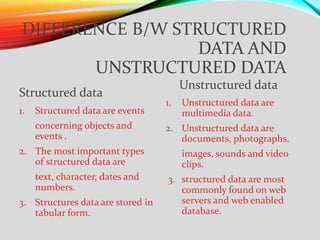
1. The document discusses modern database management systems and their components. It defines key concepts like databases, structured vs unstructured data, metadata, and database approaches.
2. Databases can be small, large, or very large depending on their size and usage. A database management system provides methods for creating, updating, storing, and retrieving data from the database.
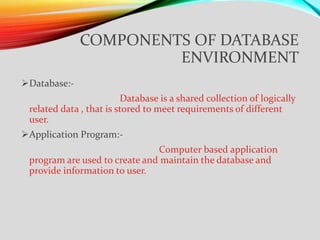
3. The main components of a database environment include the database itself, application programs, users, administrators, developers, and management tools. Together these components allow for effective data management and use.