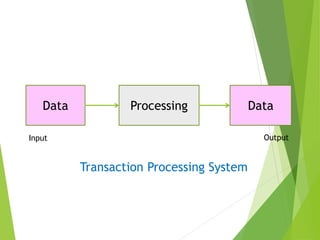
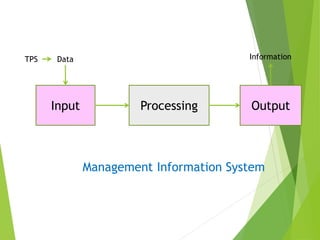
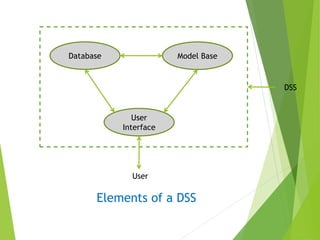
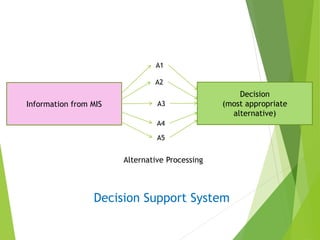
The document categorizes information systems as either operations support systems or management support systems. Operations support systems process transactional data to support daily business operations, including transaction processing systems, process control systems, and office automation systems. Management support systems provide information and decision support, including management information systems, decision support systems, executive support systems, and enterprise systems which integrate business functions across an organization.