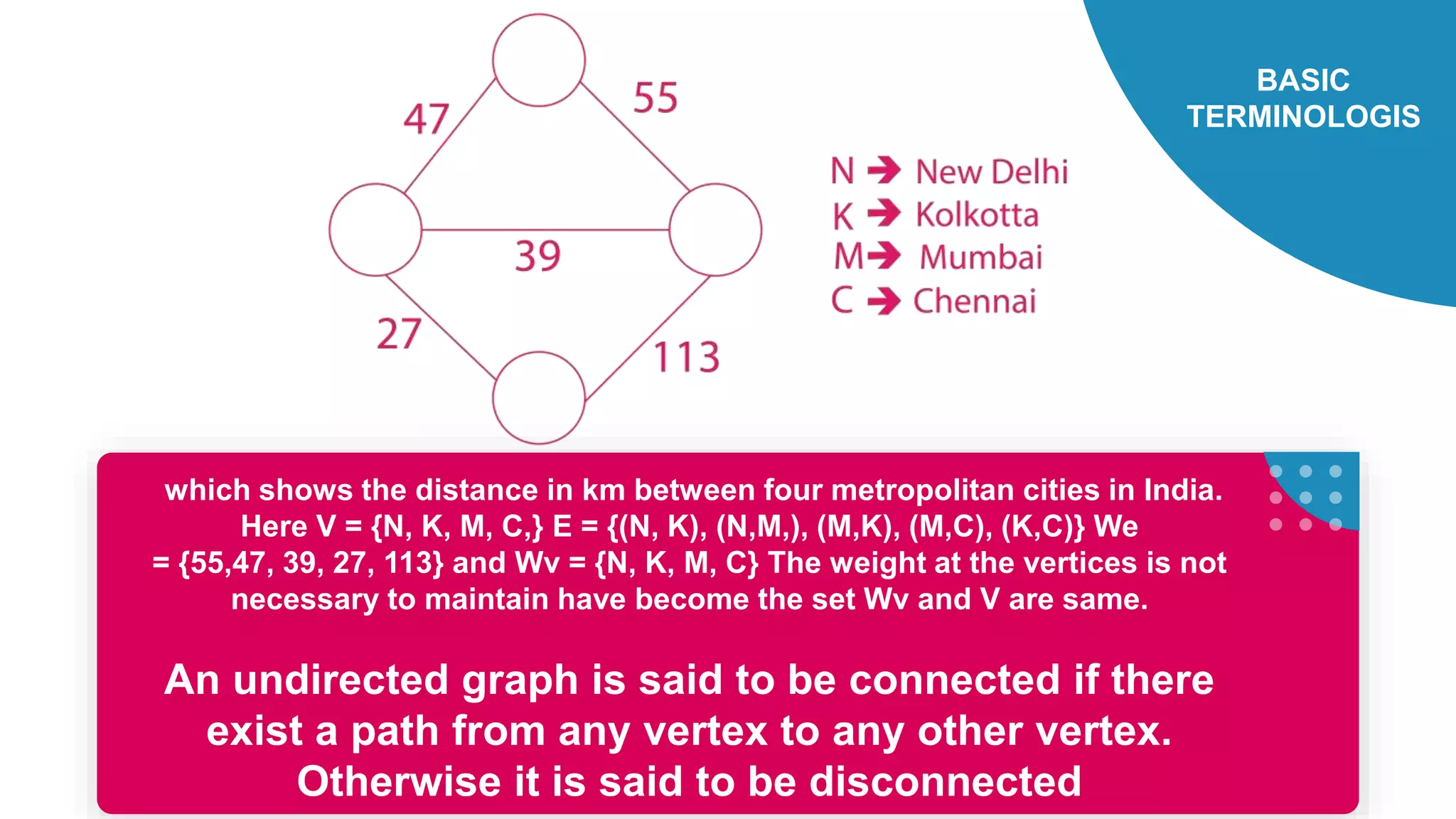
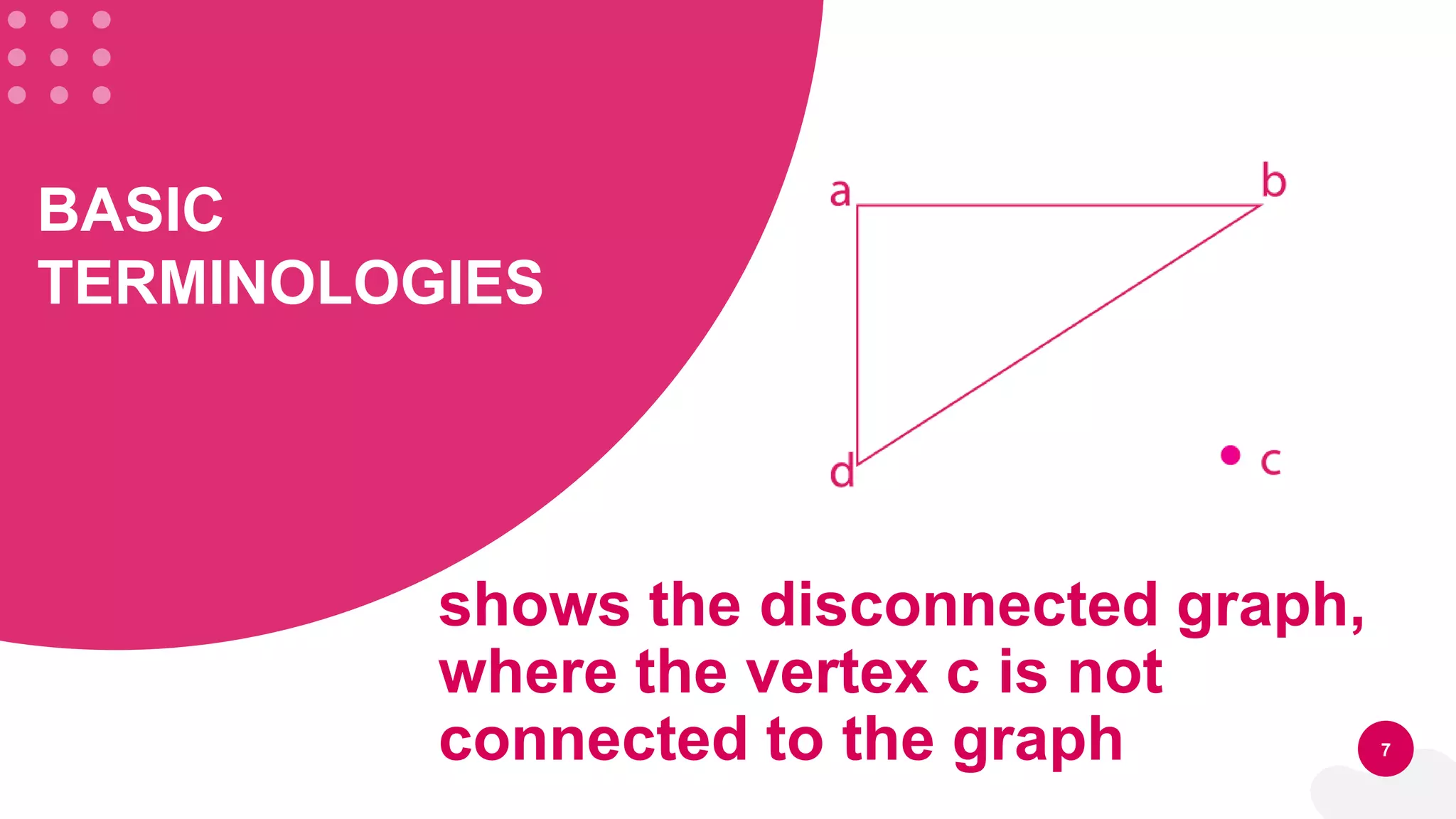
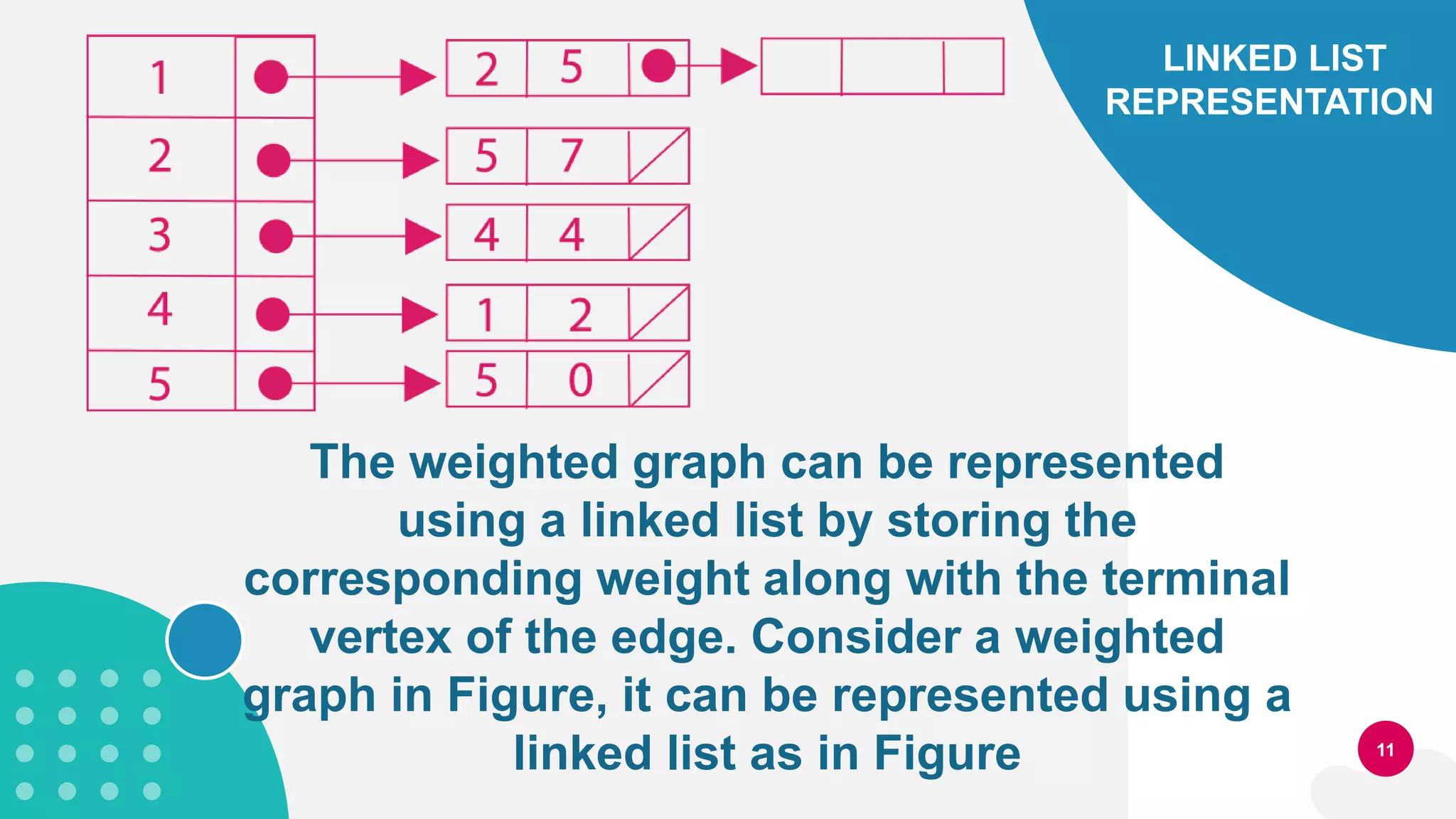
This document discusses three types of graphs: directed graphs, undirected graphs, and weighted graphs. It provides examples and definitions of basic graph terminology like vertices, edges, and paths. It also describes two common ways to represent graphs in computer memory: sequential representation using adjacency lists and linked representation using linked lists. Finally, it outlines high-level processes for creating a graph and searching or deleting elements from a graph.