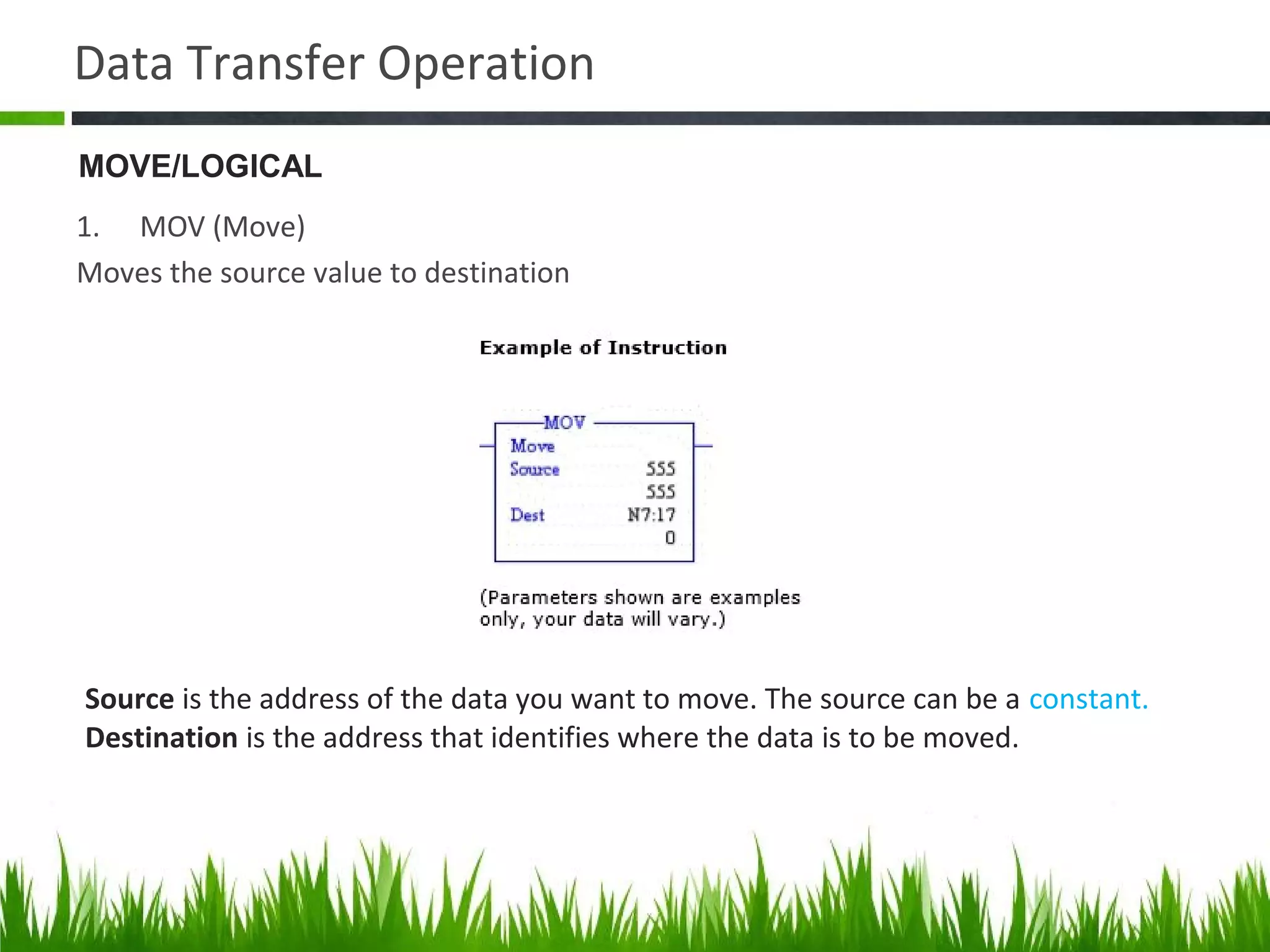
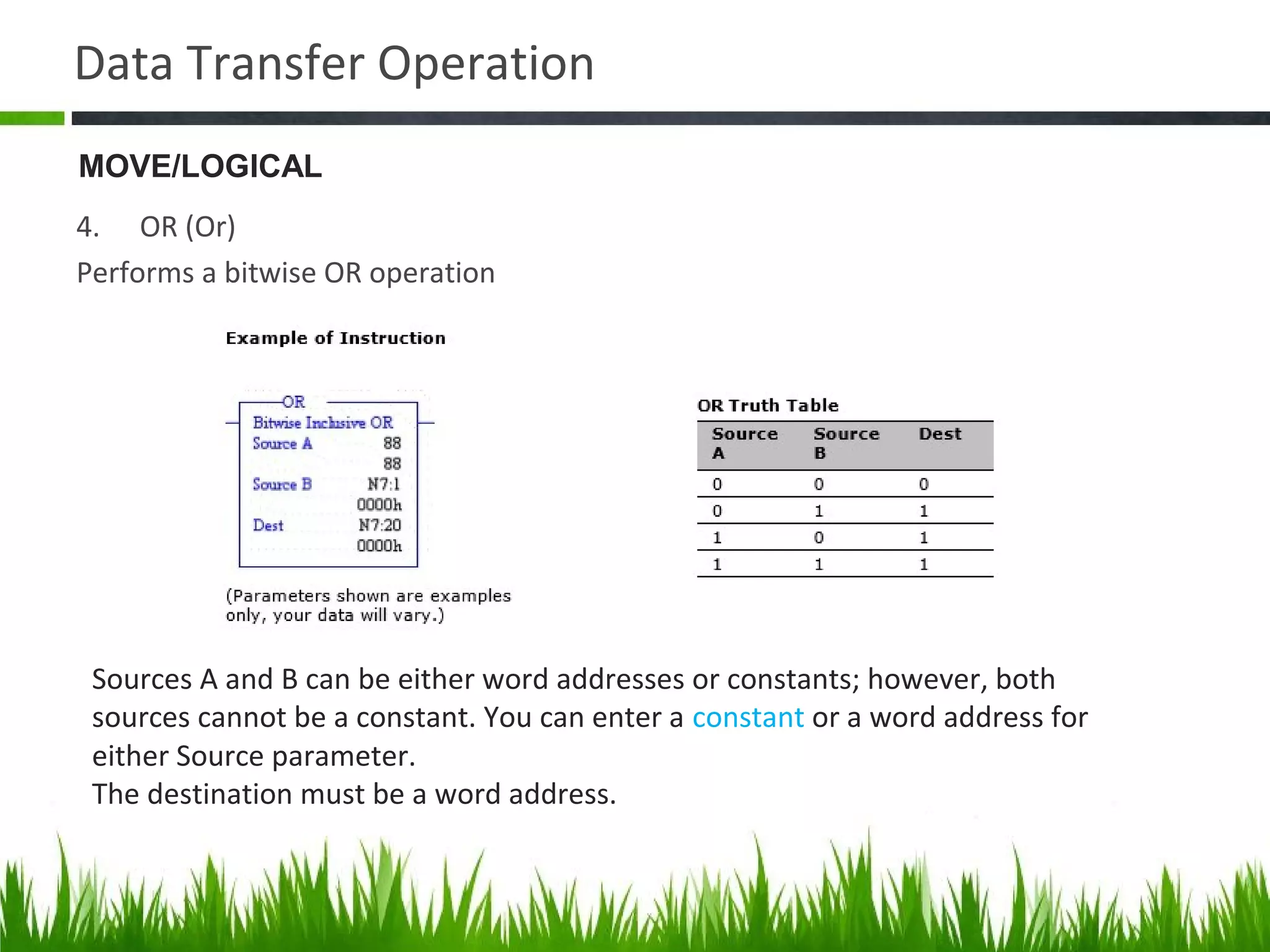
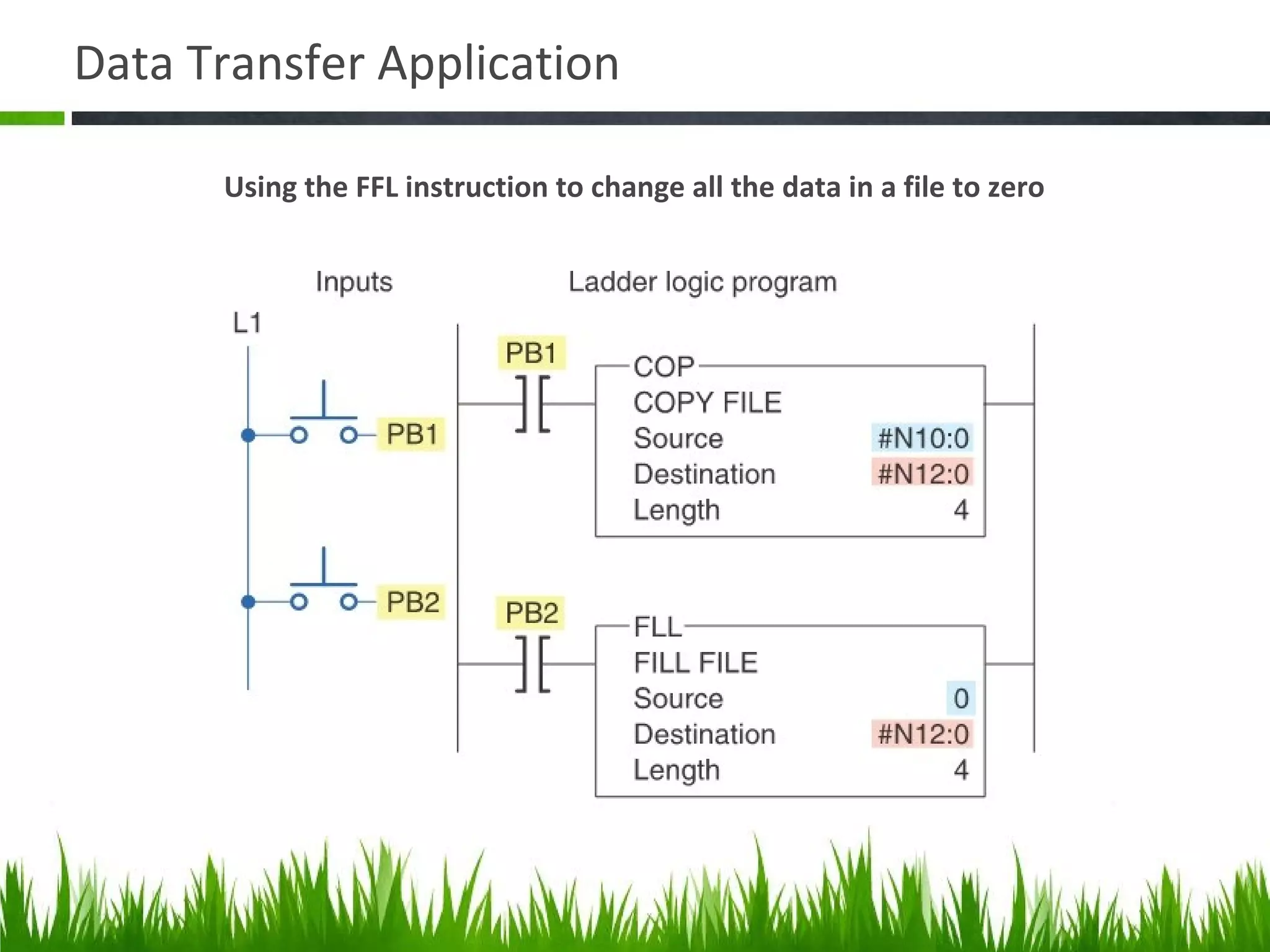
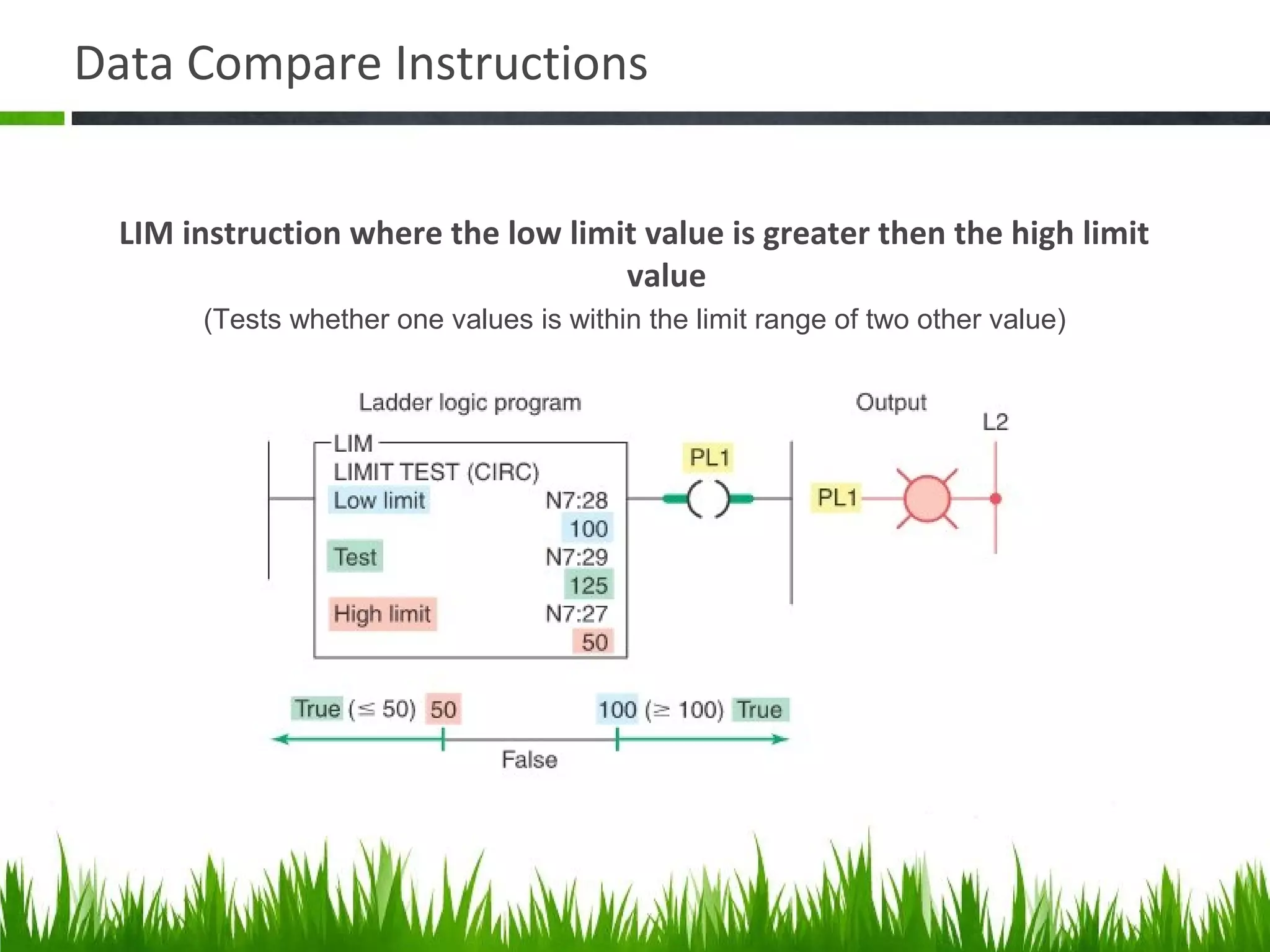
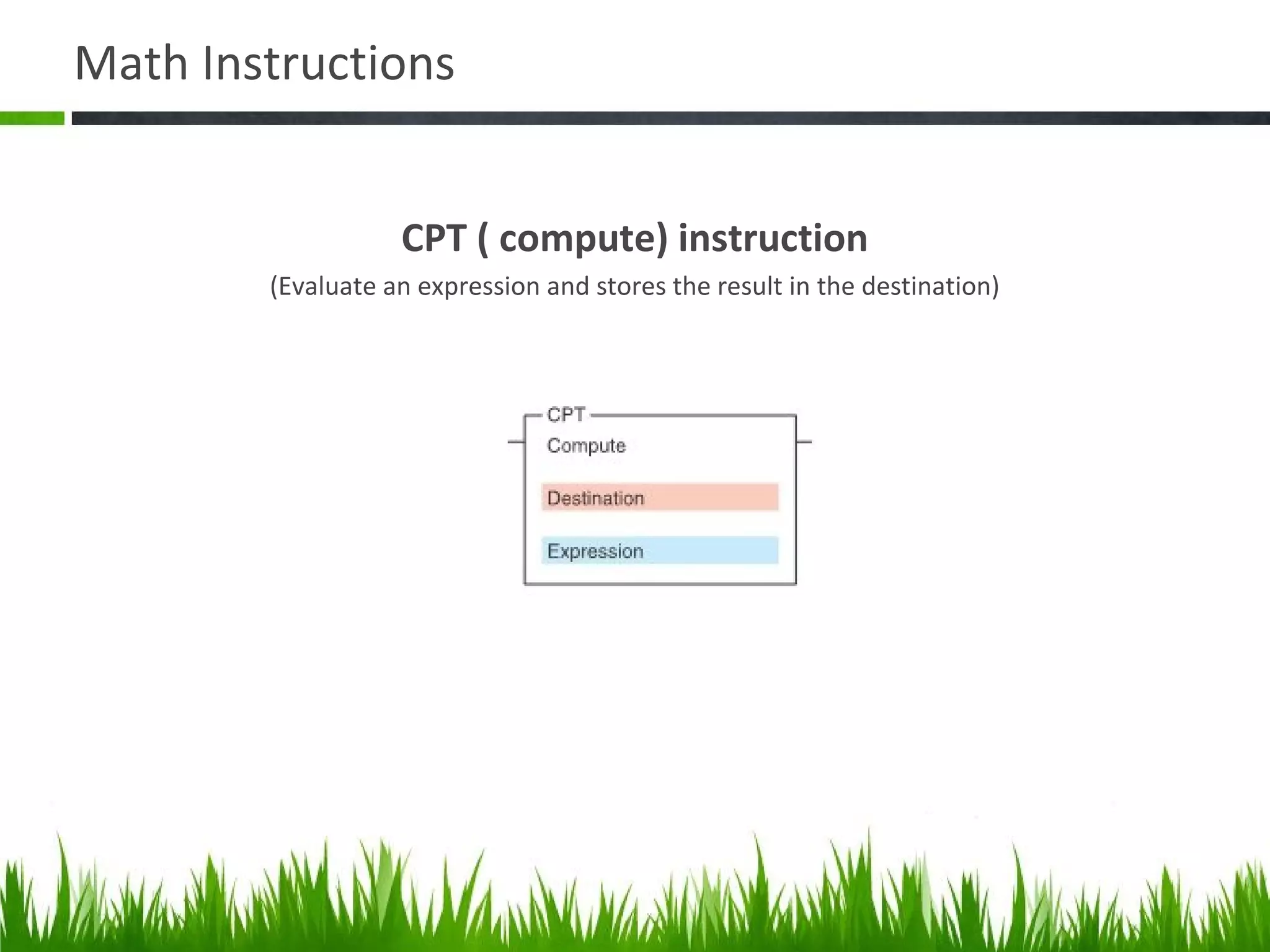
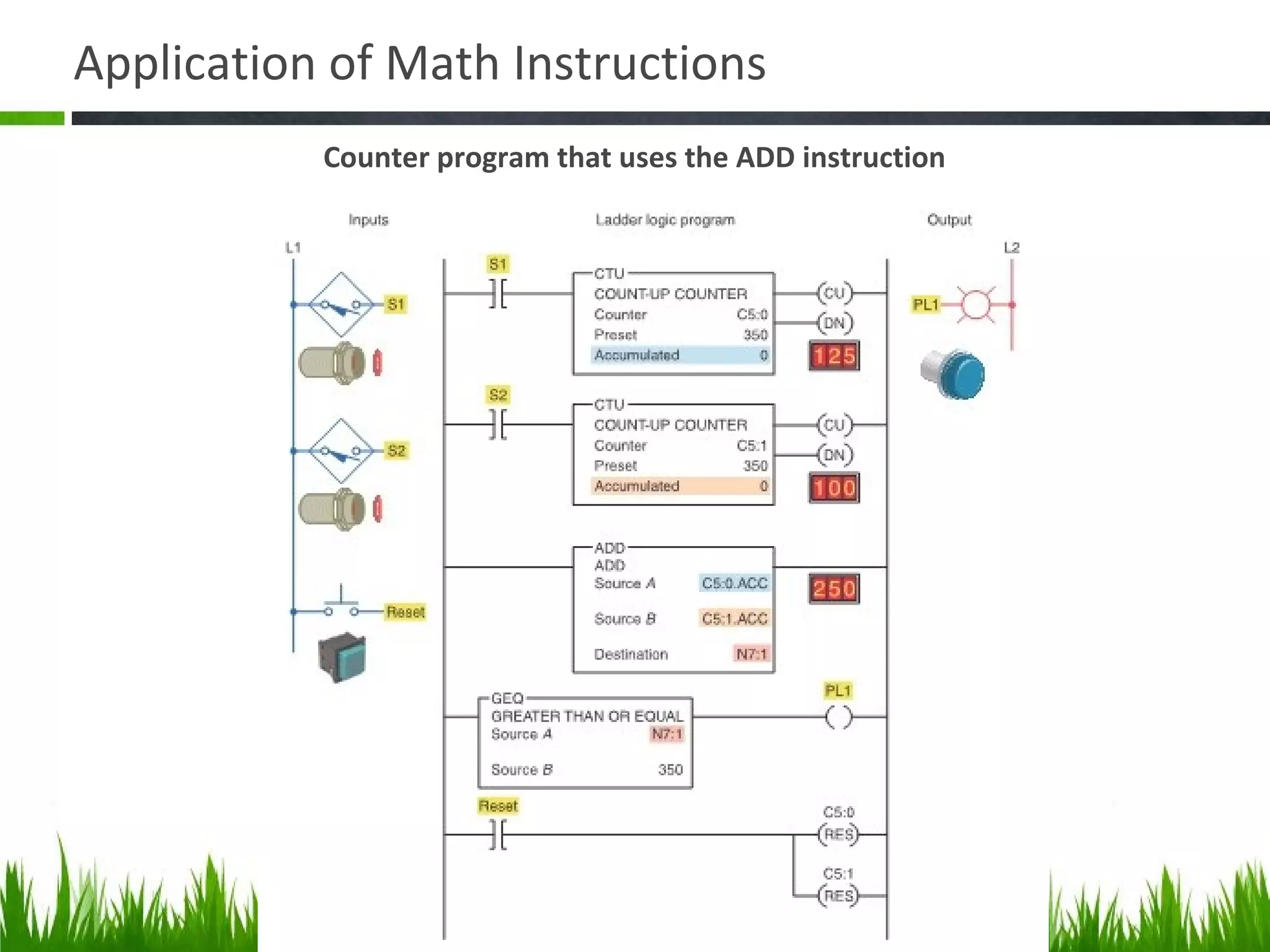
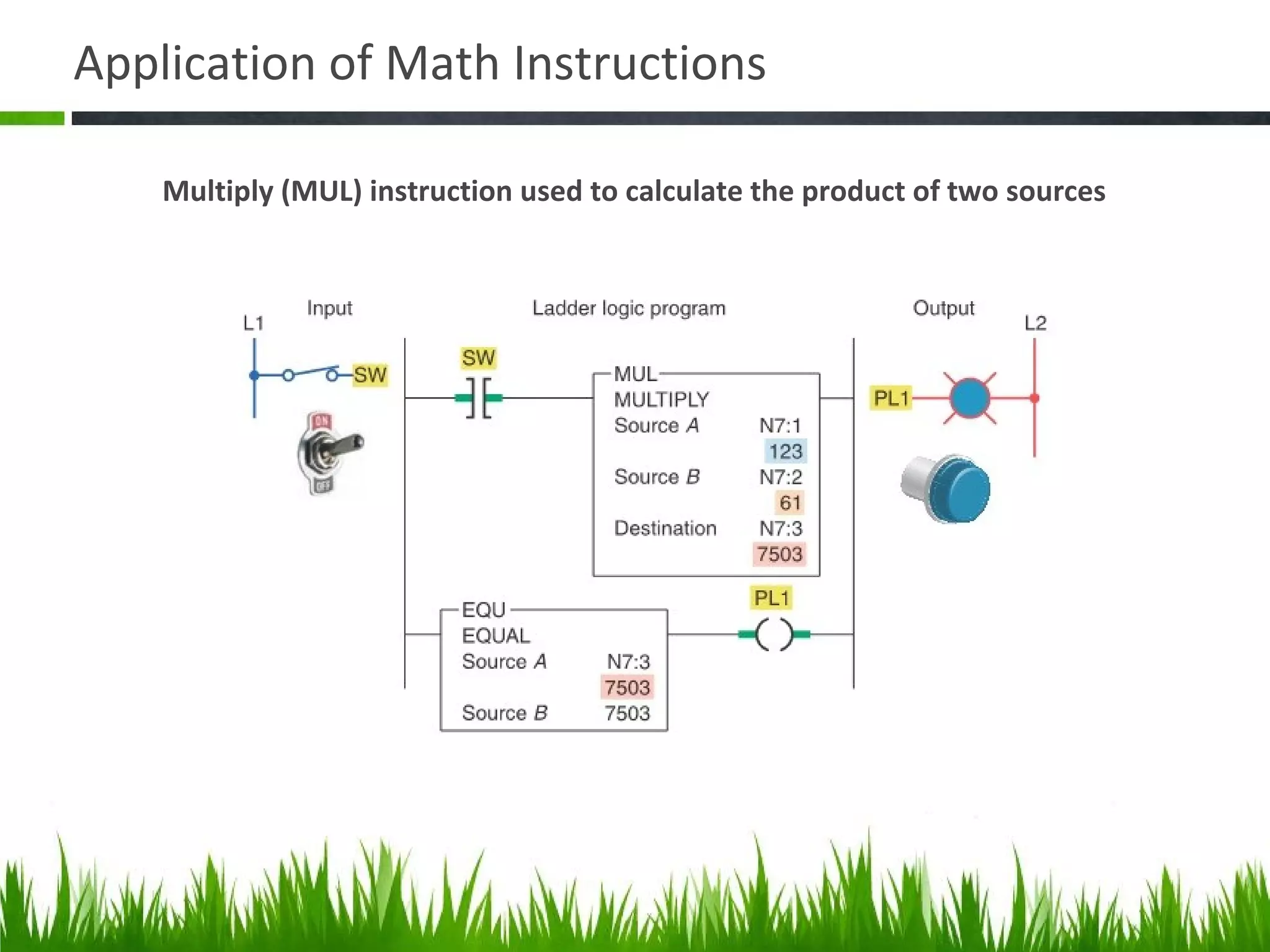
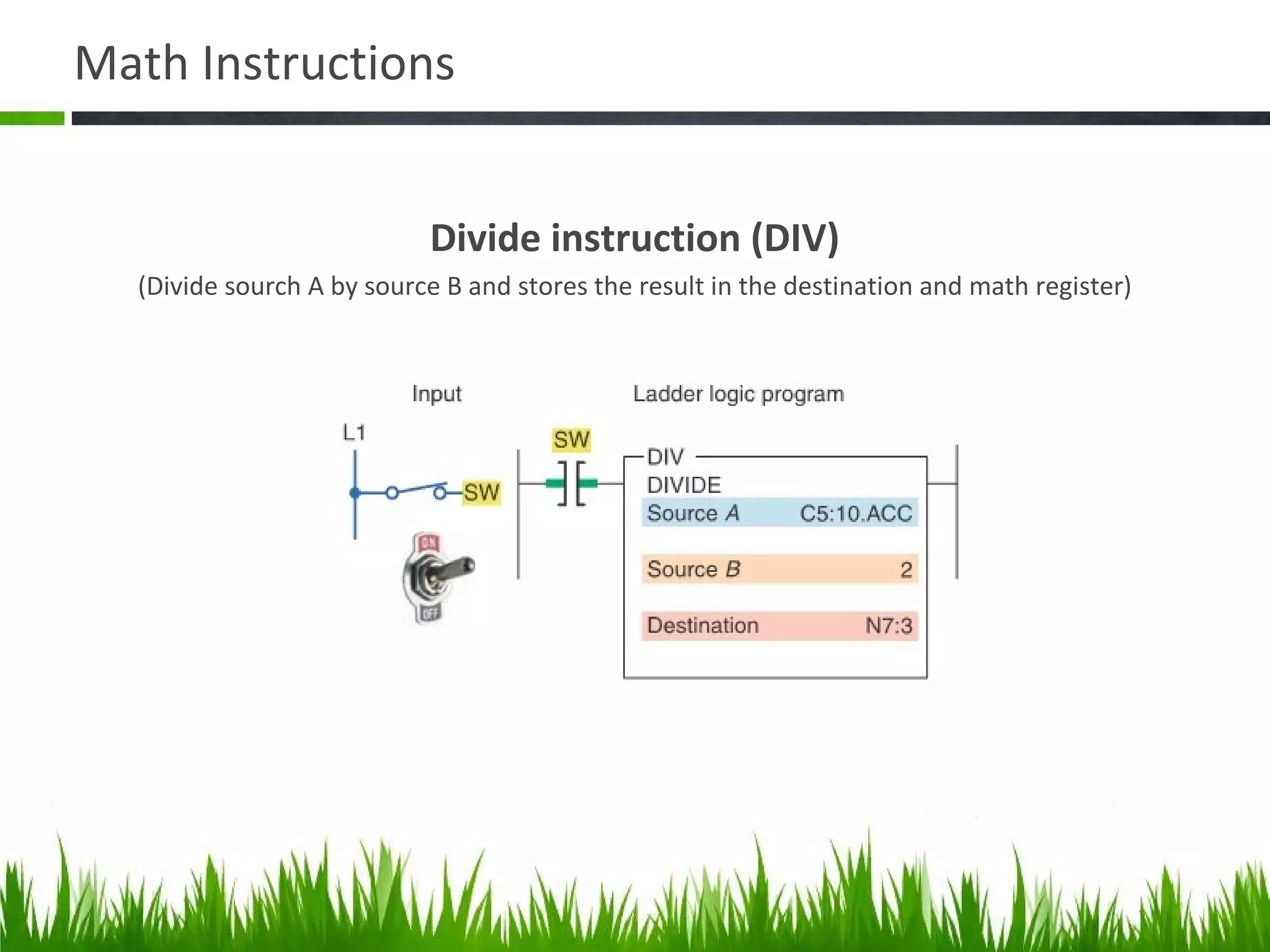
The document elaborates on data manipulation and math instruction within the context of programming, detailing various operations such as data transfer, comparison, and mathematical computations. It explains specific instructions like MOV, MVM, AND, OR, and others, providing examples of their applications in industrial settings. The document also addresses common questions related to data manipulation and math instructions, emphasizing their relevance in programmable logic controllers (PLCs).